 ) sulfate heptahydrate
) sulfate heptahydrate ) sulfate heptahydrate
) sulfate heptahydrate )¼·¿åÏÂʪ
)¼·¿åÏÂʪ
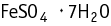
Ferrous sulfate heptahydrate was studied for oral toxicity in rats in an OECD combined repeated dose and reproductive/developmental toxicity screening test at doses of 0, 30, 100, 300, and 1000 mg/kg/day.
Deaths were noted of 1 animal of each sex given 1000 mg/kg. Body weight was low in the males at 1000 mg/kg and tended to be low in the females at 1000 mg/kg in the final stages of pregnancy. Food consumption was transiently low in both sexes at 1000 mg/kg. On urinalysis, a high value for volume and a low value for specific gravity were noted in the males at 1000 mg/kg. In the hematological examination, low values for the red blood cell count and APTT and high values for MCV, MCH, and the reticulocyte count were noted in the males at 1000 mg/kg. In the blood chemical analysis, a high value for inorganic phosphate was noted in the females at 300 mg/kg, low values for total protein, albumin, and Ca and high values for ALT, ¦Ã-GTP, and A/G in the males at 1000 mg/kg, and high values for ¦Ã-GTP and inorganic phosphate in the females at 1000 mg/kg. On organ weight measurement, high values for the absolute and relative adrenal weights and the relative liver weights were noted in the males at 1000 mg/kg, and high values for the absolute and relative liver weights were obtained for the females at 1000 mg/kg. On histopathological examination, extramedullary hematopoiesis of the spleen was noted in the males at 300 mg/kg, atrophy of the thymus, inflammatory cell filtration in the glandular submucosa, deposit of yellowish brown pigment in the periportal hepatocytes, deposits of yellowish brown pigment in periportal Kupffer cells, extramedullary hematopoiesis of the spleen, deposits of yellowish brown pigment in the red pulp of the spleen, and basophilic changes in the tubular epithelium of the kidney were noted mainly in the males at 1000 mg/kg. Deposits of yellowish brown pigment in the red pulp of the spleen and of yellowish brown pigment in the periportal hepatocytes were noted in the females at 1000 mg/kg. The NOEL for repeated dose toxicity is considered to be 100 mg/kg/day for both sexes.
Regarding the reproductive and developmental toxicity, no changes attributable to the test substance were noted in parental animals or pups. The NOEL for reproductive performance is considered to be at 1000 mg/kg/day for parental animals and pups.
Ferrous sulfate heptahydrate was not mutagenic in Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537 and Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA/pKM101, with or without an exogenous metabolic activation system.
Ferrous sulfate heptahydrate induced structural chromosomal aberrations in CHL/IU cells after short term treatment with and without an exogenous metabolic activation system. Polyploidy was not induced in any treatment group.
| Purity | : | 91.6 % |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD(SD)IGS |
| Test method | : | OECD Test Guideline 401 |
| ¡¡Route | : | Oral (gavage) |
| ¡¡Dosage | : | 0 (vehicle), 250, 500, 1000, 2000 mg/kg |
| ¡¡Number of animals/group | : | Males, 5; females, 5 |
| ¡¡Vehicle | : | Water for injection |
| GLP | : | Yes |
¡¡Test results:
| Purity | : | 91.1 and 90.6 % |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD(SD)IGS |
| Test method | : | OECD Test Guideline 422 |
| ¡¡Route | : | Oral (gavage) |
| ¡¡Dosage | : | 0 (vehicle), 30, 100, 300, 1000 mg/kg |
| ¡¡Number of animals/group | Males, 12; females, 12 | |
| ¡¡Vehicle | : | Water for injection |
| ¡¡Administration period | : | Males, 49 days Females, from 14 days before mating to day 5 of lactation |
| ¡¡Terminal killing | : | Males, day 50 Females, day 6 of lactation |
| GLP | : | Yes |
¡¡Test results:
Deaths were noted of 1 animal of each sex at 1000 mg/kg. Body weights were low in the males at 1000 mg/kg and tended to be low in the females at 1000 mg/kg in the final stages of pregnancy. Food consumption was transiently lowered in both sexes at 1000 mg/kg. On urinalysis, a high value for volume and a low value for specific gravity were noted in the males at 1000 mg/kg. In the hematological examination, low values for the red blood cell count and APTT and high values for MCV, MCH, and the reticulocyte count were noted in the males at 1000 mg/kg. In the blood chemical analysis, a high value for inorganic phosphate was noted in the females at 300 mg/kg, low values for total protein, albumin, and Ca and high values for ALT, ¦Ã-GTP, and A/G in the males at 1000 mg/kg, and high values for ¦Ã-GTP and inorganic phosphate in the females at 1000 mg/kg. On necropsy, dark red spots in the glandular mucosa and ulcers were noted in the males at 1000 mg/kg. High values for the absolute and relative adrenal weights and the relative liver weights were noted in the males at 1000 mg/kg, and high values for the absolute and relative liver weights were obtained for the females at 1000 mg/kg. On histopathological examination, extramedullary hematopoiesis of the spleen was noted in males at 300 mg/kg. Atrophy of the thymus, ulcers and erosion in the glandular stomach, inflammatory cell filtration in the glandular submucosa, hemorrhage in the stomach, vacuolization in the forestomach epithelium, deposit of yellowish brown pigment in the periportal hepatocytes, deposits of yellowish brown pigment in periportal Kupffer cells, extramedullary hematopoiesis of the spleen, deposits of yellowish brown pigment in the red pulp of the spleen, basophilic changes in the tubular epithelium of the kidney, and increased hematopoiesis of the femoral bone marrow were noted in the males at 1000 mg/kg. Deposits of yellowish brown pigment in the periportal hepatocytes and of yellowish brown pigment in the red pulp of the spleen were noted in the females at 1000 mg/kg.
