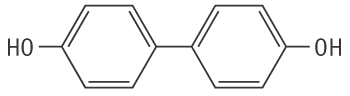
Molecular formula: C12H10O2 Molecular weight: 186.21

4,4'-Biphenyldiol was studied for acute oral toxicity in female rats at a dose of 2000 mg/kg.
Rats did not die and only showed reddish urine and slight suppression of body weight gain after administration. They had recovered after 2 or 3 days and there were no abnormal findings at autopsy.
The test substance is classified in category 5 of GHS regarding acute toxicity.
A combined repeat dose and reproductive/developmental toxicity screening test of 4,4'-biphenyldiol was conducted in rats according to the OECD Test Guideline 422. At the dose level of 200 mg/kg, excreted urine became cloudy with elapse of time. On urinalysis, turbidity was found in males and females given 40 mg/kg or more. Calcium oxalate-like urinary crystal sediment was found in the males given 200 mg/kg and in the females given 40 mg/kg or more. Urinary gravity was decreased in the females given these doses. At necropsy after the final treatment, 200 mg/kg of the compound affected male livers by increasing their relative weights, darkening and enlarging their macroscopic appearance, and altering the histopathological appearance, including development of centrilobular hepatocyte hypertrophy and reduction in occurrence of periportal fatty change. Fourteen days after the final treatment the recovery group of males and the satellite females demonstrated that all of the changes caused by the compound had disappeared and no delayed toxicity was evident. The treatment did not affect reproductive performance of parent animals or early development of their offspring.
The no observed effect dose level (NOEL) for repeat dose toxicity of 4,4'-biphenyldiol is considered to be 8 mg/kg/day for both sexes of animals. The NOEL for reproductive/developmental toxicity is considered to be 200 mg/kg/day for females and males, and the NOEL for offspring is considered to be 200 mg/kg/day.
Genotoxicity of 4,4'-biphenyldiol was studied by a reverse mutation test in bacteria. The substance was not mutagenic in Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA98, TA1535, TA1537 or Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA, with or without an exogenous metabolic activation system.
4,4'-Biphenyldiol induced structural chromosomal aberrations and polyploidy in CHL/IU cells after short-term (6 hr) treatment with and without metabolic activation.
| Purity | : | 99.96 % |
| Test species/strain/sex | : | Rat/Crj:CD(SD)IGS/Female |
| Test method | : | OECD Test Guideline 423 |
| Route | : | Oral(gavage) |
| Dosage | : | 2000 mg/kg |
| Number of animals/group | : | Females, 3 |
| Vehicle | : | 0.5 % Sodium carboxymethylcellulose solution |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
The test substance is classified in category 5 of GHS regarding acute toxicity.
| Purity | : | 99.96 % |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD(SD)IGS |
| Test method | : | OECD Test Guideline 422 |
| Route | : | Oral(gavage) |
| Dosages | : | 0, 8, 40, 200 mg/kg |
| Dosages for recovery | : | 0, 200 mg/kg |
| Number of animals/group | : | Males, 12 (5 for recovery); females, 12; satellite females, 5 |
| Vehicle | : |
0.5 % Sodium carboxymethylcellulose solution |
| Administration period | : |
Males, 42 days |
| Recovery period | : | Males, 14 days Females(satellite), 14 days |
| Terminal killing | : | Males, day 43 of treatment and day 15 of recovery Females, day 5 of lactation Females (satellite), day 15 of recovery Offspring, 4 days after birth |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
Oral administration of the compound at dose levels up to 200 mg/kg did not cause death or a moribund condition in any animals, and no scores obtained on detailed clinical observation differed between the control and the compound-treated groups. No apparent changes were observed in general conditions, except that urine in the 200 mg/kg-treated group became cloudy with elapse of time after excretion. On urinalysis performed on treatment days 31 and 32 in male and female rats, respectively, calcium oxalate-like urinary crystal sediments were found in males given 200 mg/kg and in females given 40 mg/kg or more. Turbidity was enhanced with 40 mg/kg or more, and urinary gravity was decreased in these females. These changes in urine were not found when urinalysis was performed at 11 days after cessation of the treatment (on day 11 of recovery) in either sex of animal. Body weight increase and food consumption were not affected by the treatment at any dose level of the compound in either sex. No animals showed any abnormality in functional parameters after the final treatment.
