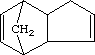
Dicyclopentadiene
ジシクロペンタジエン
CAS No. 77-73-6
3a,4,7,7a-Tetrahydro-4,7-methanoindene
3a,4,7,7a-テトラヒドロ-4,7-メタノインデン
Molecular formula: C10H12 Molecular weight: 132.22

With regard to repeat dose toxicity, a suppression of body weight gain and a decrease in food consumption were observed in both sexes of the 100 mg/kg/day group and two female rats of the same group died. Increases in GOT and GPT were also observed in this group. Histopathological examination revealed fatty droplets in zona fasciculate of adrenals of both sexes and single cell necroses in liver and hyaline droplets in tubular epithelium of kidneys of male rats in the 100 mg/kg/day group. Similar histopathological changes were found in the kidneys of male rats receiving 4 and 20 mg/kg/day. The NOELs for repeat dose toxicity are considered to be less than 4 mg/kg/day for males and 20 mg/kg/day for females. In terms of reproductive/developmental toxicity, the compound had the effects on the body weight of neonates and the viability index in the 100 mg/kg/day group. The NOELs for reproductive/developmental toxicity are considered to be 100 mg/kg/day for parental males, and 20 mg/kg/day for parental females and offspring.
Dicyclopentadiene did not induce structural chromosomal aberrations or polyploidys in CHL/IU cells up to a concentration more than that causing 50% cell growth inhibition, in the absence or presence of an exogenous metabolic activation system. Structural chromosomal aberrations were marginally induced by a high concentration (0.057 mg/ml) after 24-h continuous treatment. However, negative finding were confirmed in the in vitro micronucleus test.
| Purity | : | 94.65% |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD (SD) |
| Test method | : | OECD Combined Repeat Dose and Reproductive/Developmental Toxicity Screening Test |
| Route | : | Oral (gavage) |
| Dosage | : | 0 (Vehicle), 4, 20, 100 mg/kg/day |
| Number of animals | : | Males, 10; females, 10/group |
| Vehicle | : | Olive oil |
| Administration period | : | Males, 44 days Females, from 14 days before mating to day 3 of lactation |
| Terminal kill | : | Males, day 45 Females, day 4 of lactation |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
| Purity | : | 95% |
| Type of cell used | : | Chinese hamster lung (CHL/IU) cells |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan) |
| Solvent | : | Acetone |
| Positive controls | : | -S9, Mitomycin C +S9, Cyclophosphamide |
| Doses | : | -S9 (continuous treatment): 0, 0.014, 0.029, 0.057 mg/ml -S9 (short-term treatment): 0, 0.014, 0.029, 0.057 mg/ml +S9 (short-term treatment): 0, 0.03, 0.05, 0.10 mg/ml |
| S-9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
This chemical substance marginally induced structural chromosomal aberrations at the highest concentration (0.057 mg/ml) after 24-h continuous treatment. However, it was confirmed to be negative in the in vitro micronucleus test.
| clastogenicity | polyploidy | ||||||
| + | ? | - | + | ? | - | ||
| without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | |
| with metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | |
| 1) | The tests were performed by the Mitsubishi Chemical Safety Institute Ltd., 14 Sunayama, Hasaki-machi, Kashima-gun, Ibaraki, 314-02, Japan. Tel +81-479-46-2871 Fax +81-479-46-2874 |
| 2) | The tests were performed by the Hatano Research Institute, Food and Drug Safety Center, 729-5 Ochiai, Hadano-shi, Kanagawa, 257, Japan. Tel +81-463-82-4751 Fax +81-463-82-9627 |