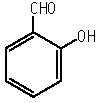

With regard to repeat dose toxicity, 1 dam in the 40 mg/kg group died during delivery on day 22 of gestation and 1 dam in the 160 mg/kg group died on day 22 of gestation. Increased liver weights and decreased ovary weights were observed in females of the 160 mg/kg group. In the histopathological findings, a decrease in the degree and incidence of cytoplasmic lipid droplets in the liver was observed in males in the groups treated with 40 mg/kg or more and slight increase in glycogen deposits in the liver were observed in females in the groups treated with 40 mg/kg or more. The NOEL for repeat dose toxicity is considered to be 10 mg/kg/day for both sexes.
With regard to the reproductive/developmental toxicity, the viability index in the 160 mg/kg group tended to be low and the body weights of the pups showed a tendency toward low values on days 0 and 4 of lactation in this group. The NOELs for reproductive and developmental toxicity are considered to be 160 mg/kg/day for males and 40 mg/kg/day for females and their offspring.
2-Hydroxybenzaldehyde was not mutagenic to Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA98, TA1535, TA1537 and Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA, with or without an exogeneous metabolic activation system.
2-Hydroxybenzaldehyde induced structural chromosomal aberrations and polyploidy in CHL/IU cells in the absence and presence of an exogeneous metabolic activation system.
| Purity | : | 99.3% |
| Test Species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD (SD) |
| Test method | : | OECD Combined Repeat Dose and Reproductive/Developmental Toxicity Screening Test |
| Route | : | Oral (gavage) |
| Doses | : | 0 (Vehicle), 2.5, 10, 40 and 160 mg/kg/day |
| Number of animals/group | : | Males, 12; females, 12 |
| Vehicle | : | Olive oil |
| Administration period | : | Males, 49 days Females, from 14 days before mating to day 3 of lactation |
| Terminal kill | : | Males, day 50 of administration Females, day 4 of lactation |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
| Purity | : | above 95 % |
| Test species/strains | : | Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537, Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA |
| Test methods | : | Guideline for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan) and OECD (471 and 472) |
| Procedures | : | Plate incorporation method |
| Solvent | : | DMSO |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix, 2-(2-Furyl)-3-(5-nitro-2-furyl)acrylamide (TA100, WP2, TA98), Sodium azide (TA1535) and 9-Aminoacridine (TA1537) +S9 mix, 2-Aminoanthracene (five strains) |
| Dosage | : | -S9 mix, 0, 15.6, 31.3, 62.5, 125, 250 and 500 μg/plate (TA100), 0, 31.3 - 1000 (TA1535, TA98 and TA1537) and 0, 125 - 4000 μg/plate (WP2)
+S9 mix, 0, 15.6 - 500 (TA100), 0, 62.5 - 2000 μg/plate (TA1535, TA98 and TA1537) and 0, 125 - 4000 μg/plate (WP2). |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 3 |
| Number of replicates | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Genetic effects:
Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| Purity | : | More than 95% |
| Type of cell used | : | Chinese hamster lung (CHL/IU) cells |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan) |
| Solvent | : | Dimethylsulfoxide |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix, Mitomycin C +S9 mix, Cyclophosphamide |
| Doses | : | -S9 mix (continuous treatment): 0, 0.0050, 0.010,0.020 mg/ml -S9 mix (short-term treatment): 0, 0.050, 0.10, 0.20 mg/ml +S9 mix (short-term treatment): 0, 0.050, 0.10, 0.20 mg/ml |
| S-9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
| Lowest concentration producing cytogenetic effects in vitro: | |
| without metabolic activation (continuous treatment ): | 0.020 mg/ml (clastogenicity) 0. 020 mg/ml (polyploidy) |
| Without metabolic activation (short-term treatment): | 0.10 mg/ml (clastogenicity) |
| With metabolic activation (short-term treatment): | 0.10 mg/ml (clastogenicity) 0. 050 mg/ml (polyploidy) |
| clastogenicity | polyploidy | |||||
| + | ? | - | + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] |
| With metabolic activation: | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] |
| 1) | The tests were performed by Bozo Research Center Inc, 1284, Kamado, Gotemba-shi, Shizuoka, 412, Japan. Tel +81-550-82-2000 Fax +81-550-82-2379 |
| 2) | The tests were performed by the Hatano Research Institute, Food and Drug Safety Center, 729-5 Ochiai, Hadano-shi, Kanagawa, 257, Japan. Tel +81-463-82-4751 Fax +81-463-82-9627 |