
In a repeated dose toxicity test, one male and seven females receiving 60 mg/kg died during the administration period. Clinical observation, including the functional observation battery (FOB), revealed mydriasis, salivation, tremors, decrease in locomotor activity, bradypnea, hypothermia, soiling of the lower abdomen, adoption of a prone or lateral position and gasping in the males and females in the 60 mg/kg group. Mydriasis and salivation were also observed in the males and females in the 30 mg/kg group. Body weights and food consumption were decreased or showed a tendency for decrease in the males and females in the 60 mg/kg group. Urinalysis showed a tendency for increase in urine volume in the males in the 30 and 60 mg/kg groups and increased urine volume in the females in the 15 mg/kg or more groups, with resulting low values for osmotic pressure and specific gravity. Hematological examination revealed a shortened APTT in the males of the 30 and 60 mg/kg groups. Blood chemical examination revealed a low value for total protein, and high values for GPT and potassium in the males and females of the 60 mg/kg group. A low value for albumin, high values for ALP and blood urea nitrogen were observed in the males of the 60 mg/kg group. Low values for GOT and sodium, high values for total cholesterol, triglycerides and phospholipids were observed in the females of the 60 mg/kg group. High values for total cholesterol and phospholipids were also observed in the females of the 30 mg/kg group. Organ weight measurement revealed a high value for relative liver weights in the females of the 30 and 60 mg/kg groups. Necropsy revealed light red spots on the mucosa of the glandular stomach, which were histopathologically confirmed to be erosion in one dead female in the 60 mg/kg group. Histopathological examination revealed hypertrophy of the centrilobular hepatocytes in one surviving female in the 60 mg/kg group. The above-mentioned changes recovered after cessation of treatment, suggesting good reversibility. As for hypertrophy of the centrilobular hepatocytes, restoration was not confirmed because examination of recovery was not performed for females of the 60 mg/kg group. The NOELs are considered to be 15 mg/kg/day for males and 7.5 mg/kg/day for females.
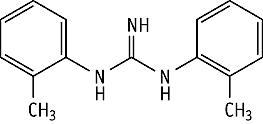
1,3-Bis(2-methylphenyl)guanidine was studied for oral toxicity in rats in an OECD preliminary reproduction toxicity screening test at doses of 0, 8, 20 and 50 mg/kg/day.
Deaths were observed of 2 males and 3 females in the 50 mg/kg group. As abnormal signs, salivation, mydriasis, hypoactivity, bradypnea, adoption of a prone position and/or tremors were observed in the males and females at 20 and 50 mg/kg. In addition, lowering of body weights and food consumption in the males and females of the 50 mg/kg group and lower food consumption in the females in the 20 mg/kg group were also observed. No effects related to administration of the test substance were noted at necropsy, or on organ weight or histopathological examination in any treatment group. The NOEL for repeated dose toxicity is considered to be 8 mg/kg/day.
As concerns reproductive toxicity, no effects related to administration of the test substance were observed on the estrous cycle, number of corpora lutea or implantations, implantation index, copulation index, male or female fertility indices, number of days required for copulation, gestational days or gestation indices. As concerns developmental toxicity, decrease in the litter size and live newborns, birth index, body weights of the male and female live newborns and viability index on day 4, and increase in the external anomaly index were observed in the 50 mg/kg group. There were no effects related to administration of the test substance on the stillbirth index or sex ratio of the live newborn. The NOELs for reproductive performance of the parents and for development of the offspring are considered to be 50 mg/kg/day and 20 mg/kg/day respectively.
Genotoxicity of 1,3-bis(methylphenyl)guanidine was studied by a reverse mutation test in bacteria and by a chromosomal aberration test in cultured Chinese hamster lung (CHL/IU) cells.
1,3-Bis(methylphenyl)guanidine was not mutagenic in Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537 or Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA, with or without an exogenous metabolic activation system.
