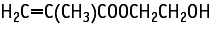
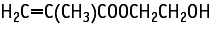
2-Hydroxyethyl methacrylate was studied for oral toxicity in rats in an OECD combined repeat dose and reproductive/developmental toxicity screening test at doses of 0, 30, 100, 300 and 1000 mg/kg/day. One male and 6 females of the 1000 mg/kg group (12 animals of each sex) died during the treatment period.
In the males, BUN was elevated or tended to be high at 30 mg/kg or more, and the relative kidney weights were increased at 100 mg/kg or more. Salivation, suppression of body weight gain, decrease in food consumption, increased K, Cl and inorganic phosphorus, decreased triglyceride, increased relative liver weights, dilatation of renal tubules and collection tubules in the kidney were seen at 1000 mg/kg. In the females, the relative kidney weights were elevated or tended to be high at 100 mg/kg or more. Salivation, decrease in locomotor activity, adoption of a prone position, lacrimation, soiled fur, hypothermia, bradypnea, suppression in body weight gain, decrease in food consumption, increases of the absolute and relative kidney weights, neutrophil cellular infiltration in the papilla and medulla and massive malacia in the medulla oblongata were seen at 1000 mg/kg. The NOELs for repeat dose toxicity are considered to be less than 30 mg/kg for males, and 30 mg/kg for females.
With regard to reproductive/developmental toxicity, no effects of the test substance on copulation, fertility, delivery or lactation were noted.
The NOELs for reproductive performance of males and females, and for pup development are considered to be 1000 mg/kg/day both.
2-Hydroxyethyl methacrylate was not mutagenic in Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537 and Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA, with or without an exogeneous metabolic activation system.
Genotoxicity of 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate was studied by the chromosomal aberration test in cultured Chinese hamster lung (CHL/IU) cells. Structural chromosomal aberrations were induced at 0.65 and 1.3 mg/ml (mid and high concentrations) with 24 h continuous treatment, at 0.16 - 0.65 mg/ml (all concentrations) with 48 h continuous treatment and at 1.3 mg/ml (high concentration) with short-term treatment and an exogenous metabolic activation system. Polyploidy was induced at 0.65 mg/ml with 48 h continuous treatment and at 0.33 and 1.3 mg/ml (low and high concentrations) with short-term treatment without the metabolic activation system.
| Purity | : | 97.6% |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD (SD) |
| Test method | : | OECD Combined Repeat Dose and Reproductive/Developmental Toxicity Screening Test |
| Route | : | Oral (gavage) |
| Dosage | : | 0 (vehicle), 30, 100, 300, 1000 mg/kg/day |
| Number of animals/goup | : | Males, 12; females, 12 |
| Vehicle | : | Water for injection |
| Administration period | : | Males, 49 days Females, from 14 days before mating to day 3 of lactation |
| Terminal kill | : | Males, day 50 Females, day 4 of lactation |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
For the females, the relative kidney weights were elevated or tended to be high in the 100 mg/kg or more groups. Salivation, decrease in locomotor activity, adoption of a prone position, lacrimation, soiled fur, hypothermia, bradypnea, suppression of body weight gain, decreased food consumption, increased absolute and relative kidney weights, neutrophil cellular infiltration in the papilla and medulla and massive malacia in the medulla oblongata were found in the 1000 mg/kg group, 6 animals of which died.
The NOELs for repeat dose toxicity are considered to be less than 30 mg/kg for males, and 30 mg/kg for females.
<Reproductive/Developmental Toxicity>
There were no effects of the test substance on the number of live pups born, birth index, number of dead pups, number of pups born, delivery index, live birth index, sex ratio, viability index, external anomalies, body weight or necropsy findings.
The NOELs for the reproductive/developmental toxicity are considered to be 1000 mg/kg/day for reproduction in both sexes as well as for development of pups.
| Purity | : | 97.6 wt% |
| Test species/strains | : | Salmonella typhimurium, TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537, Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan) and OECD Guideline No. 471 and 472 |
| Procedures | : | Pre-incubation method |
| Solvent | : | Water |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix, 2-(2-Furyl)-3-(5-nitro-2-furyl) acrylamide (TA100, TA98, WP2), Sodium azide (TA1535) and 9-Aminoacridine (TA1537) +S9 mix, 2-Aminoanthracene (five strains) |
| Doses | : | -S9 mix; 0, 313, 625, 1250, 2500, 5000μg/plate (five strains) +S9 mix; 0, 313 - 5000 μg/plate (five strains) |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 3 |
| Number of replicates | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
Genetic effects:
Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| Purity | : | 97.6% |
| Type of cell used | : | Chinese hamster lung (CHL/IU) cells |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan) and OECD Guideline No. 473 |
| Solvent | : | Distilled water |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix, Mitomycin C
+S9 mix, Cyclophosphamide |
| Doses | : | -S9 mix (continuous treatment):0, 0.16, 0.33, 0.65, 1.3 mg/ml
-S9 mix (short-term treatment):0, 0.33, 0.65, 1.3 mg/ml +S9 mix (short-term treatment):0, 0.33, 0.65, 1.3 mg/ml |
| S-9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
| Without metabolic activation (continuous treatment) | :0.16 mg/ml (clastogenicity)
:0.65 mg/ml (polyploidy) |
| Without metabolic activation (short-term treatment) | :0.33 mg/ml (polyploidy) |
| With metabolic activation (short-term treatment) | :1.3 mg/ml (clastogenicity)
:0.65 mg/ml (polyploidy) |
| clastogenicity | polyploidy | |||||
| + | ? | - | + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] |
| With metabolic activation: | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] |
| 1) | The test was performed by Nihon Bioresearch Inc. Hashima Laboratory, 6-104 Majima, Fukuju-cho, Hashima, Gifu, 501-62 Japan Tel +81-58-392-6222 Fax +81-58-391-3171 |
| 2) | The tests were performed by the Hatano Research Institute, Food and Drug Safety Center, 729-5 Ochiai, Hadano-shi, Kanagawa, 257, Japan. Tel +81-463-82-4751 Fax +81-463-82-9627 |