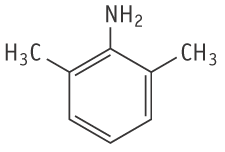
Molecular formula: C8H11N Molecular weight: 121.18

2,6-Dimethylaniline was studied for oral toxicity in female rats in the OECD single dose toxicity test (acute toxic class method) at doses of 300 and 2000 mg/kg, and in the OECD combined repeated dose and reproductive/developmental toxicity screening test at doses of 0, 2, 10, 50 and 250 mg/kg/day.
With regard to single dose toxicity, at 300 mg/kg no deaths were observed and there were signs such as slight decreased locomotor activity and ptosis. The 2000 mg/kg dose in contrast caused severe decrease in locomotor activity, adoption of a prone position, abnormal gait, hypotonia and deep respiration and all rats died. Necropsy revealed red urine in the bladder. 2,6-Dimethylaniline is classifiable in category 4 of the GHS regarding acute toxicity.
With regard to repeated toxicity, the following were noted in the 250 mg/kg group: signs of salivation, decreased locomotor activity, ptosis and decrease in grip strength, motor activity and body weight gain in both males and females. Three females became moribund and were killed. Urinary findings in males were increase of urine volume and decrease of specific gravity, Na, K, protein, ketone bodies and pH. Hematological examination revealed increase in the methemoglobin concentration in males and females, decreased erythrocyte counts and mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentrations and an increase in the reticulocyte counts in males. Blood biochemical examination revealed increase in levels of inorganic phosphorus in males, and increases in GOT, total bilirubin and total cholesterol in females. Increased relative weights of the kidney in males and females, the liver in males, and the thyroid in females were also observed. In addition, the absolute and relative spleen weights were increased in males. Histopathological examination revealed centrilobular hepatocelluar hypertrophy in males and females, increased basophilic tubules and necrosis of the renal papilla in males and females, increased hyaline droplet in the proximal tubular epithelium and proteinaceous casts of the kidney in males, and diffuse dilatation of distal tubules in females. Increased hemosiderin deposits in the spleen in both sexes and increased extramedullary hematopoiesis of the spleen in males were also observed. In the 50 mg/kg group, decreased locomotor activity in both sexes, increase in serum levels of total cholesterol in females and hepatocellular hypertrophy in both sexes were observed. These changes demonstrated reversibility or a tendency for reversibility in the recovery group of males and the satellite group of females.
The NOELs for repeated dose toxicity are considered to be 10 mg/kg/day for parental animals of both sexes.
With regard to reproductive and developmental toxicity, male parental animals exhibited no alterations in reproductive parameters. Female parental animals revealed a tendency for decrease in the numbers of corpora lutea and of implantation sites in the 250 mg/kg group. On examination of neonates, tendency for decrease in the number of pups born and a decrease in the total number of pups of both sexes alive at 4 days.
The NOELs for reproductive/developmental toxicity are considered to be 250 mg/kg/day for reproductive performance of male parental animals and 50 mg/kg/day for reproductive performance of female parental animals and for offspring development.
Reverse mutation tests using microorganisms (Salmonella typhimurium, Escherichia coli) were conducted to assess the potential of 2,6-dimethylaniline to induce gene mutations. 2,6-Dimethylaniline induced gene mutations in the TA100 and TA1535 strains with the metabolic activation method.
In vitro chromosomal aberration tests using cultured Chinese hamster cells (CHL/IU) were conducted to assess the potential of 2,6-dimethylaniline to induce chromosomal aberrations. 2,6-Dimethylaniline induced chromosomal aberrations in cultured cells with the short-term treatment.
| Purity | : | 99.7% |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD(SD)IGS |
| Test method | : | OECD Test Guideline 423 |
| Route | : | Oral(gavage) |
| Dosage | : | 300, 2000 mg/kg |
| Number of animals | : | Females, 6; females, 3 |
| Vehicle | : | Olive oil |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
The chemical is classified in category 4 of the GHS regarding acute toxicity.
| Purity | : | 99.7% |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD(SD)IGS |
| Test method | : | OECD Test Guideline 422 |
| Route | : | Oral(gavage) |
| Dosage | : | 0(vehicle), 2, 10, 50, 250 mg/kg/day |
| Number of animals/group | : | Males, 12; females, 12 (satellite group for recovery of females: 0 mg/kg/day, 5; 250 mg/kg/day, 5) |
| Vehicle | : | Olive oil |
| Administration period | : |
Males, 42 days |
| Terminal killing | : |
Males, day 43 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
In the 250 mg/kg group, salivation, decreased locomotor activity, ptosis, decreased grip strength, decreased motor activity and decreased body weight gain were observed in males and females. Three females were killed in extremis. Urinary assessment in males revealed increase of urine volume and decreases of specific gravity, concentrations of Na, K, protein and ketone bodies and pH. Hematological examination revealed increase in methemoglobin concentrations in males and females, and decreases in erythyocyte count and mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentrations and increase in the reticulocyte count in males. Blood biochemical examination revealed increase in levels of inorganic phosphorus in males, and in GOT, total bilirubin and total cholesterol in females. Increased relative kidney weights in males and females, liver in males and thyroid in females were observed. Absolute and relative weights of the spleen were increased in males. Histopathological examination revealed hepatocelluar centrilobular hypertrophy in males and females and increased basophilic tubules and necrosis of the renal papilla in males and females, increased hyaline droplets of proximal tubular epithelium and proteinaceous casts in the kidneys in males, diffuse dilatation of distal tubules of the kidneys in females, and hemosiderin deposits in the spleen in males and females, along with a tendency for increase in extramedullary hematopoiesis of the spleen in males.
