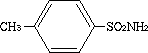

4-Methylbenzenesulfonamide was studied for oral toxicity in rats in a single dose toxicity test at doses of 889, 1333, 2000 and 3000 mg/kg in females and 2000 mg/kg in males, and in an OECD combined repeat dose and reproductive/developmental toxicity screening test at doses of 0, 120, 300 and 750 mg/kg/day in both sexes. 4-Methylbenzenesulfonamide was also tested for mutagenicity with assays for reverse mutation in bacteria and chromosomal aberrations in cultured Chinese hamster (CHL) cells.
The single dose toxicity test revealed LD50 values of above 2000 mg/kg for both sexes.
For repeat dose toxicity caused, daily administration of 300 mg/kg or more in males and females displayed an increase in salivation and a reduction in body weight gain, as well as a suppression of food consumption. No compound-related deaths were observed. Hematuria was observed within 3 days administration of 750 mg/kg in 4/13 males. Hematological examination and blood chemistry measurements in males showed a decrease in white blood cell count with an increase in lymphocyte count, increases in blood urea nitrogen and chloride, and slight elevation in GOT in medium and high dose groups and a decrease in potassium concentration,and increased GPT levels in the high dose group. Histopathological examination showed cytoplasmic changes in the epithelium of the urinary bladder in both sexes and an accelerated involution in the thymus especially in females. Signs of toxicity, such as salivation and urinary bladder changes, were observed in animals given 120 mg/kg and above. The NOEL for repeat dose toxicity was less than 120 mg/kg/day. For reproductive/developmental toxicity, females given 750 mg/kg/day demonstrated possible delivery or lactation state dysfunction and developmental suppression of embryos. NOELs for reproductive performance and offspring development were both 300 mg/kg/day. No teratogenic effects were observed.
The mutagenicity tests performed were all negative. 4-Methylbenzenesulfonamide was not mutagenic for bacteria either with or without an exogenous metabolic activation system up to 5000 μg/plate. No chromosomal aberrations or polyploidy were induced in CHL cells up to 1.7 mg/ml with metabolic activation and 1.3 mg/ml without metabolic activation.
| Purity | : | 99.9% |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD (SD) |
| Test method | : | OECD Test Guideline 401 |
| Doses | : | 889, 1333, 2000, 3000 mg/kg |
| Number of animals | : | Male, 5; Female, 5/group |
| GLP | : | Yes |
| Test results | : | LD50: Male, > 2,000 mg/kg; Female, > 2,000 mg/kg |
| Purity | : | 99.9 % |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD (SD) |
| Test method | : | OECD Combined Repeat Dose and Reproductive/Developmental Toxicity Screening Test |
| Route | : | Oral (gavage) |
| Doses | : | 0 (vehicle), 120, 300, 750 mg/kg/day |
| Number of animals | : | Male, 13; Female, 13 |
| Vehicle | : | 5% Gum arabic solution |
| Administration period | : | Male, 42 days Female, from 14 days before mating to day 3 of lactation |
| Terminal kill | : | Male, day 43 Female, day 4 of lactation |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
Body weights of the high-dose males were significantly lower than those of the controls throughout the dosing period. A reduction in body weight gain was also observed in the medium- and high-dose females during the gestation and/or lactation periods.
Food consumption of the high-dose males was significantly suppressed in the first week of dosing and in the medium- and high-dose females during the gestation period.
At terminal necropsy, gross pathological changes included a dark-colored liver in 6/13 high-dose males and decrease in the thymus weight in high- and medium-dose females. Slight, but statistically significant, increases in relative kidney and testicular weights were found in the high-dose males, and in relative kidney and liver weights in high-dose females. This was probably due to their decreased body weight gain.
Hematological examinations indicated dose-dependent increase in white blood cell count (WBC) in medium- and high-dose males. A significant increase in the proportion of neutrophils was also observed in the high-dose males.
Blood chemistry examinations demonstrated levels of blood urea nitrogen, GOT and chloride to be significantly elevated in the medium- and high-dose males. A significant elevation in GPT level and a decrease in potassium concentration were also observed in the high-dose males.
Histopathological examination revealed thickened urinary bladder epithelium in 6/13 low- and 11/13 each in of the medium- and high-dose males, as well as in 1/13 low-, 12/13 medium- and 7/13 high-dose females. In addition, a dose-dependent acceleration of involution of the thymus was found in the medium- and high-dose females. No remarkable histopathological changes in the ovaries were observed in any of the nonpregnant females or in females which showed total litter loss after parturition.
<Reproductive and developmental toxicity>
Mating performance and fertility were not affected by the test compound. Two of 10 females in the high-dose group showed signs of difficult delivery and all of their offspring died by day 3 of lactation.
Reproduction parameters (i.e., duration of gestation, numbers of corpora lutea, implantations and resorptions, litter size, and sex distribution) were comparable among all four groups, including the control. However, significant decreases in both survival rate and body weight of newborns on day 0 of lactation were observed in the high-dose group. Morphological observations of offspring revealed no teratogenic effects of 4-methylbenzenesulfonamide.
| Purity | : | 99.9% |
| Test species/strains | : | S. typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537 E. coli WP2 uvrA |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan) |
| Procedure | : | Plate method |
| Solvent | : | DMSO |
| Positive controls | : | -S9, AF-2 (TA100, WP2 uvrA, TA98), sodium azide (TA1535) and 9-aminoacridine (TA1537) +S9, 2-aminoanthracene (all strains) |
| Doses | : | 0, 312.5, 625, 1250, 2500, 5000 μg/plate |
| S-9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 3 |
| Number of replicates | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Genotoxic effects:
S. typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537
| + | ? | - | |
| with metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
E. coli WP2 uvrA
| + | ? | - | |
| with metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| Purity | : | 99.9% |
| Type of cell used | : | Chinese hamster CHL cells |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan) |
| Solvent | : | DMSO |
| Positive controls | : | -S9, Mitomycin C +S9, Cyclophosphamide |
| Doses | : | -S9: 0, 0.33, 0.65, 1.30 mg/ml +S9: 0, 0.43, 0.85, 1.70 mg/ml |
| S-9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
| + | ? | - | |
| with metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| 1) | The tests were performed by the Hatano Research Institute, Food and Drug Safety Center, 729-5 Ochiai, Hadano-shi, Kanagawa, 257, Japan. Tel. 81-463-82-4751 Fax 81-463-82-9627 |