At necropsy on termination of the treatment, no apparent effects of the compound were found on hematological or blood-biochemical examination at any dose level of the compound in either sex. No effects of the compound were apparent in the female organs, including their weights or macroscopic or microscopic findings. In contrast, 200 mg/kg of the compound exerted effects on male livers, with significant increase in relative weight, darkening or enlargement of the macroscopic appearance, development of centrilobular hepatocyte hypertrophy and reduction in occurrence of periportal fatty change. However, no animals showed any abnormality in functional observations on day 14 of the recovery period. At necropsy on day 15 of recovery, changes in the liver were not found in males given 200 mg/kg. In females given 200 mg/kg for 42 days and killed for necropsy on day 15 of recovery (satellite group), there were similarly no abnormal findings.
2. Reproductive and developmental toxicity
The treatment did not affect parameters of reproductive performance, such as the estrous cycle, ovulation, mating, implantation, delivery or lactational condition at any dose level. No adverse effects of the compound were observed on viability, morphology or growth of offspring.
3. Evaluation
From the above results, no observed effect dose level (NOEL) for repeat dose toxicity of 4,4'-biphenyldiol is considered to be 8 mg/kg/day in both sexes of animals. The NOEL for reproductive/developmental toxicity is considered to be 200 mg/kg/day for females and males. The NOEL for offspring is considered to be 200 mg/kg/day.
| Purity | : | 99.96 % |
| Test species/strains | : | Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537, Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Chemical Substances Control Law of Japan) and OECD Test Guideline 471 |
| Procedures | : | Pre-incubation method |
| Solvent | : | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix; 2-(2-Furyl)-3-(5-nitro-2-furyl)acrylamide (TA100, TA98, WP2 uvrA), sodium azide (TA1535) and 9-aminoacridine (TA1537) +S9 mix; 2-Aminoanthracene (five strains) |
| Dosage | : | -S9 mix; 0, 78.1, 156, 313, 625, 1250, 2500 μg/plate (TA100), 0, 156, 313, 625, 1250, 2500, 5000 μg/plate (TA1535, TA98, TA1537, WP2 uvrA) +S9 mix; 0, 78.1, 156, 313, 625, 1250, 2500 μg/plate (TA100), 0, 156, 313, 625, 1250, 2500, 5000 μg/plate (TA1535, TA98, TA1537, WP2 uvrA) |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5, 6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 3 (1 for the cytotoxicity test) |
| Number of replicates | : | 2 (plus 1 for the cytotoxicity test) |
| GLP | : | Yes |
This chemical did not induce gene mutation in S. typhimurium TA100, TA98, TA1535, TA1537 or E. coli WP2 uvrA strains with or without S9 mix. Growth inhibition was observed at 1250 μg/plate and above in TA100, and at 2500 μg/plate and above in TA1535, TA98 and TA1537, both with and without S9 mix.
Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA98, TA1535, TA1537
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| Purity | : | 99.96 % |
| Type of cell used | : | Chinese hamster lung (CHL/IU) cells |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Chemical Substances Control Law of Japan) and OECD Test Guideline 473 |
| Solvent | : | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix; Mitomycin C +S9 mix; Cyclophosphamide |
| Dosage | : | -S9 mix(short-term treatment); 0, 0.030, 0.060, 0.12 mg/mL +S9 mix(short-term treatment); 0, 0.030, 0.060, 0.12 mg/mL |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 4 (2: chromosome specimens, 2: measurement of growth rate) |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Cells with structural chromosomal aberrations were increased significantly at all the doses after short-term treatment without metabolic activation (9.0-15.0 %), and the middle and the high doses after short-term treatment with metabolic activation (11.0 % and 16.0 %). Statistically significant increase in polyploidy was observed with the middle and high doses after short-term treatment, with and without metabolic activation (1.0- 6.0 %).
Lowest concentration producing cytogenetic effects in vitro :
| Without metabolic activation(short-term treatment): | 0.030 mg/mL(clastogenicity) |
| 0.060 mg/mL(polyploidy) | |
| With metabolic activation(short-term treatment): | 0.060 mg/mL(clastogenicity) |
| 0.060 mg/mL(polyploidy) |
| Clastogenicity | Polyploidy | |||||
| + | ? | - | + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] |
| With metabolic activation: | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] |
| 1) | The test was performed by the Safety Research Institute for Chemical Compounds Co., Ltd., 363-24 Shin-ei, Kiyota-ku, Sapporo, Hokkaido, 004-0839, Japan. Tel +81-11-885-5031, Fax +81-11-885-5313. |
| 2) | The tests were performed by the Hatano Research Institute, Food and Drug Safety Center, 729-5 Ochiai, Hadano-shi, Kanagawa, 257-8523, Japan. Tel +81-463-82-4751, Fax +81-463-82-9627. |