In the 50 mg/kg group, decreased locomotor activity in the early administration period was observed in males and females. Blood biochemical examination revealed increase in levels of total cholesterol in females. Histopathological examination revealed centrilobular hepatocellular hypertrophy in males and females.
These changes demonstrated recovery or a tendency for reversibility in the recovery group of males and the satellite group of females.
The NOELs for repeated dose toxicity are considered to be 10 mg/kg/day for parental animals of both sexes.
<Reproductive and developmental toxicity>
The male parental animals exhibited no alterations in reproductive parameters. The female parental animals demonstrated a tendency for decrease in the numbers of corpora lutea and decreased number of implantation sites in the 250 mg/kg group. On examination of neonates, tendencies for decreased numbers of pups born and decreased total number of pups alive were noted in both sexes.
The NOELs for reproductive/developmental toxicity are considered to be 250 mg/kg/day for reproductive performance of male parental animals and 50 mg/kg/day for reproductive performance of female parental animals and for offspring development.
| Purity | : | 99.8% |
| Test species/strains | : | Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537, Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Chemical Substances Control Law of Japan) and OECD Test Guideline 471 |
| Procedures | : | Pre-incubation method |
| Solvent | : | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| Positive controls | : | -S9mix;2-(2-Furyl)-3-(5-nitro-2-furyl)acrylamide(TA100,TA98,WP2uvrA),sodiumazide(TA1535)and9-aminoacridinehydrochloride(TA1537) +S9mix;2-Aminoanthracene(allstrains) |
| Dosage | : | -S9 mix [all strains for dose-finding study]; 0, 2.29, 6.86, 20.6, 61.7, 185, 556, 1667, 5000 μg/plate +S9 mix [all strains for dose-finding study]; 0, 2.29, 6.86, 20.6, 61.7, 185, 556, 1667, 5000 μg/plate -S9 mix [main study]; 0, 39.1, 78.1, 156, 313, 625, 1250, 2500 μg/plate (TA100), 0, 156, 313, 625, 1250, 2500, 5000 μg/plate (TA1535, WP2 uvrA, TA98, TA1537) +S9 mix [main study]; 0, 39.1, 78.1, 156, 313, 625, 1250, 2500 μg/plate (TA100, TA1535, TA1537 ), 0, 156, 313, 625, 1250, 2500, 5000 μg/plate (WP2 uvrA, TA98) +S9 mix [confirmative study]; 0, 273, 341, 426, 532, 666, 832, 1040, 1300 μg/plate (TA100) |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 3 |
| Number of replicates | : | 3 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Increase in revertant colonies was observed for TA100 and TA1535 with the metabolic activation method (+S9 mix).
| + | ? | - | |
| without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| with metabolic activation: | [*] | [ ] | [ ] |
| + | ? | - | |
| without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| with metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| + | ? | - | |
| without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| with metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| Purity | : | 99.8% |
| Type of cell used | : | Chinese hamster lung (CHL/IU) cells |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Chemical Substances
Control Law of Japan) and OECD Test Guideline 473 |
| Solvent | : | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix; Mitomycin C +S9 mix; Cyclophosphamide |
| Dosage | : | -S9 mix(short-term treatment); 0, 303, 606, 1212 μg/mL +S9 mix(short-term treatment); 0, 633, 744, 876 μg/mL |
| S9 | : | Ratliver,inducedwithphenobarbitaland5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Lowest concentration producing cytogenetic effects in vitro:
Without metabolic activation (short-term treatment): 303 μg/mL(clastogenicity)
With metabolic activation (short-term treatment): 633 μg/mL(clastogenicity)
| clastogenicity | polyploidy | |||||
| + | ? | - | + | ? | - | |
| without metabolic activation: | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| with metabolic activation: | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| 1) | The tests were performed by the Research Institute for Animal Science in Biochemistry and Toxicology, 3-7-11 Hashimotodai, Sagamihara-shi, Kanagawa, 229-1132, Japan. Tel +81-42-762-2775, Fax +81-42-762-7979. |
| 2) | The tests were performed by the Biosafety Research Center, Foods, Drugs and Pesticides(An-pyo Center), 582-2 Shioshinden, Fukude-cho, Iwata-gun, Shizuoka, 437-1213, Japan. Tel +81-538-58-1266, Fax +81-538-58-1393. |