The NOEL for repeated dose toxicity is considered to be at 100 mg/kg/day for both sexes.
<Reproductive and developmental toxicity>
Regarding the reproductive and developmental toxicity, no changes attributable to the test substance were noted in terms of the number of estrous cases, copulation index, number of days before copulation, fertility index, gestation length, gestation index, delivery conditions, nursing conditions, number of corpora lutea, number of implantation sites, or implantation rate.
The NOEL for reproductive performance of parental animals is considered to be 1000 mg/kg/day for both sexes.
Regarding the pups, no changes attributable to the test substance were noted in terms of the number, number of stillbirths, number of live pups on Day 0 of lactation, sex ratio, delivery index, birth index, live birth index, general signs, number of live pups on Day 4 of lactation, viability index on Day 4 of lactation, external observation, body weight change, or necropsy findings.
The NOEL for pups is considered to be 1000 mg/kg/day.
| Purity | : | 91.6 % |
| Test species/strain | : | Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537, Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA/pKM101 |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Chemical Substances Control Law of Japan) and OECD Test Guideline 471 |
| ¡¡Procedures | : | Pre-incubation method |
| ¡¡Vehicle | : | Water for injection |
| ¡¡Positive controls | : | -S9 mix; 2-(2-Furyl)-3-(5-nitro-2-furyl)acrylamide (TA100, TA98), Sodium azide (TA1535), 9-Aminoacridine hydrochloride (TA1537) and N-Ethyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine (WP2 uvrA/pKM101) +S9 mix; 2-Aminoanthracene (five strains) |
| ¡¡Dosage | : | -S9 mix; 0, 156, 313, 625, 1250, 2500, 5000 ¦Ìg/plate (five strains) +S9 mix; 0, 156, 313, 625, 1250, 2500, 5000 ¦Ìg/plate (five strains) |
| ¡¡S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| ¡¡Plates/test | : | 3 |
| ¡¡Number of replicates | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
¡¡Test results:
Genetic effects:
Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA/pKM101
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| Purity | : | 91.6 % |
| Type of cell used | : | Chinese hamster CHL/IU cells |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Chemical Substances Control Law of Japan) and OECD Test Guideline 473 |
| ¡¡Vehicle | : | Isotonic sodium chloride solution |
| ¡¡Positive controls | : | -S9 mix, Mitomycin C +S9 mix, Benzo[a]pyrene |
| ¡¡Dosage | : | -S9 mix (6 hr short-term treatment); 0, 250, 500, 1000, 1500, 2000 ¦Ìg/mL (main test) -S9 mix (6 hr short-term treatment); 0, 1200, 1300, 1400, 1500, 1600 ¦Ìg/mL (confirmation test) +S9 mix (6 hr short-term treatment); 0, 125, 250, 500, 1000, 1500 ¦Ìg/mL (main test) +S9 mix (6 hr short-term treatment); 0, 600, 700, 800, 900, 1000 ¦Ìg/mL (confirmation test) |
| ¡¡S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| ¡¡Plates/test | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
¡¡Test results:
| Lowest concentration producing cytogenetic effects in vitro | : | ||
| Without metabolic activation (short-term treatment) | : | 1.2 mg/mL (clastogenicity) | |
| With metabolic activation (short-term treatment) | : | 0.6 mg/mL (clastogenicity) | |
Genotoxic effects:
| clastogenicity | polyploidy | |||||
| + | ? | - | + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| 1) | The tests were performed by Nihon Bioresearch Inc., 6-104, Majima, Fukuju-cho, Hashima, Gifu, 501-6251, Japan. Tel +81-58-392-6222 Fax +81-58-392-1284 |
| 2) | The tests were performed by the Mitsubishi Chemical Safety Institute Ltd., 14 Sunayama, Hasaki-machi, Kashima-gun, Ibaraki 314-0255, Japan. Tel +81-479-46-2871 Fax +81-479-46-2874 |