1,3-Bis(methylphenyl)guanidine induced chromosomal aberrations in CHL/IU cells, with an exogenous metabolic activation system.
| Purity | : | 99.6 % |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD(SD)IGS |
| Test method | : | OECD Test Guideline 401 |
| Route | : | Oral (Gavage) |
| Dosage | : | 0 (Vehicle), 15, 30, 60, 120 mg/kg |
| Number of animals/group | : | Males, 5; females, 5 |
| Vehicle | : | 0.5 % Sodium carboxymethylcellulose solution mixed with 0.1 % Tween 80 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
LD50: Males, 85.3 mg/kg; females, 56.0 mg/kg
| Purity | : | 99.6 % |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD(SD)IGS |
| Test method | : | Guideline for 28-Day Repeated Dose Toxicity Test in Mammalian Species (Chemical Substances Control Law of Japan) |
| Route | : | Oral (Gavage) |
| Dosage | : | 0 (Vehicle), 7.5, 15, 30, 60 mg/kg/day |
| Number of animals/group | : | Males, 6 ; females, 6 |
| Vehicle | : | 0.5 % Sodium carboxymethylcellulose solution mixed with 0.1 % Tween 80 |
| Administration period | : | Males and females, 28 days |
| Terminal killing | : | Males and females, days 29 or 43 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
In the functional observation (FOB), mydriasis was noted in the males and females in the 30 and 60 mg/kg groups, and tremors, bradypnea and salivation in the males and females in the 60 mg/kg group. A weakened pupillary reflex was observed in the males and females, a decrease in visual reaction was observed in the females in the 60 mg/kg group. Measurement of motor activity showed a decrease or a tendency toward a decrease in the number of locomotor counts in the males and females in the 60 mg/kg group, suggesting a decrease in motor activity.
A decrease or a tendency toward a decrease in body weight was noted in the males in the 60 mg/kg group from Day 8 to the last day of recovery period, and in the females in the 60 mg/kg group from Days 8 to 28. A decrease in food consumption was noted in the males and females in the 60 mg/kg group on Days 2, 8, 15 and 28.
Urinalysis showed a tendency toward increase in urine volume in the males in the 30 and 60 mg/kg groups and an increase in urine volume in the females in the 15 mg/kg or more groups, with resulting low values for osmotic pressure and specific gravity.
Hematological examination revealed a shortened APTT in the males of the 30 and 60 mg/kg groups.
Blood chemical examination revealed a low value for total protein, high values for GPT and potassium in the males and females in the 60 mg/kg group. A low value for albumin, and high values for alkaline phosphatase and blood urea nitrogen were observed in the males of the 60 mg/kg group. Low values for GOT and sodium, high values for total cholesterol, triglycerides and phospholipids were noted in the females of the 60 mg/kg group. High values for total cholesterol and phospholipids were also observed in females of the 30 mg/kg group.
Organ weight measurement revealed a high value for relative liver weight in the females of the 30 and 60 mg/kg groups.
Necropsy revealed light red spots on the mucosa of the glandular stomach, which were histopathologically confirmed to be erosion of the glandular stomach in one dead female of the 60 mg/kg group. Histopathological examination revealed hypertrophy of the centrilobular hepatocytes in one surviving animal in the 60 mg/kg group.
The above-mentioned changes had recovered at the end of the recovery period, suggesting good reversibility. As for hypertrophy of the centrilobular hepatocytes, restoration could not be confirmed because examination of recovery was not performed for females of the 60 mg/kg group.
The NOELs are considered to be 15 mg/kg/day for males and 7.5 mg/kg/day for females.
