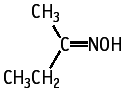

Ethyl methyl ketoxime was not mutagenic to Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA98, TA1535, TA1537 and Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA, with or without an exogeneous metabolic activation system.
Ethyl methyl ketoxime induced neither structural chromosomal aberrations nor polyploidy in CHL/IU cells up to the limit concentration of 10 mM (0.87 mg/ml), in the absence or presence of an exogenous metabolic activation system.
| Purity | : | 99.0% |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD (SD) |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for 28-Day Repeat Dose Toxicity Testing for Chemicals (Japan) |
| Route | : | Oral (gavage) |
| Doses | : | 0 (vehicle), 4, 20, 100 mg/kg/day |
| Number of animals/group | ||
| Administration period | : | Males and females, 14, 7, 7 and 14/group for the 0, 4, 20 and 100 mg/kg cases, respectively |
| Recovery period | : | Males and females, 7 and 7/group for the 0 and 100 mg/kg cases, respectively |
| Vehicle | : | Olive oil |
| Administration period | : | Males and females, 28 days |
| Terminal kill | : | Days 29 or 43 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
| Purity | : | 99.98% |
| Test species/strains | : | Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537, Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA |
| Test methods | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan) and OECD (471 and 472) |
| Procedures | : | Plate incorporation method |
| Solvent | : | Acetone |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix, 2-(2-Furyl)-3-(5-nitro-2-furyl)acrylamide (TA100, WP2, TA98), Sodium azide (TA1535)and 9-Aminoacridine (TA1537), +S9 mix, 2-Aminoanthracene (five strains) |
| Doses | : | 0, 313, 625, 1250, 2500 and 5000 μg/plate in five strains, -S9 mix and +S9 mix. |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 3 |
| Number of replicates | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Genetic effects:
Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| Purity | : | 99.98% |
| Type of cell used | : | Chinese hamster lung (CHL/IU) cells |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan) |
| Solvent | : | Acetone |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix, Mitomycin C +S9 mix, Cyclophosphamide |
| Doses | : | -S9 mix (continuous treatment): 0, 0.22, 0.44, 0.87 mg/ml
-S9 mix (short-term treatment): 0, 0.22, 0.44, 0.87 mg/ml +S9 mix (short-term treatment): 0, 0.22, 0.44, 0.87 mg/ml |
| S-9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
| clastogenicity | polyploidy | |||||
| + | ? | - | + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| 1) | The tests were performed by the Safety Research Institute for Chemical Compounds Co., Ltd., 363-24, Shin-ei, Toyohira-ku, Sapporo, Hokkaido, 004, Japan. Tel +81-11-885-5031 Fax +81-11-885-5313 |
| 2) | The tests were performed by the Hatano Research Institute, Food and Drug Safety Center, 729-5 Ochiai, Hadano-shi, Kanagawa, 257, Japan. Tel +81-463-82-4751 Fax +81-463-82-9627 |

Ethyl methyl ketoxime was studied for oral toxicity in rats in an OECD preliminary reproductive toxicity screening test at doses of 0, 10, 30 and 100 mg/kg/day.
In the repeat dose toxicity, no dead animals were found in any groups. There were no adverse effects of test substance on general condition, body weight or food consumption throughout the administration period. The spleen weights of the animals in both sexes receiving 30 mg/kg or more showed significant increase compared with the control group values, and liver weights in males and heart weights in females of the 100 mg/kg group were also increased. In the necropsy findings, black and enlargement of spleen were observed in both sexes receiving 30 mg/kg or more of test substance. As histopathological findings, congestion, deposition of pigment and extramedullary hematopoiesis in the spleen, deposition of glycogen, deposition of pigment in Kupffer cells and extramedullary hematopoiesis in the liver and deposition of brown pigment in the kidney were observed in both sexes receiving 10 mg/kg or more. The incidences or degrees of these findings in the treatment groups were greater than those in the control group.
The NOEL for repeat dose toxicity in parent animals in both sexes is considered to be less than 10 mg/kg/day.
In terms of reproductive/developmental toxicity, delivery index in the 100 mg/kg group showed significant decrease compared with the control group value. With regard to the neonates, no adverse effects of the test substance were observed in any groups.
NOELs for reproductive/developmental toxicity are considered to be 100 mg/kg/day for males, 30 mg/kg/day for females, and 100 mg/kg/day for the F1 generation.
| Purity | : | 99.99 wt% |
| Test species/strains | : | Rat/Crj:CD(SD) |
| Test method | : | OECD Preliminary Reproductive Toxicity Screening Test |
| Route | : | Oral(gavage) |
| Doses | : | 0(Vehicle), 10, 30, 100 mg/kg/day |
| Number of animals | : | Males, 12; females, 12/group |
| Vehicle | : | Distilled water for injection |
| Administration period | : | Males, 48 days Females, from 14 days before mating to day 3 of lactation |
| Terminal kill | : | Male, day 48 Females, day 4 of lactation |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
In the repeat dose study, no animals were found dead in any groups. There were no adverse effects of the test substance on general condition, body weight or food consumption throughout the administration period.
The spleen weights of the animals in both sexes receiving 30 mg/kg or more showed significant increase as compared with the control group values, and liver weights in males and heart weights in females of the 100 mg/kg group were also elevated. In the necropsy findings, black and enlargement of spleen were observed in both sexes receiving 30 mg/kg or more of the test substance. As histopathological findings, congestion, deposition of pigment and extramedullary hematopoiesis in the spleen, deposition of glycogen, deposition of pigment in Kupffer cells and extramedullary hematopoiesis in the liver and deposition of brown pigment in the kidney were observed in both sexes receiving 10 mg/kg or more. The incidences or degrees of these findings in treatment groups were greater than in the control group.
The NOEL for repeat dose toxicity in parent animals in both sexes is considered to be less than 10 mg/kg/day.
<Reproductive and Developmental toxicity>
As for the reproductive ability of parent animals, no effects were detected in males, while the delivery index in the 100 mg/kg group showed significant decrease compared with control group value. With regard to the effects on neonates, no adverse effects of the test substance were observed in any group.
On the basis of these findings , NOELs for reproductive/developmental toxicity are considered to be 100 mg/kg/day for males, 30 mg/kg/day for females,and 100 mg/kg/day for the F1 generation,
| 1) | The tests were performed by the Biosafety Research Center, Foods, Drugs and Pesticides(An-pyo Center), Japan, 582-2 Shioshinden Arahama, Fukude-cho, Iwata-gun, Shizuoka, 437-1213, Japan. Tel +81-538-58-1266 Fax +81-538-58-1393 |