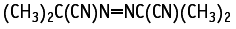
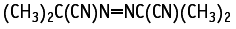
With regard to repeated dose toxicity, in males, temporary salivation after each administration was observed in the 10 mg/kg or more groups. Suppression of body weight gain and food consumption during the early administration period was noted in the 50 mg/kg group. Increases in kidney weights in all of the compound-treated groups and in liver weights in the 10 mg/kg or more groups were observed. Increases in eosinophilic bodies and basophilic changes of the renal tubular epithelial cells in the kidneys of males treated with the compound at any dose levels tested were observed. Elevated platelet and white blood cell counts were observed after the administration of the compound at 50 mg/kg, as well as increases in total protein, concentration of albumin, total cholesterol, Ca, and inorganic phosphorus, and decreases in the A/G ratio and Cl concentration.
In the females, slight decreases in body weight gain and food consumption during the early administration period were observed in the 10 mg/kg or more groups. In addition, body weight gain and food consumption were decreased during pregnancy in the 50 mg/kg group, and one female died on postpartum day 3. Centrilobular hypertrophy of hepatocytes was observed in the 10 mg/kg or more groups.
With respect to reproductive and developmental toxicity, the compound showed no adverse effects on reproduction at any of the dose levels tested. No adverse effects on viability, sex ratio and body weight gain of pups were apparent. However, viability of newborns at birth and body weights of nurslings on postnatal day 4 were lower than the control levels. No morphological abnormalities were observed in the pups of any treated group.
In conclusion, the NOELs for toxicity was suggested to be less than 2 mg/kg/day in males, and 2 mg/kg/day in females, and that for reproductive and developmental toxicity was 50 mg/kg/day in males and 10 mg/kg/day in females and in pups.
2,2'-Azobis(2-methylpropionitlrile) was not mutagenic in Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537 and Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA, with and without an exogeneous metabolic activation system. It was not mutagenic in TA97 without metabolic activation.
Genotoxicity of 2, 2'-azobis(2-methylpropionitrile) was studied in cultured Chinese hamster lung (CHL/IU) cells. 2, 2' and no structural chromosomal aberrations and/or polyploidy up to a maximum concentration of 1.6 mg/ml (10 mM) were observed, with and without an exogenous metabolic activation system.
| Purity | : | 99.9% |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD (Sprague-Dawley) |
| Test method | : | OECD Combined Repeat Dose and Reproductive/Developmental Toxicity Screening Test |
| Route | : | Oral (Gavage) |
| Doses | : | 0 (vehicle), 2, 10, 50 mg/kg/day |
| Number of animals/group | : | Males, 13; Females, 13 |
| Vehicle | : | Corn oil |
| Administration period | : | Males, 42 days Females, from 14 days prior to mating to day 3 of lactation |
| Terminal killing | : | Males, day 43 Females, day 4 of lactation |
| GLP | : | Yes |
<Reproductive and developmental toxicity>
The compound showed no adverse effects on copulation and fertility, duration of pregnancy, gestation index and parturition at any of the dose levels tested. Three dams in the 50 mg/kg group showed abnormal lactation. The compound did not demonstrate any adverse effects on viability, sex ratio and body weight gain of pups. However, viability of newborns at birth and body weight of nurslings on postnatal day 4 were lower than the control levels. No morphological abnormalities in pups were observed in any treated groups.
The no observed effect level (NOELs) for toxicity was suggested to be less than 2 mg/kg/day in males, and 2 mg/kg/day in females, and that for reproductive and developmental toxicity was 50 mg/kg/day in males and 10 mg/kg/day in females and in pups.
| Purity | : | 99.9 wt % |
| Test species/strains | : | Salmonella typhimurium, TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537, TA97 (without S9 mix), Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan) and OECD Guideline No. 471 and 472 |
| Procedures | : | Pre-incubation method |
| Solvent | : | DMSO |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix, 2-(2-Furyl)-3-(5-nitro-2-furyl) acrylamide (TA100, TA98, WP2), Sodium azide (TA1535) and 9-Aminoacridine (TA1537, TA97) +S9 mix, 2-Aminoanthracene (five strains) |
| Doses | : | -S9 mix; 0, 313, 625, 1250, 2500, 5000 μg/plate (six strains) (TA97, WP2) +S9 mix; 0, 313 - 5000 μg/plate (five strains) |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 3 |
| Number of replicates | : | 2 and 4 (TA1537) |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Genetic effects:
Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
Salmonella typhimurium TA97
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | Not done | ||
Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| Purity | : | 99.9% |
| Type of cell used | : | Chinese hamster lung (CHL/IU) cells |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan) and OECD Guideline No. 473 |
| Solvent | : | 0.5% Carboxymethylcellulose sodium solution |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix, Mitomycin C +S9 mix, Cyclophosphamide |
| Doses | : | -S9 mix (continuous treatment):0, 0.40, 0.80, 1.6 mg/ml -S9 mix (short-term treatment):0, 0.40, 0.80, 1.6 mg/ml +S9 mix (short-term treatment):0, 0.40, 0.80, 1.6 mg/ml |
| S-9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
| clastogenicity | polyploidy | |||||
| + | ? | - | + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| 1) | The tests were performed by the Hatano Research Institute, Food and Drug Safety Center, 729-5 Ochiai, Hadano-shi, Kanagawa, 257, Japan. Tel +81-463-82-4751 Fax +81-463-82-9627 |