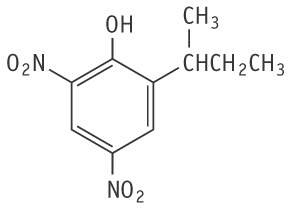
Molecular formula: C10H12N2O5 Molecular weight: 240.21

2-sec-Butyl-4,6-dinitrophenol was studied in female rats in a single dose oral toxicity test at 50 mg/kg in the first trial and at 5 mg/kg in second and third trials. All the 3 animals receiving 50 mg/kg died by 1 day after administration. Adoption of a prone position, bradypnea, diarrhea, and decrease in locomotor activity were noted before death. The chemical is classified in category 2 of the GHS regarding acute toxicity.
2-sec-Butyl-4,6-dinitrophenol was further studied in rats in an OECD combined repeated dose toxicity study with the reproductive/developmental toxicity screening at oral dosed of 0, 0.78, 2.33, and 7 mg/kg.
With 7 mg/kg, 8 females died and 2 females were moribund in the final course of pregnancy. Decrease in locomotor activity, adoption of a prone position, hypothermia, dyspnea, cyanosis, or bradypnea were noted in the dying or moribund females. In addition, low body weights were noted in the males during the administration period and in the females before the start of mating and during the mating period. Transiently low food consumption was noted in the males of the 2.33 and 7 mg/kg groups during the administration period. On hematological examination of the males, red blood cell counts and the hematocrit level were high or tended to be elevated in the groups treated with 0.78 mg/kg and above, hemoglobin concentrations were increased in the groups treated with 2.33 mg/kg or 7 mg/kg, and the mean corpuscular volume was high in the group receiving 7 mg/kg. On hematological examination of the females, red blood cell counts were high or tended to be elevated in the groups treated with 0.78 and 2.33 mg/kg. On blood chemical examination, creatinine was increased, and ALP tended to be increased in the 7 mg/kg males. Sperm analysis performed at the end of the administration period demonstrated the motile sperm rate, progressive sperm rate, straight line velocity, sperm viability rate, and sperm survival rate to be low or a tendency for decrease, and the amplitude of lateral head displacement, abnormal sperm rate, abnormal sperm tail rate, and abnormal sperm head rate were high or tended to be increased in the group treated with 7 mg/kg. On sperm analysis performed at the end of the recovery period, the sperm viability rate and sperm survival rate were low, and the abnormal sperm and sperm head rates were elevated with 7 mg/kg. On histopathological examination, congestion was noted in the lungs and livers in the dead females. In the sacrificed females, extramedullary hematopoiesis in the spleen was low or tended to be low in the groups treated with 2.33 and 7 mg/kg at the end of the administration period, and showed a tendency for continued decrease with 7 mg/kg at the end of the recovery period.
The NOEL for repeated dose toxicity was estimated to be less than 0.78 mg/kg/day in both sexes.
No changes attributable to the chemical were noted in the number of estrous cases, copulation index, number of conceiving days, number of pregnant females, fertility index, gestation length, delivery conditions, nursing conditions, number of corpora lutea, number of implantation sites, or the implantation rate. The gestation index was low in the group treated with 7 mg/kg.
The NOEL for reproductive performance of parental animals was estimated to be 2.33 mg/kg/day in both sexes.
Regarding the pups, no changes attributable to the chemical were noted in the number, number of stillbirths, sex ratio, delivery index, birth index, live birth index, general signs, number of live pups on Day 4 of lactation, viability index of pups on Day 4 of lactation, appearance, body weight, or necropsy findings in the groups treated with 0.78 or 2.33 mg/kg.
The NOEL for pups was estimated to be 2.33 mg/kg/day.
A reverse mutation test using bacteria was performed to examine the mutagenic potential of 2-sec-butyl-4,6-dinitrophenol. 2-sec-Butyl-4,6-dinitrophenol did not induce gene mutations in bacteria under the conditions of this study.
An in vitro chromosomal aberration test of 2-sec-butyl-4,6-dinitrophenol was performed using a fibroblast cell line (CHL/IU) established from the lung of a Chinese hamster. 2-sec-Butyl-4,6- dinitrophenol did not induce chromosomal aberrations under the conditions of this study.
| Purity | : | 96.0 % |
| Test Species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD(SD)IGS |
| Test method | : | OECD Test Guideline 423 |
| Route | : | Oral(gavage) |
| Dosage | : | 5, 50 mg/kg |
| Number of animals/group | : | Females, 6(5 mg/kg), 3(50 mg/kg) |
| Vehicle | : | Corn oil |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
All 3 animals reciving the dose of 50 mg/kg died by 1 day after administration. Observation for general signs revealed adoption of a prone position, bradypnea, diarrhea, and decrease in locomotor activity before death. No abnormalities were noted at the 5 mg/kg dose and body weight changes were normal. At necropsy, no abnormalities were noted at doses of 50 or 5 mg/kg. The chemical is classifiable into category 2 of the GHS regarding acute toxicity.