| Purity | : | 99.6 % |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD(SD)IGS |
| Test method | : | OECD Test Guideline 421 |
| Route | : | Oral (Gavage) |
| Dosage | : | 0 (Vehicle), 8, 20, 50 mg/kg/day |
| Number of animals/group | : | Males, 12; females, 12 |
| Vehicle | : | 0.5 % Sodium carboxymethylcellulose solution mixed with 0.1 % Tween 80 |
| Administration period | : | Males, 49 days Females, from 14 days before mating to day 3 of lactation |
| Terminal killing | : | Males, day 50 Females, day 4 of lactation |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
Deaths were observed for 2 males and 3 females of the 50 mg/kg group. As abnormal signs, salivation was observed in males and females of the 20 and 50 mg/kg groups and mydriasis, hypoactivity, bradypnea, prone position and tremor in females of 20 mg/kg group and the males and females of the 50 mg/kg group. These signs, except for salivation, were observed on the initial day of administration. Thereafter, the incidences of these changes decreased dose by dose. Salivation was observed sporadically from the middle to the end of the administration period. Lowering of body weights and food consumption were observed in males and females of the 50 mg/kg group, and lower food consumption in females of the 20 mg/kg group. No effects related to administration of the test substance were observed on necropsy, organ weights or histopathological examination in any treatment group. The NOEL for repeated dose toxicity is considered to be 8 mg/kg/day.
<Reproductive and developmental toxicity>
As concerns reproductive performance, no effects related to administration of the test substance were observed on the estrous cycle, numbers of corpora lutea or implantations, implantation index, copulation index, male or female fertility index or number of days required for copulation. In the examination at delivery and during the lactation period, decrease in the litter size and live newborns, birth index, body weights of male and female live newborn and the viability index on day 4 and increase in the external anomaly index were noted for the 50 mg/kg group. There were no effects related to administration of the test substance on the gestational days, stillbirth or gestation index or sex ratio of the live newborn. The NOELs for reproductive performance of the parents and for development of the offspring are considered to be 50 mg/kg/day and 20 mg/kg/day, respectively.
| Purity | : | 99.6 % |
| Test species/strain | : | Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537, Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Chemical Substances Control Law of Japan) and OECD Test Guideline 471 |
| Procedures | : | Pre-incubation method |
| Solvent | : | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix; 2-(2-Furyl)-3-(5-nitro-2-furyl)acrylamide (TA100, TA98, WP2 uvrA), Sodium azide (TA1535) and 9-Amino-acridine (TA1537) +S9 mix; 2-Aminoanthracene (all strains) |
| Dosage | : | -S9 mix ; 0, 78.1, 156, 313, 625, 1250, 2500 μg/plate (TA100, TA1537) -S9 mix; 0, 156, 313, 625, 1250, 2500, 5000 μg/plate (TA98, TA1535, WP2 uvrA) +S9 mix; 0, 156, 313, 625, 1250, 2500, 5000 μg/plate (all strains) |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 3 |
| Number of replicates | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
Genotoxic effects:
Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| Purity | : | 99.6 % |
| Type of cell used | : | Chinese hamster lung (CHL/IU) cells |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Chemical Substances Control Law of Japan) and OECD Test Guideline 473 |
| Solvent | : | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix; 1-Methyl-3-nitro-1-nitrosoguanidine +S9 mix; 3,4-Benzo[a]pyrene |
| Dosage | : | -S9 mix(6 hr short-term treatment); 0, 75, 150, 300, 450, 600 μg/mL +S9 mix (6 hr short-term treatment); 0, 75, 150, 300, 450, 600 μg/mL +S9 mix(6 hr short-term treatment :Confirmation test); 0, 400, 600, 800 μg/mL |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
Cytotoxicity was observed at 600 μg/mL after 6 hr short-term treatment without S9 mix, and at 800 μg/mL after 6 hr short-term treatment with S9 mix.
| Lowest concentration producing cytogenetic effects in vitro | : | ||
| With metabolic activation (short-term treatment) | : | 0.6 mg/mL (clastogenicity) | |
Genotoxic effects:
| clastogenicity | polyploidy | |||||
| + | ? | - | + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| 1) | The tests were performed by the Safety Assessment Laboratory, Panapharm Laboratories Co., Ltd., 1285 Kurisaki-machi, Uto-shi, Kumamoto, 869-0425, Japan. Tel +81-964-23-5111 Fax +81-964-23-2282 |
| 2) | The tests were performed by the Research Institute for Animal Science in Biochemistry and Toxicology, 3-7-11 Hashimotodai, Sagamihara-shi, Kanagawa, 229-1132, Japan. Tel +81-42-762-2775 Fax +81-42-762-7979 |