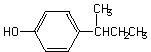
In the repeat dose study, all dosed male and female rats revealed transiently increased salivation after every dosing of the test compound. Body weight gain and food consumption of the 1000 mg/kg males significantly decreased when compared to the controls. Clinical chemistry showed decreased glucose and potassium levels and increased sodium, GPT and γ-GTP levels in 1000 mg/kg males, and increased GPT and GOT levels in the 1000 mg/kg females. The histopathological examination revealed diffuse hyperplasia of mucous epithelium in the forestomach in all the 1000 mg/kg males and females and one 300 mg/kg male, and papillary necrosis in the kidneys in a few males and females that received 300 mg/kg or more. Eosinophilic debris in the papillary interstitium was also noted in these rats. A 14-day recovery test indicated recovery from these compound-related alterations except for papillary necrosis of the kidney. The NOEL is considered to be 100 mg/kg/day both for both males and females.
4-(1-Methyl propyl)phenol was not mutagenic in Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA98, TA1535, TA1537 and Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA. Neither structural nor numerical chromosomal aberrations were induced in CHL/IU cells up to the concentration going 50% cell growth inhibition, in the absence or presence of an exogenous metabolic activation system.
| Purity | : | > 66% |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD (SD) |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for 28-Day Repeat Dose Toxicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan) |
| Route | : | Oral (gavage) |
| Dosage | : | 0 (vehicle), 100, 300, 1000 mg/kg/day |
| Number of animals | : | 100 and 300 mg/kg groups, 5 males and 5 females; 0 and 1000 mg/kg groups, 10 males and 10 females |
| Vehicle | : | Sesame Oil |
| Administration period | : | Males and females, 28 days |
| Terminal kill | : | 5 males and 5 females/group, 29 days; 5 males and 5 females each in the 0 and 1000 mg/kg group, 44 days |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
The NOEL is considered to be 100 mg/kg/day for both males and females in terms of general toxicological effects.
| Purity | : | 66% |
| Test species/strains | : | S.typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537, E. coli WP2 uvrA |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan) |
| Procedures | : | Plate incorporation method |
| Solvent | : | DMSO |
| Positive controls | : | -S9, AF-2 (TA100, WP2, TA98), sodium azide (TA1535) and 9-aminoacridine (TA1537) +S9, 2-aminoanthracene (all strains) |
| Dosage | : | without metabolic activation; 0, 6.25, 12.5, 25, 50, 100, 200 μg/plate metabolic activation method 0, 12.5, 25, 50, 100, 200 μg/plate |
| S-9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 3 |
| Number of replicates | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Genetic effects:
S. typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA 98, TA1537
| + | ? | - | |
| with metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
E. coli WP2 uvrA
| with metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| Purity | : | 66% |
| Type of cell used | : | Chinese hamster CHL/IU cells |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan) |
| Solvent | : | DMSO |
| Positive controls | : | -S9, Mitomycin C +S9, Cyclophosphamide |
| Dosage | : | -S9 (continuous treatment): 0, 0.012, 0.025, 0.049 mg/ml -S9 (short-term treatment): 0, 0.012, 0.025, 0.049 mg/ml +S9 (short-term treatment): 0, 0.017, 0.034, 0.067 mg/ml |
| S-9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
| clastogenicity | polyploidy | |||||
| + | ? | - | + | ? | - | |
| without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| with metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| 1) | The tests were performed by the Hatano Research Institute, Food and Drug Safety Center, 729-5 Ochiai, Hadano-shi, Kanagawa 257, Japan. Tel +81-463-82-4751 Fax +81-463-82-9627 |