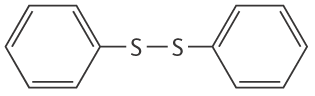
Molecular formula: C12H10S2 Molecular weight: 218.34
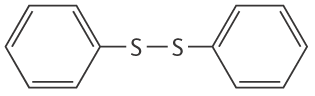
Diphenyl disulfide was administered once by oral gavage to female Crj:CD(SD)IGS rats aged 8 to 8.5 weeks and its acute toxicity was examined according to the OECD Test Guideline 423. Dosages were set at 300 mg/kg (1st and 2nd steps) and 2000 mg/kg (3rd and 4th steps).
No dead or moribund animals were observed in the 300 mg/kg group, and there were no changes considered attributable to the test substance in clinical signs, body weights or necropsy findings.
Emaciation, lateral position, hunchback position, decrease in locomotor activity, bradypnea, and/or hypothermia were noted in the 2000 mg/kg group from Day 4. Decreases in body weights were observed from Days 1 to 8. Finally, 1 animal died and 2 animals were subjected to sacrifice as moribund in the 2000 mg/kg group on Days 8 to 10. Necropsy revealed hemorrhage in the glandular stomach, raised patches and thickening of the forestomach wall, small thymi, reduction in the size of the spleen, dark reddish spleen, distention of colon, enlargement of adrenals, abnormal contents of jejunum, and/or retention of yellowish chromaturia in urinary bladder. Abnormal clinical signs disappeared by Day 14 in the surviving animals. Body weights began to recover from Day 8. However, necropsy of the surviving animals revealed raised patches in the forestomach and/or reduced thymus size.
From the above results, diphenyl disulfide was classified as category 4 (>300-2000 mg/kg) of the GHS (Globally Harmonized Classification System) under the conditions of this study.
Diphenyl disulfide was studied for oral toxicity in rats in an OECD combined repeated dose and reproductive/developmental toxicity screening test at doses of 0, 1, 6, and 30 mg/kg/day.
As a main effect of repeated dose toxicity, anemia was seen in both sexes of the 30 mg/kg group. Increase in hematopoietic cells was seen in the spleen and bone marrow as a corresponding biological reaction. Several changes were also seen in the liver and kidney. In the kidney, especially, intensification of hyaline droplet generation in proximal tubular epithelium was seen in males of the 1 mg/kg or higher groups. The above changes, however, disappeared within the 2-weeks of the recovery period, or became less pronounced concerning their incidence and degree, and thus were confirmed to have tendencies for reversibility. The NOELs for repeated dose toxicity are considered to be less than 1 mg/kg/day for males, and 1 mg/kg/day for females.
With the regard to reproductive and development toxicity, the test substance showed no adverse effects on any relevant parameters. The NOELs for reproductive and development toxicity are considered to be 30 mg/kg/day for both parental animals and offspring.
Diphenyl disulfide was not mutagenic in Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537 and Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA/pKM101, with or without an exogenous metabolic activation system.
Diphenyl disulfide did not induce structural chromosomal aberrations or polyploidy in CHL/IU cells with or without exogenous metabolic activation.
| Purity | : | 99.8% |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD(SD)IGS |
| Test method | : | OECD Test Guideline 423 |
| Route | : | Oral(gavage) |
| Dosage | : | 300 (1st and 2nd steps) and 2000 (3rd and 4th steps) mg/kg/day |
| Number of animals/group | : | Females, 3 |
| Vehicle | : | 0.5 % Tragacanth gum solution |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results
No dead animals were observed in the 300 mg/kg group (1st and 2nd steps).
One animal was subjected to moribund sacrifice on Day 8 and 1 animal died on Day 9 in the 2000 mg/kg group (3rd step). In the 2000 mg/kg group (4th step), 1 animal was subjected to moribund sacrifice on Day 10.
Clinical observation revealed no abnormalities in the 300 mg/kg group. Emaciation, adoption of a lateral or hunchback position, decrease in locomotor activity (3rd and 4th steps), bradypnea (3rd step), and hypothermia (4th step) were observed from Day 4 in the 2000 mg/kg group. The abnormal clinical signs had disappeared by Day 14 in the surviving animals.
Body weights in the 300 mg/kg group increased normally. In the 2000 mg/kg group, decreases in body weights were noted on Days 4 and/or 8, resulting in decreased body weight gain for Days 1-4 and/or 4-8. Body weights in surviving animals in the 2000 mg/kg group decreased until Day 8; however, values increased thereafter, resulting in higher body weight gain on Days 8-15 than in the 300 mg/kg group.
At necropsy, no abnormalities were detected in the 300 mg/kg group. Dead and moribund sacrificed animals in the 2000 mg/kg group showed reduced thymus size, small spleens and focal hemorrhage in the glandular stomach (all animals), raised patches in forestomach and enlargement of adrenals (2 animals), dark reddish spleen, thickening of the forestomach wall, distention of colon, abnormal tar-like material in the jejunum, and/or retention of yellowish chromaturia in the urinary bladder (1 animal). Necropsy of the 3 surviving animals in the 2000 mg/kg group revealed small thymus in 1 animal and raised patches in the forestomach in all animals.