| Purity | : | 96.0 % |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD(SD)IGS |
| Test method | : | OECD Test Guideline 422 |
| Route | : | Oral(gavage) |
| Dosage | : | 0(vehicle), 0.78, 2.33, 7 mg/kg |
| Number of animals/group | : | Males, 6 + 6(recovery group) Females, 12 + 6(recovery group) |
| Vehicle | : | Corn oil |
| Administration period | : |
Males, 42 days |
| Terminal killing | : |
Males, 43 or 57 days |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
With 7 mg/kg, 8 females died and 2 females were moribund in the final course of pregnancy. On observation for general signs, decrease in locomotor activity, adoption of a prone position, hypothermia, dyspnea, cyanosis and/or bradypnea were noted in the dying or moribund females. With 7 mg/kg, low body weights were noted in the males during the administration period and in the females before the start of mating and during the mating period. Transiently decreased food consumption was noted in the males of the 2.33 and 7 mg/kg groups during the administration period. No changes attributable to the chemical were noted in behavioral functions (FOB), sensory reactions, grip strength, spontaneous motor activity, or urinalysis in either sex. On hematological examination of the males, red blood cell counts and the hematocrit level were high or tended to be increased in the groups treated with 0.78 mg/kg and above, the hemoglobin concentration was high with 2.33 mg/kg and 7 mg/kg and the mean corpuscular volume was high with 7 mg/kg. On hematological examination of the females, red blood cell counts were high or tended to be increased in the groups treated with 0.78 or 2.33 mg/kg. On blood chemical examination, creatinine was high, and ALP tended to be increased in the males of the 7 mg/kg group at the end of the administration period. On necropsy and organ weight measurement, no changes attributable to the chemical were noted in either sex. Sperm analysis performed at the end of the administration period, demonstrated the motile sperm rate, progressive sperm rate, straight line velocity, sperm viability rate, and sperm survival rate to be low or tending to decrease and amplitude of lateral head displacement, abnormal sperm rate, abnormal sperm tail rate, and abnormal sperm head rate were high or tended to be increased with 7 mg/kg. On sperm analysis performed at the end of the recovery period, the sperm viability rate and sperm survival rate were still low, and the abnormal sperm and sperm head rates were high with 7 mg/kg. On histopathological examination, congestion was noted in the lungs and livers in the dead females. Extramedullary hematopoiesis in the spleen was low or tended to be decreased in the 2.33 and 7 mg/kg females at the end of the administration period, and also tended to be decreased with 7 mg/kg at the end of the recovery period.
The NOEL for repeated dose toxicity was estimated at less than 0.78 mg/kg/day in both sexes.
<Reproductive and developmental toxicity>
No changes attributable to the chemical were noted in the number of estrous cases, copulation index, number of conceiving days, number of pregnant females, fertility index, gestation length, delivery conditions, nursing conditions, number of corpora lutea, number of implantation sites or the implantation rate. However, the gestation index was low in the group treated with 7 mg/kg.
The NOEL for reproductive performance of parental animals was estimated to be 2.33 mg/kg/day in both sexes.
Regarding the pups, no changes attributable to the chemical were noted in the number, number of stillbirths, sex ratio, delivery index, birth index, live birth index, general signs, number of live pups on Day 4 of lactation, viability index of pups on Day 4 of lactation, appearance, body weight, or necropsy findings in the groups treated with 0.78 or 2.33 mg/kg.
The NOEL for pups was estimated to be 2.33 mg/kg/day.| Purity | : | 96.0 % |
| Type species/strains | : | Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537, Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Chemical Substances Control Law of Japan) and OECD Test Guideline 471 |
| Procedures | : | Pre-incubation method |
| Solvent | : | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix; 2-(2-Furyl)-3-(5-nitro-2-furyl)acrylamide (TA100, TA98, WP2 uvrA), sodium azide (TA1535) and 9-aminoacridine (TA1537) +S9 mix; 2-Aminoanthracene (all strains) |
| Dosage | : | -S9 mix; 0, 9.77, 19.5, 39.1, 78.1, 156.3, 312.5 μg/plate (TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537), 0, 39.1, 78.1, 156.3, 312.5, 625, 1250 μg/plate (WP2 uvrA) +S9 mix; 0, 9.77, 19.5, 39.1, 78.1, 156.3, 312.5 μg/plate (TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537), 0, 39.1, 78.1, 156.3, 312.5, 625, 1250 μg/plate (WP2 uvrA) |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates / test | : | 3 |
| Number of replicates | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
This chemical did not induce gene mutations either in S. typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98 or TA1537 or in E. coli WP2 uvrA strains with or without S9 mix. Toxicity was observed at 156.3 μg/plate or more for TA100, TA1535, TA98 and TA1537, at 625 μg/plate or more for WP2 uvrA without S9 mix, at 312.5 μg/plate for TA100, TA1535, TA98 and TA1537, and at 625 μg/plate or more for WP2 uvrA with S9 mix.
Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| Purity | : | 96.0 % |
| Type of cell used | : | Chinese hamster lung (CHL/IU) cells |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Chemical Substances Control Law of Japan)and OECD Test Guideline 473 |
| Solvent | : | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix; Mitomycin C +S9 mix; Dimethyl nitrosamine |
| Dosage | : | -S9 mix(6 hr short treatment method); 0, 12.5, 25, 50, 100, 200 μg/mL +S9 mix(6 hr short treatment method); 0, 12.5, 25, 50, 100, 200 μg/mL -S9 mix(24 hr continuous treatment method); 0, 3.1, 6.3, 12.5, 25, 50 μg/mL |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
This chemical did not induce structural chromosomal aberrations or polyploidy under the conditions of this study.
| clastogenicity | polyploidy | |||||
| + | ? | - | + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| 1) | The tests were performed by Hashima Laboratory, Nihon Bioresearch Inc., 6-104 Majima, Fukuju-cho, Hashima, Gifu, 501-6251, Japan. Tel +81-58-392-6222, Fax +81-58-392-1284. |