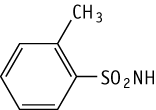

o-Toluenesulfonamide was studied for oral toxicity in rats in an OECD preliminary reproductive toxicity screening test at doses of 0, 4, 20 and 100 mg/kg/day.
With regard to repeated dose toxicity, decreased spontaneous motor activity and salivation were observed and body weights were reduced in both sexes given 100 mg/kg. Thus, the NOEL for repeat dose toxicity is considered to be 20 mg/kg/day for both sexes. In terms of reproductive/developmental toxicity, the compound had no effects on any relevant parameters. The NOEL for reproductive/developmental toxicity is considered to be 100 mg/kg/day for parental animals and offspring.
| Purity | : | 99.95 wt% |
| Test species/strain | : | Rats/Crj:CD(SD)IGS |
| Test method | : | Guideline for 28-Day Repeated Dose Toxicity Test in Mammalian Species (Chemical Substances Control Law of Japan) |
| Route | : | Oral (gavage) |
| Dosage | : | 0 (vehicle), 4, 20, 100 mg/kg/day |
| Number of animals/group | : | Males, 10; females, 10 (0, 100 mg/kg) Males, 5; females, 5 (4, 20 mg/kg) |
| Vehicle | : | 0.5 % CMC-Na solution |
| Administration period | : | Males and females, 28 days |
| Terminal killing | : | Males and females, days 29 or 43 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
Increase of spleen weight, decrease in erythrocyte count and increase of MCV and MCHC were observed at the end of the recovery period in males given 100 mg/kg. Moreover, increase of urinary pH was observed at the end of the recovery period in females given 100 mg/kg. These changes were concluded to be due to the chemical. With administration of 100 mg/kg of o-toluenesulfonamide, decreased locomotor activity and salivation was observed in both sexes and eosinophilic bodies were increased in epithelial cells of renal tubules in males; therefore, the NOEL for repeated dose toxicity is considered to be 20 mg/kg/day for both sexes.
| Purity | : | 99.95 wt% |
| Test species/strain | : | Rats/Crj:CD(SD)IGS |
| Test method | : | OECD Test Guideline 421 |
| Route | : | Oral (gavage) |
| Dosage | : | 0 (vehicle), 4, 20, 100 mg/kg/day |
| Number of animals/group | Males, 13; females, 13 | |
| Vehicle | : | 0.5 % CMC-Na solution |
| Administration period | : | Males, 47 days Females, from 14 days before mating to day 3 of lactation |
| Terminal killing | : | Males, day 48 Females, day 4 of lactation |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
No deaths occurred in any group. Decreased spontaneous motor activity and salivation were observed and body weights were reduced in both sexes given 100 mg/kg. The compound had no effects on food consumption or necropsy findings.
The NOEL for repeated dose toxicity is considered to be 20 mg/kg/day for both sexes.
<Reproductive and developmental toxicity>
The compound had no effect on reproductive parameters. In neonates, there were no significant differences in number of offspring, the sex ratio, the live birth index, the viability index or body weights. No abnormal findings ascribable to the compound were found for external features, clinical signs or on necropsy of the offspring.
The NOEL for reproductive and developmental toxicity is considered to be 100 mg/kg/day for parental animals and offspring.
| 1) | The tests were performed by the Hatano Research Institute, Food and Drug Safety Center, 729-5 Ochiai, Hadano-shi, Kanagawa, 257-8523, Japan. Tel +81-463-82-4751 Fax +81-463-82-9627 |