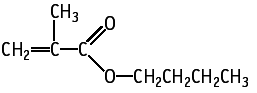

Butyl methacrylate was studied for oral toxicity in rats in an OECD combined repeat dose and reproductive/developmental toxicity screening test at doses of 0, 30, 100, 300 and 1000 mg/kg/day.
With regard to repeat dose toxicity in males, weight gain depression and a decrease in food consumption were observed at a dose of 1000 mg/kg. Urinary examination revealed increases in ketone bodies and occult blood, and hematological and blood chemical examinations showed increases in prothrombin time and urea nitrogen at a dose of 1000 mg/kg. Absolute and relative weights of the spleen were decreased at a dose of 100 mg/kg or more, and relative kidney weights were increased at a dose of 1000 mg/kg. Histopathological examination revealed atrophy of the splenic red pulp at doses of 100 mg/kg or more. The kidney showed no histopathological abnormalities attributable to the test substance. In females, there were weight gain depression and a decrease in food consumption at a dose of 1000 mg/kg. Atrophy of the red pulp in the spleen was also observed histopathologically at a dose of 1000 mg/kg. The NOELs for repeat dose toxicity are considered to be 30 mg/kg/day for males and 300 mg/kg/day for females. In terms of reproductive and developmental toxicity, there were decreases in numbers of corpora lutea and implantations in the parental females. The test substance showed no effects on any reproductive parameters of the parental males or developmental parameters of the offspring. The NOELs for reproductive and developmental toxicity are considered to be 1000 mg/kg/day for the parental males and offspring, and 300 mg/kg/day for the parental females.
Butyl methacrylate was not mutagenic in Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537 and Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA, with or without an exogenous metabolic activation system.
Butyl methacrylate did not induce structural chromosomal aberrations or polyploidy in CHL cells, with or without an exogenous metabolic activation system.
| Purity | : | 99.6 % |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD(SD) |
| Test method | : | OECD Combined Repeat Dose and Reproductive/ Developmental Toxicity Screening Test |
| Route | : | Oral(gavage) |
| Doses | : | 0(vehicle), 30, 100, 300, 1000 mg/kg/day |
| Number of animals/group | : | Males, 10; females, 10 |
| Vehicle | : | Sesame oil |
| Administration period | : | Males, 44 days Females, from 14 days before mating to day 3 of lactaion |
| Terminal kill | : | Males, 45 days Females, day 4 of lactation |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
In males, there were weight gain depression and a decrease in food consumption at a dose of 1000 mg/kg. Urinary examination revealed increases in ketone bodies and occult blood, and hematological and blood chemical examinations showed increases in prothrombin time and urea nitrogen at a dose of 1000 mg/kg. Absolute and relative weights of the spleen were decreased at a dose of 100 mg/kg or more, and relative kidney weights were increased at a dose of 1000 mg/kg. Histopathological examination revealed atrophy of the splenic red pulp at doses of 100 mg/kg or more. The kidneys showed no histopathological abnormalities attributable to the test substance.
In females, there were weight gain depression and a decrease in food consumption at a dose of 1000 mg/kg. Atrophy of the red pulp in the spleen was also observed histopathologically at a dose of 1000 mg/kg.
The NOELs for repeat dose toxicity are considered to be 30 mg/kg/day for males and 300 mg/kg/day for females.
<Reproductive and developmental toxicity>
There were decreases in numbers of corpora lutea and implantations in the parental females. The test substance showed no effects on any reproductive parameters of the parental males or developmental parameters of the offspring.
The NOELs for reproductive and developmental toxicities are considered to be 1000 mg/kg/day for the parental males and offspring, and 300 mg/kg/day for the parental females.
| Purity | : | 99.6 % |
| Test species/strains | : | S. typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537 E. coli WP2 uvrA |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan)and OECD Guidelines No. 471 and 472 |
| Procedures | : | Pre-incubation method |
| Solvent | : | DMSO |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix; 2-(2-Furyl)-3-(5-nitro-2-furyl)acrylamide(TA100, TA98 and WP2 uvrA), Sodium azide(TA1535), 9-Aminoacridine hydrochloride(TA1537) +S9 mix; 2-Aminoanthracene(all strains) |
| Doses | : | -S9 mix; 9.77, 19.5, 39.1, 78.1, 156 and 313 μg/plate(TA100, TA1535, TA98 and TA1537); 9.77, 19.5, 39.1, 78.1, 156, 313 and 625 μg/plate(WP2 uvrA) +S9 mix; 9.77, 19.5, 39.1, 78.1, 156, 313 and 625 μg/plate (TA100); 19.5, 39.1, 78.1, 156, 313, 625 and 1250 μg/plate (TA1535, TA1537 and WP2 uvrA); 9.77, 19.5, 39.1, 78.1, 156 and 313 μg/plate (TA98) |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 3 |
| Number of replicates | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
Toxicity was observed at a concentration of 156 μg/plate in the five strains without an S9 mix, and at 313 μg/plate or greater(TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537) and 625 μg/plate or greater(WP2 uvrA) with an S9 mix.
Genetic effects:
S. typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98 and TA1537
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
E. coli WP2 uvrA
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| Purity | : | 99.6 % |
| Type of cell used | : | Chinese hamster lung(CHL)cells |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan)and OECD Guideline No. 473 |
| Solvent | : | DMSO |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix, Mitomycin C +S9 mix, Cyclophosphamide |
| Doses | : | -S9 mix(continuous exposure): 0, 178, 355, 710, 1420 μg/mL -S9 mix(short-term exposure): 0, 178, 355, 710, 1420 μg/mL +S9 mix(short-term exposure): 0, 355, 710, 1420 μg/mL |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Genetic effects:
| clastogenicity | polyploidy | |||||
| + | ? | - | + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| 1) | The tests were performed by the Research Institute for Animal Science in Biochemistry and Toxicology, 3-7-11 Hashimotodai, Sagamihara-shi, Kanagawa 229-1132, Japan. Tel +81-42-762-2775 Fax +81-42-762-7979 |
| 2) | The tests were performed by the Biosafety Research Center, Foods, Drugs and Pesticides(An-pyo Center), Japan, 582-2 Shioshinden Arahama, Fukude-cho, Iwata-gun, Shizuoka, 437-1213, Japan. Tel +81-538-58-1266 Fax +81-538-58-1393 |