Since a 1 animal died and 2 animals were subjected to moribund sacrifice in the 2000 mg/kg group, diphenyl disulfide was classified as category 4 (>300-2000 mg/kg) of the GHS under the conditions of this study.
| Purity | : | 99.8% |
| Test species/strain | : | Rats/Crj:CD(SD)IGS |
| Test method | : | OECD Test Guideline 422 |
| Route | : | Oral(gavage) |
| Dosage | : | 0(vehicle), 1, 6, 30 mg/kg |
| Number of animals/group | : | Males, 12; females, 12 Satellite females, 5 (control and 30 mg/kg groups) |
| Vehicle | : | 0.5 % Tragacanth gum solution |
| Administration period | : |
Males and satellite females, 42 days |
| Terminal killing | : |
Males, days 43 and 57 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
Diphenyl disulfide was studied for oral toxicity in rats in an OECD combined repeated dose and reproductive/developmental toxicity screening test at doses of 0, 1, 6, and 30 mg/kg/day.
Increases in the spleen weight in both sexes, as well as enlargement and dark reddish coloring in females were seen in the 30 mg/kg group. On histopathological examination, hemosiderin deposition and intensification of erythrocytic extramedullary hematopoiesis in the spleen were seen in both sexes, along with increased erythrocytic hematopoiesis in bone marrow among females, were seen in the 6 mg/kg or higher groups.
As hematological changes associated with the hematopoietic system, decreases in red blood cell count in both sexes, as well as anemic changes such as decreases in hemoglobin concentration and increased reticulocyte counts in males were seen in the 30 mg/kg group.
As effects on the liver, increases in the weight, enlargement, and hypertrophy of centrilobular hepatocytes were seen in both sexes of the 30 mg/kg group. Histopathological changes were also apparent in males of the 6 mg/kg group. In blood chemistry data, increases in total cholesterol and decreases in glucose in males, as well as increases in total cholesterol, total protein, and albumin in females, were seen in the 30 mg/kg group.
Increased kidney weights were evident in males of the 6 and 30 mg/kg groups and females of the 30 mg/kg group, and kidney enlargement was noted in males of the 1 mg/kg or higher groups. On histological examination, increased hyaline droplet generation in proximal tubular epithelium and basophilic proximal tubules were seen in males and lipofuscin deposition on tubular epithelium was seen in females. As effects on the thyroid gland, hypertrophy of follicular cells was seen in males of the 30 mg/kg group.
The above changes were apparent at the end of the dosing period; however, they had disappeared within the 2-weeks of the recovery period, or had become less pronounced concerning the incidence and degree, and thus were confirmed to be reversible.
<Reproductive and developmental toxicity>
The compound had no effects on reproductive parameters such as the estrous cycle, mating index, fertility index, gestation index, gestation length, number of corpora lutea or implantations, implantation index, delivery index, parturition or maternal behavior. On examination of neonates, there were no significant differences in numbers of offspring or live offspring, the sex ratio, the live birth index, viability index or body weight. No abnormal findings ascribable to the compound were evident for external features, clinical signs, or necropsy findings for the offspring.
The NOELs for reproductive and developmental toxicity are considered to be 30 mg/kg/day for both sexes and offspring.
| Purity | : | 99.8% |
| Test species/strain | : | Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537, Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA/pKM101 |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Chemical Substances
Control Law of Japan) and OECD Test Guideline 471 |
| Procedures | : | Pre-incubation method |
| Solvent | : | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix; 2-(2-Furyl)-3-(5-nitro-2-furyl)acrylamide (TA100, WP2 uvrA/pKM101,
TA98), sodium azide (TA1535) and 9-aminoacridine hydrochloride (TA1537) +S9 mix; 2-Aminoanthracene (all strains) |
| Dosage | : | -S9 mix; 0, 0.153, 0.305, 0.610, 1.22, 2.44, 4.88, 9.77 μg/plate (TA100, TA1535), 0, 39.1, 78.1, 156, 313, 625, 1250, 2500 μg/plate (WP2 uvrA/pKM101), 0, 0.305, 0.610, 1.22, 2.44, 4.88, 9.77, 19.5 μg/plate (TA98, TA1537) +S9 mix; 0, 1.22, 2.44, 4.88, 9.77, 19.5, 39.1, 78.1 μg/plate (TA100, TA1535), 0, 78.1, 156, 313, 625, 1250, 2500, 5000 μg/plate (WP2 uvrA/pKM101), 0, 2.44, 4.88, 9.77, 19.5, 39.1, 78.1, 156 μg/plate (TA98, TA1537) |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 3 |
| Number of replicates | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Genetic effects :
Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537
| + | ? | - | |
| without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| with metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA/pKM101
| + | ? | - | |
| without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| with metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| Purity | : | 99.8% |
| Type of cell used | : | Chinese hamster CHL/IU cells |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Chemical Substances Control Law of Japan) and OECD Test Guideline 473 |
| Solvent | : | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix; Mitomycin C +S9 mix; Benzo[a]pyrene |
| Dosage | : | -S9 mix(6 hr short-term treatment); 5, 10, 15, 20, 25 μg/mL +S9 mix(6 hr short-term treatment); 10, 15, 20, 25, 30 μg/mL -S9 mix(24 hr continuous treatment); 5, 10, 15, 20, 25 μg/mL |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
This chemical did not induce structural chromosomal aberrations or polyploidy under the conditions of the experiment.
| clastogenicity | polyploidy | |||||
| + | ? | - | + | ? | - | |
| without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| with metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| 1) | The tests were performed by the Kashima Laboratory, Mitsubishi Chemical Safety Institute Ltd., 14 Sunayama, Hasaki-machi, Kashima-gun, Ibaraki, 314-0255, Japan. Tel +81-479-46-2871, Fax +81-479-46-2874.. |