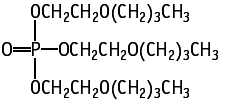
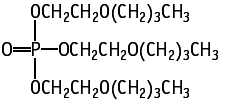
A 28-day repeat dose oral toxicity test of tris(2-butoxyethyl) phosphate was conducted in Sprague-Dawley rats of both sexes at dose levels of 0 (vehicle control), 100, 300, and 1000 mg/kg/day.
There were no mortalities in any group. Transient salivation was observed immediately after exposure to the test chemical in both sexes of all dosed groups and this was considered to be caused by the test chemical. Muscle weakness, adoption of a prone position and deep respiration were also noted in some females of the 1000 mg/kg group after the first exposure to the test chemical and continued for several hours.
On blood biochemical examination, the cholinesterase activity was found to be decreased with statistical significance in both sexes of the 1000 mg/kg group.
Absolute and relative liver weights increased in males and females of the 1000 mg/kg group and in females of the 300 mg/kg group. On histological examination, microgranulomas in the liver tended to be increased in females of the 300 and 1000 mg/kg groups.
The incidence or severity of vacuolation of hepatocytes in the periportal area tended to increase in males and females of the 300 and 1000 mg/kg groups. These findings for toxicity had vanished after the withdrawal of test chemical for 14 days.
The NOEL for repeat dose toxicity was 100 mg/kg/day.
Tris(2-butoxyethyl) phosphate was not mutagenic in Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537 and Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA, with or without an exogeneous metabolic activation system.
Genotoxicity of tris(2-butoxyethyl) phosphate was studied by chromosomal aberration test in cultured Chinese hamster lung (CHL/IU) cells.
Tris(2-butoxyethyl) phosphate did not induce structural chromosomal aberrations and/or polyploidy in the concentration range of 0.011 - 0.20 mg/ml with and without an exogenous metabolic activation system.
| Purity | : | 98.2% |
| Test species/strain | : | Rats/Crj:CD (SD) |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for 28-Day Repeat Dose Toxicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan) |
| Route | : | Oral (gavage) |
| Doses | : | 0 (vehicle), 100, 300, 1000 mg/kg/day |
| Number of animals/group | : | Males,5; females,5 |
| Vehicle | : | Corn oil |
| Administration period | : | Males and females, 28 days |
| Terminal kill | : | Males and females, days 29 or 43 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
| Purity | : | 98.2 % |
| Test species/strains | : | Salmonella typhimurium, TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537, Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan) and OECD Guideline No. 471 and 472 |
| Procedures | : | Pre-incubation method |
| Solvent | : | DMSO |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix, 2-(2-Furyl)-3-(5-nitro-2-furyl) acrylamide (TA100, TA98, WP2), Sodium azide (TA1535) and 9-Aminoacridine (TA1537) +S9 mix, 2-Aminoanthracene (five strains) |
| Doses | : | -S9 mix; 0, 7.81, 15.6, 31.3, 62.5, 125, 250 μg/plate (TA100, TA1537) 0, 15.6 - 500 μg/plate (TA1535, TA98) 0, 156 - 5000 μg/plate (WP2)
+S9 mix; |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 3 |
| Number of replicates | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
Genetic effects:
Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| Purity | : | 98.2% |
| Type of cell used | : | Chinese hamster lung (CHL/IU) cells |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan) and OECD Guideline No. 473 |
| Solvent | : | Dimethylsulfoxide |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix, Mitomycin C +S9 mix, Cyclophosphamide |
| Doses | : | -S9 mix (continuous treatment):0, 0.011, 0.023, 0.045, 0.090 mg/ml -S9 mix (short-term treatment):0, 0.023, 0.045, 0.090 mg/ml +S9 mix (short-term treatment):0, 0.050, 0.10, 0.20 mg/ml |
| S-9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
Genotoxic effects:
| clastogenicity | polyploidy | |||||
| + | ? | - | + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| 1) | The tests were performed by the Hatano Research Institute, Food and Drug Safety Center, 729-5 Ochiai, Hadano-shi, Kanagawa, 257, Japan. Tel +81-463-82-4751 Fax +81-463-82-9627 |