3-Nitrobenzenamine
3-ニトロベンゼナミン
CAS No. 99-09-2
m-Nitroaniline
m −ニトロアニリン
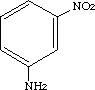
3-Nitrobenzenamine was studied for oral toxicity in rats in a 28-day repeat dose toxicity test at doses of 0, 15, 50 and 170 mg/kg/day and in an OECD preliminary reproduction toxicity screening test at doses of 0, 5, 15 and 50 mg/kg/day. 3-Nitrobenzenamine was also tested for mutagenicity with assays for reverse mutation in bacteria, chromosomal aberrations in cultured Chinese hamster (CHL) cells and micronuclei induction in mice.
In the repeat dose study, inhibition of body weight gain, hemolytic anemia and methemoglobinemia in both sexes and testicular atrophy in males were observed in the rats given 170 mg/kg/day. Increases in organ weight were observed in the liver, kidneys and spleen of both sexes in a dose-related fashion. Histologically, reduction in spermatogenesis, lipofuscin deposition in renal proximal tubules, hemosiderin deposition in spleen, erythroid hyperplasia in bone marrow, and swelling of hepatocytes were observed. The NOEL for repeat dose toxicity was less than 15 mg/kg/day.
In the study of reproductive and developmental toxicity, the 50 mg/kg-dose females showed signs of difficulty in labor, and all their offspring died by the day of parturition. Some females of this group also showed total litter loss in the early lactation period. Body weight gain and food consumption were significantly suppressed in both sexes given 50 mg/kg. At the scheduled necropsy, 15 or 50 mg/kg dose males and females exhibited enlarged and/or dark-colored spleens. NOELs for reproductive performance were 50 mg/kg/day in males and 5 mg/kg/day in females, and 50 mg/kg/day for offspring development.
3-Nitrobenzenamine was mutagenic for S. typhimurium TA100 and TA98 with and without exogenous metabolic activation. The test chemical induced chromosomal aberrations in CHL cells with exogenous metabolic activation. Polyploidy was also induced with and without exogenous metabolic activation. The test chemical also induced micronucleated polychromatic erythrocytes at a dose of 300 mg/kg in male BDF1 mice.
3-Nitrobenzenamine[99-09-2]
1. Repeat Dose Toxicity 1)
| Purity | : | 99.8 % |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:F344 |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for 28-Day Repeat Dose Toxicity Test of Chemicals (Japan) |
| Route | : | Oral (gavage) |
| Doses | : | 0 (vehicle), 15, 50, 170 mg/kg/day |
| Number of animals | : | Males, 5; Females, 5/group |
| Vehicle | : | Olive oil |
| Administration period | : | Male and Female, 28 days |
| Terminal kill | : | Days 29 or 43 |
- Test results:
- Inhibition of body weight gain, and induction of cyanosis and methemoglobinemia were observed in the highest dose groups of both sexes, without mortality. Testicular atrophy was evident but there were no effects on the ovaries in the same group. In addition to these findings, hemolytic anemia and increases of liver, spleen and kidney weights were also observed in both sexes in a dose-related fashion. Histologically, the highest dose group showed reduction of spermatogenesis with multinucleated giant cell formation of the testis and lipofuscin deposition mainly occurring in the proximal renal tubules. Increased hemosiderin deposition in the spleen, erythroid hyperplasia in the bone marrow and swelling of hepatocytes were observed in all treated groups.
NOEL: < 15mg/kg/day
2. Reproductive/Developmental Toxicity 2)
| Purity | : | 99.9 % |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD (SD) |
| Test method | : | OECD Preliminary Reproductive/Developmental Toxicity Screening Test |
| Route | : | Oral (gavage) |
| Doses | : | 0 (vehicle), 5, 15, 50 mg/kg/day |
| Number of animals | : | Male, 13; Female, 13 |
| Vehicle | : | 5% CMC-sodium solution |
| Administration period | : | Male, 42 days
Female, from 14 day before mating to day 3 of lactation |
| Terminal kill | : | Male, day 43
Female, day 4 of lactation |
| GLP | : | Yes |
- Test results:
- Mating performance and fertility were not affected by the test compound. However, 1/13 medium-dose and 2/13 high-dose females showed signs of difficult labor, and all of their offspring died by the day of parturition. In addition, one other medium-dose female and 1 high-dose female showed total litter loss in the early lactation period (by day 3 of lactation). Reproduction parameters (i.e., duration of gestation, number of corpora lutea, implantations and resorptions, litter size, and sex distribution) were comparable among all four groups including the control. Survival and body weights as well as the morphological development of pups were comparable among all groups.
