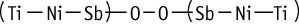
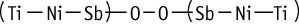
The single dose toxicity test revealed an LD50 value of more than 2000 mg/kg for males and females.
With regard to repeated dose toxicity, no treatment related adverse effects were observed regarding clinical findings, body weights, food consumption, urinalysis, blood chemical and hematological parameters, organ weights, and gross pathological and histopathological examinations in any of the treated groups. Therefore, the NOEL is considered to be 1000 mg/kg/day or more for males and females.
With regard to reproductive and developmental toxicity, no adverse effects were observed. The NOEL for reproductive/developmental toxicity is thus considered to be 1000 mg/kg/day or more for reproductive performance and offspring development.
Reverse mutation assays using microorganisms (Salmonella typhimurium, Escherichia coli) were conducted to assess the potential of C.I. Pigment Yellow 53 to induce gene mutations.
C.I. Pigment Yellow 53 did not induce gene mutations in bacteria under the conditions of this study.
In vitro chromosomal aberration tests using cultured cells (CHL/IU) were conducted to assess the potential of C.I. Pigment Yellow 53 to induce chromosomal aberrations.
C.I. Pigment Yellow 53 did not induce chromosomal aberrations in cultured cells under the conditions of this study.
| Purity | : | 100 % |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD(SD)IGS |
| Test method | : | OECD Test Guideline 401 |
| Route | : | Oral (gavage) |
| Dosage | : | 0 (vehicle), 2000 mg/kg |
| Number of animals/group | : | Males, 5; females, 5 |
| Vehicle | : | 1 % Carmellose sodium solution |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
The LD50 values are estimated to be more than 2000 mg/kg for both sexes.
| Purity | : | 100 % |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD(SD)IGS |
| Test method | : | OECD Test Guideline 422 |
| Route | : | Oral (gavage) |
| Dosage | : | 0 (vehicle), 250, 500, 1000 mg/kg |
| Number of animals/group | Males, 12; females, 12 | |
| Vehicle | : | 1 % Carmellose sodium solution |
| Administration period | : | Males, 46 days Females, from 14 days before mating to day 4 of lactation |
| Terminal killing | : | Males, day 47 Females, day 5 of lactation |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
No abnormal findings were observed with the 250 mg/kg dose. In the 500 and 1000 mg/kg groups, all of the males and females showed yellow or yellowish brown feces throughout the administration period. Gross pathological examination of these groups revealed yellowish green discoloring of the contents in the cecum in some of the animals. However, it was considered that the contents in the digestive organs were colored yellow with oral administration of a large amount of C.I. Pigment Yellow 53, and that these changes did not indicate biological adversity. There were no treatment related adverse effects on body or organ weights, food consumption, findings of urinalysis, hematological and blood chemical examinations, and histopathological examination in any animal in these groups.
The NOEL is considered to be 1000 mg/kg/day or more for males and females.
<Reproductive and developmental toxicity>
No effects were observed on reproductive performances in males and females given any of the doses, or on developmental performances in the pups.
The NOEL for reproductive/developmental toxicity is considered to be 1000 mg/kg/day or more for reproductive performance and offspring development.
| Purity | : | 100 % |
| Test species/strains | : | Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537, Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals(Chemical Substances Control Law of Japan) and OECD Test Guideline 471 |
| Procedures | : | Pre-incubation method |
| Solvent | : | Water for injection |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix; 2-(2-Furyl)-3-(5-nitro-2-furyl)acrylamide (TA100, TA98 and WP2 uvrA), Sodium azide (TA1535), 9-Aminoacridine hydrochloride (TA1537) +S9 mix; 2-Aminoanthracene (all strains) |
| Dosage | : | -S9 mix; 0, 156, 313, 625, 1250, 2500, 5000 μg/plate (all strains) +S9 mix; 0, 156, 313, 625, 1250, 2500, 5000 μg/plate (all strains) |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 3 |
| Number of replicates | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
Genetic effects:
Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535,TA98, TA1537
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| Purity | : | 100 % |
| Type of cell used | : | Chinese hamster lung (CHL/IU) cells |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals(Chemical Substances Control Law of Japan) and OECD Test Guideline 473 |
| Solvent | : | Water for injection |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix; Mitomycin C +S9 mix; Cyclophosphamide |
| Dosage | : | -S9 mix (short-term treatment); 0, 9.79, 19.5, 39.1 μg/mL +S9 mix (short-term treatment); 0, 19.5, 39.1, 78.1 μg/mL -S9 mix (continuous treatment 24 hr); 0, 4.88, 9.75, 19.5 μg/mL |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
Genotoxic effects:
| clastogenicity | polyploidy | |||||
| + | ? | - | + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| 1) | The tests were performed by the Safety Research Institute for Chemical Compounds Co., Ltd., 363-24 Shin-ei, Kiyota-ku, Sapporo, Hokkaido, 004-0839, Japan. Tel +81-11-885-5031 Fax +81-11-885-5313 |
| 2) | The tests were performed by the Biosafety Research Center, Foods, Drugs and Pesticides(An-pyo Center), 582-2 Shioshinden, Fukude-cho, Iwata-gun, Shizuoka, 437-1213, Japan. Tel +81-538-58-1266 Fax +81-538-58-1393 |