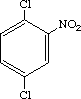

With regard to reproductive/developmental toxicity, yellowish brown urine and salivation were found in both sexes at 60 and 200 mg/kg, and perigenital soiling, decrease in locomotor activity, extension of hindlimbs etc. were found in both sexes at 200 mg/kg. Death of one dam occurred during the gestation period, one during the delivery period and four during the lactation period in the 200 mg/kg group. Reduced body weight gains were found in both sexes at 200 mg/kg. On histopathological examination, degeneration of seminiferous epithelium in the testes and debris in epididymides ducts were found in the 200 mg/kg group. In addition, there were indications that the test substance affected growth of newborn pups at 200 mg/kg. The test substance is concluded to affect dams during the perinatal period and neonatal development in spite of no changes in copulation or fertility indexes. NOELs are suggested to be 200 mg/kg and 20 mg/kg for reproductive performance of males and females, respectively, and 60 mg/kg for development of pups in terms of reproductive developmental toxicological effects.
1,4-Dichloro-2-nitrobenzene was mutagenic in Salmonella typhimurium TA 100 with and without metabolic activation and TA1537 without metabolic activation. Structural chromosomal aberrations were induced at the highest concentration (0.15 mg/ml) with 48-hr continuous treatment of CHL/IU cells. Polyploid cells were not induced.
| Purity | : | >99.5% |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD (SD) |
| Test method | : | OECD Preliminary Reproduction Toxicity Screening Test |
| Route | : | Oral (gavage) |
| Dosage | : | 0 (Vehicle), 6, 20, 60, 200 mg/kg/day |
| Number of animals | : | Males, 12; Females, 12/group |
| Vehicle | : | Corn oil |
| Administration period | : | Males, 49 days Females, from 14 days before mating to Day 3 of lactation |
| Terminal killing | : | Males, Day 50 of administration Females, Day 4 of lactation |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
| Purity | : | above 99.5% |
| Test species/strain | : | S.typhimurim TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537 E. coli WP2 uvrA |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan) |
| Procedures | : | Plate incorporation method |
| Solvent | : | DMSO |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 Mix, AF-2 (TA100, WP2, TA98) sodium azide (TA1535) and 9-aminoacridine (TA1537) +S9 Mix; 2-aminoanthracene (all strains) |
| Doses | : | - S9 Mix; 0, 78.13 - 2500 μg/plate (TA100) +S9 Mix; 78.13 - 2500 [156.3 - 5000 (WP2 and TA1537)] 0, 156.3, 312.5, 625, 1250, 2500 and 5000 (WP2) |
| S-9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 3 |
| Number of replicates | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
| + | ? | - | |
| without metabolic activation: | [*] | [ ] | [ ] |
| with metabolic activation: | [*] | [ ] | [ ] |
S. typhimurium TA1535
| + | ? | - | |
| without metabolic activation: | [*] | [ ] | [ ] |
| with metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
S. typhimurium TA 98 and TA1537
| + | ? | - | |
| without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| with metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
E. Coli WP2 uvrA
| + | ? | - | |
| without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| with metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| Purity | : | More than 99.5% |
| Type of cell used | : | Chinese hamster lung (CHL/IU) cells |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan) |
| Solvent | : | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| Positive controls | : | -S9, Mitomycin C +S9, Cyclophosphamide |
| Doses | : | -S9 (continuous treatment): 0, 0.04, 0.08, 0.15 mg/ml -S9 (short-term treatment): 0, 0.024, 0.047, 0.094 mg/ml +S9 (short-term treatment): 0, 0.024, 0.047, 0.094 mg/ml |
| S-9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
| clastogenicity | polyploidy | |||||
| + | ? | - | + | ? | - | |
| without metabolic activation: | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| with metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| 1) | The test was performed by Nihon Bioresearch Inc. Hashima Laboratory, 6-104 Majima, Fukuju-cho, Hashima, Gifu, 501-62 Japan Tel +81-58-392-6222 Fax +81-58-391-3171 |
| 2) | The tests were performed by the Hatano Research Institute, Food and Drug Safety Center, 729-5 Ochiai, Hadano-shi, Kanagawa, 257, Japan. Tel +81-463-82-4751 Fax +81-463-82-9627 |