NOEL for P generation: Male, 50 mg/kg/day; Female, 5 mg/kg/day
NOEL for F1 generation: 50 mg/kg/day
- <Maternal and paternal general toxicity>
- All of the males survived the period of dosing, and no compound-related clinical signs were observed in any of the males except for one high-dose animal which transiently demonstrated pale extremities in the late dosing period. Body weight gain and food consumption during the first week of dosing were significantly suppressed in the high-dose males but in the low- and medium-dose males were comparable to the control values throughout the study. At the scheduled necropsy, all high-dose and 3 medium-dose males revealed enlarged and/or dark-colored spleens, and a few in the high-dose group showed enlarged livers. Testicular and epididymal weights were comparable among all four groups. No compound-related histopathological changes in these organs were found in any of the males. One high-dose female died during delivery on day 23 of gestation. This high-dose female did not reveal any apparent signs of toxicity before death. No compound-related clinical signs were observed in any of the females, except for 1 surviving high-dose female which transiently demonstrated pale extremities in the late gestation period. Body weights of the high-dose group during the dosing period were slightly but consistently lower than those of the controls. Food consumption of the high-dose group was significantly suppressed in the first week of dosing. In the low- and medium-dose females, body weight and food consumption were comparable to control values throughout the study. At the scheduled necropsy, 8/9 high-dose and 1/10 medium-dose females revealed enlarged and/or dark-colored spleens. No remarkable histopathological changes in the ovaries were observed in any of the nonpregnant females or in the females which showed total litter loss after parturition.
3. Genetic Toxicity
3-1 Bacterial test (Ames test) 1)
| Purity | : | 99.8% |
| Test species/strains | : | S. typhimurium TA100, TA98, TA102, TA97 |
| Test method | : | Maron & Ames (1983) |
| Procedure | : | Preincubation assay |
| Solvent | : | DMSO |
| Positive controls | : | -S9, AF-2 (TA100, TA98)
ICR-191 (TA97)
Mitomycin C (TA102) |
| Doses | : | 0, 25, 50, 100, 250, 500, 1,000, 2,500, 5,000 μg/plate |
| S-9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 2 |
| Number of replicates | : | 1 |
- Test results:
- Minimum concentration of test substance at which toxicity to bacteria was observed: No toxicities were observed up to a concentration of 5000 μg/plate with or without metabolic activation.
Genotoxic effects:
TA100, TA98
| + | ? | - |
| with metabolic activation: | [*] | [ ] | [ ] |
| without metabolic activation: | [*] | [ ] | [ ] |
TA102, TA97
| + | ? | - |
| with metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
3-2 Non-bacterial in vitro test (Chromosomal aberration test) 1)
-
| Purity | : | 99.8% |
| Type of cell used | : | Chinese hamster CHL cells |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan) |
| Solvent | : | DMSO |
| Doses | : | -S9, 0, 0.4, 0.8, 1.6 mg/ml
+S9, 0, 0.4, 0.8, 1.6 mg/ml |
| S-9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 1 |
- Test results:
- 3-Nitrobenzenamine induced chromosomal aberrations at a concentration of 1.6 mg/ml with exogenous metabolic activation. Polyploid cells were also induced after 6 h treatment at 0.8 mg/ml with and without metabolic activation.
- Lowest concentration producing cytogenetic effects in vitro:
- with metabolic activation: 0.8 mg/ml
- without metabolic activation: 1.6 mg/ml
- Genotoxic effects:
| + | ? | - |
| with metabolic activation: | [*] | [ ] | [ ] |
| without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
3-3 Non-bacterial in vivo test ( Micronucleus test) 2)
-
| Purity | : | 99.9 % |
| Test species/strain | : | Mice/Crj:BDF1, male and female |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan) |
| Doses | : | 0, 75, 150, 300 mg/kg |
| Solvent | : | 0.5 % CMC sodium |
| GLP | : | Yes |
- Test results:
- The frequency of micronucleated polychromatic erythrocytes was significantly increased in males at a dose of 300 mg/kg 72h after oral gavage treatment. Inhibition of bone marrow cell proliferation was not observed under the test conditions. The results suggest that 3-nitrobenzenamine induced a significant increase of micronuclei.
- Lowest concentration producing toxicity: 300 mg/kg/day
-
| Genotoxic effects: |
| Micronucleus test: | + | ? | - |
| [*] | [ ] | [ ] |
| 1) | The tests were performed by the Biological Safety Research Center, National Institute of Health Sciences, 1-18-1 Kamiyoga, Setagaya-ku, Tokyo, 158, Japan. Tel 81-3-3700-1141 Fax 81-3-3700-2348 |
| 2) | The tests were performed by the Hatano Research Institute, Food and Drug Safety Center, 729-5 Ochiai, Hadano-shi, Kanagawa, 257, Japan. Tel 81-463-82-4751 Fax 81-463-82-9627 |

