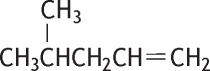
4-Methyl-1-pentene was studied for oral toxicity in rats in a single dose toxicity test at doses of 300 and 2000 mg/kg, and in a repeat dose and reproductive/developmental toxicity test at doses of 0, 40, 200 and 1000 mg/kg/day.
With regard to the single dose toxicity, no female dosed at 300 or 2000 mg/kg died, and none showed any symptoms. 4-Methyl-1-pentene was therfore estimated to belong to category 5(>2000-50000 mg/kg) of the GHS.
With regard to repeat dose and reproductive/developmental toxicity, increase of urea nitrogen was observed at the end of the administration period, and increases of creatinine and chloride were observed at the end of the recovery period in females given 1000 mg/kg/day. Hyaline droplets and eosinophilic bodies in proximal tubular epithelium were observed in males given 200 mg/kg or more.
However no effects were observed on reproductive performance of parents or on developmental performance in the pups.
The NOAELs for systemic toxicity for parents are considered to be 40 mg/kg/day for males, 200 mg/kg/day for females, but for reproductive and developmental toxicity are considered to be 1000 mg/kg/day for parents and pups.
4-Methyl-1-pentene did not induce gene mutations in Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537 and Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA, with or without exogenous metabolic activation under the conditions of this study.
4-Methyl-1-pentene did not induce structural aberrations or polyploidy under the conditions of this study.
| Purity | : | 98.36 % |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD(SD)IGS |
| Test method | : | OECD Test Guideline 423 |
| Route | : | Oral (gavage) |
| Dosage | : | 300, 2000 mg/kg |
| Number of animals/group | : | Females, 3 |
| Vehicle | : | Corn oil |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
| Purity | : | 98.36 % |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD(SD)IGS |
| Test method | : | OECD Test Guideline 422 |
| Route | : | Oral (gavage) |
| Dosage | : | 0(vehicle), 40, 200, 1000 mg/kg |
| Number of animals/group | : | Males, 12; females, 12 Satellite females, 5 |
| Vehicle | : | Corn oil |
| Administration period | : |
Males and satellite females, 42 days |
| Terminal killing | : |
Males and satellite females, days 43 or 57 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
In females, increase of urea nitrogen was apparent at 1000 mg/kg/day at the end of the administration period, and increases of creatinine and chloride were observed at the end of the recovery period. Hyaline droplets and eosinophilic bodies in the proximal tubular epithelium were observed in males given 200 mg/kg or more.
However, no effects were observed on reproductive performance of parents or on developmental performance in the pups.
The NOAELs for systemic toxicity for parents are considered to be 40 mg/kg/day for males, 200 mg/kg/day for females, but that for reproductive and developmental toxicity is considered to be 1000 mg/kg/day for parents and pups.
| Purity | : | 98.36 % |
| Test species/strains | : | Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537, Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Chemical Substances Control Law of Japan) and OECD Test Guideline 471 |
| Procedures | : | Pre-incubation method |
| Solvent | : | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix; 2-(2-Furyl)-3-(5-nitro-2-furyl) acrylamide (TA100, TA98, WP2 uvrA), sodium azide (TA1535) and 9-aminoacridine hydrochloride (TA1537) +S9 mix; 2-Aminoanthracene (all strains) [Dose-finding study] |
| Dosage | : | -S9 mix; 5, 15, 50, 150, 500, 1500, 5000 μg/plate (all strains) +S9 mix; 5, 15, 50, 150, 500, 1500, 5000 μg/plate (all strains) [Main study] -S9 mix; 46.9, 93.8, 188, 375, 750, 1500, 3000 μg/plate (all strains) +S9 mix; 46.9, 93.8, 188, 375, 750, 1500, 3000 μg/plate (all strains) |
| S9 | : | Rat liver; induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 3(1 for the dose-finding test) |
| Number of replicates | : | 2(1 for the dose-finding test) |
| GLP | : | Yes |
This chemical did not induce gene mutations in Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537 or Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA under the conditions of this study. Growth inhibition was observed at 750 μg/plate and above in TA1535, TA98 and TA1537, and at 1500 μg/plate and above in TA100 and WP2 uvrA, with and without S9 mix.
Genetic effects:
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| Purity | : | 98.36 % |
| Type of cell used | : | Chinese hamster lung (CHL/IU) cells |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Chemical Substances Control Law of Japan) and OECD Test Guideline 473 |
| Solvent | : | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix; Mitomycin C +S9 mix; Benzo[a]pyrene |
| Dosage | : | -S9 mix (short-term treatment); 98.6, 113, 130, 150 μg/mL +S9 mix (short-term treatment); 197, 227, 261 μg/mL -S9 mix (24 hr continuous treatment); 37.5, 56.3, 75.0, 85.8, 98.6, 113, 130, 150 μg/mL |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 4(2: chromosome specimens, 2: measurement of growth rate) |
| GLP | : | Yes |
This chemical did not induce structural aberrations or polyploidy under the conditions of this study.
| Clastogenicity | polyploidy | |||||
| + | ? | - | + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| 1) | The tests were performed by the Safety Research Institute for Chemical Compounds Co., Ltd., 363-24 Shin-ei, Kiyota-ku, Sapporo, Hokkaido, 004-0839, Japan. Tel +81-11-885-5031, Fax +81-11-885-5313 |