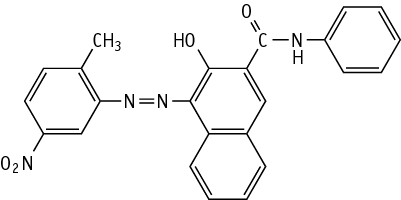

C.I. Pigment Red 22 was studied for oral toxicity in rats in an OECD combined repeated dose and reproductive/developmental toxicity screening test at doses of 0, 100, 300, and 1000 mg/kg/day.
With regard to repeated dose toxicity, increase of liver weight was observed in both sexes of the 1000 mg/kg group. No changes were apparent in clinical signs, body weights, food consumption, hematological examination, blood chemical examination, necropsy or histopathological examination findings. The NOEL for repeated dose toxicity is considered to be 300 mg/kg/day for both sexes.
With regard to reproductive and developmental toxicity, the compound had no effects on any relevant parameters. The NOEL for reproductive and developmental toxicity is considered to be 1000 mg/kg/day for parental animals and offspring.
The mutagenic potential of C.I. Pigment Red 22 was examined with a reverse mutation test in bacteria. C.I. Pigment Red 22 induced gene mutations in S. typhimurium TA100, TA98, TA1537 with and without S9 mix, and in E. coli WP2 uvrA with S9 mix.
The chromosomal aberration potential of C.I. Pigment Red 22 was examined in cultured mammalian cells (CHL/IU).
C.I. Pigment Red 22 did not induce chromosomal aberrations under the conditions of this study.
| Purity | : | > 99 % |
| Test species/strain | : | Rats/Crj:CD(SD)IGS |
| Test method | : | OECD Test Guideline 401 |
| Route | : | Oral (gavage) |
| Dosage | : | 0 (vehicle), 500, 1000, 2000 mg/kg |
| Number of animals/group | : | Males, 5; females, 5 |
| Vehicle | : | 0.5 % Sodium carboxymethylcellulose mixed with 0.1 % Tween 80 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
The LD50 value is considered to be more than 2000 mg/kg for both sexes.
| Purity | : | > 99 % |
| Test species/strain | : | Rats/Crj:CD(SD)IGS |
| Test method | : | OECD Test Guideline 422 |
| Route | : | Oral (gavage) |
| Dosage | : | 0 (vehicle), 100, 300, 1000 mg/kg |
| Number of animals/group | Males, 12; females, 12 | |
| Vehicle | : | 0.5 % Sodium carboxymethylcellulose mixed with 0.1 % Tween 80 |
| Administration period | : | Males, 37 days Females, from 14 days before mating to day 4 of lactation |
| Terminal killing | : | Males, day 38 Females, day 5 of lactation |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
In the 1000 mg/kg group, liver weights were increased in both males and females. No changes were evident regarding clinical signs, body weights, food consumption, hematological examination, blood chemical examination, necropsy or histopathological examination findings.
The NOEL for repeated dose toxicity is considered to be 300 mg/kg/day for both sexes.
<Reproductive and developmental toxicity>
The compound had no effects on reproductive parameters such as the mating index, the fertility index, numbers of corpora lutea or implantations, the implantation index, the delivery index, the gestation index, gestation length, parturition or maternal behavior. On examination of neonates, there were no significant differences in numbers of offspring or live offspring, the sex ratio, the live birth index, the viability index or body weights. No abnormal findings ascribable to the compound were found for external features, clinical signs or necropsy findings for the offspring.
The NOEL for reproductive and developmental toxicity is considered to be 1000 mg/kg/day for parental animals and offspring.
| Purity | : | 99.8 % |
| Test species/strains | : | Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98 and TA1537, Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA |
| Test method | : | Guideline for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Chemical Substances Control Law of Japan) and OECD Test Guideline 471 |
| Procedures | : | Pre-incubation method |
| Solvent | : | Absolute ethanol |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix; 2-(2-Furyl)-3-(5-nitro-2-furyl)acrylamide (TA100, TA98, WP2 uvrA), Sodium azide (TA1535) and 9-Aminoacridine (TA1537) +S9 mix; 2-Aminoanthracene (all strains) |
| Dosage | : | -S9 mix; 0, 19.5, 39.1, 78.1, 156.3, 312.5, 625, 1250, 2500, 5000 μg/plate (TA100) -S9 mix; 0, 78.1, 156.3, 312.5, 625, 1250, 2500, 5000 μg/plate (TA98) -S9 mix; 0, 312.5, 625, 1250, 2500, 5000 μg/plate (TA1535, TA1537, WP2 uvrA) +S9 mix; 0, 312.5, 625, 1250, 2500, 5000 μg/plate (all strains) |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 3 |
| Number of replicats | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
Toxicity was not observed at 5000 μg/plate with or without S9 mix (all strains).
Genotoxic effects:
Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA98, TA1537
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [*] | [ ] | [ ] |
| With metabolic activation: | [*] | [ ] | [ ] |
Salmonella typhimurium TA1535
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [*] | [ ] | [ ] |
| Purity | : | 99.8 % |
| Type of cell used | : | Chinese hamster lung (CHL) cells |
| Test method | : | Guideline for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Chemical Substances Control Law of Japan) and OECD Test Guideline 473 |
| Solvent | : | Absolute ethanol |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix; Mitomycin C +S9 mix; Dimethylnitrosamine |
| Dosage | : | -S9 mix (24 and 48 hr continuous treatment); 0, 37.5, 75, 150, 300, 600 μg/mL -S9 mix (6 hr short-term treatment); 0, 37.5, 75, 150, 300, 600 μg/mL +S9 mix (6 hr short-term treatment); 0, 37.5, 75, 150, 300, 600 μg/mL |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
Genotoxic effects:
| clastogenicity | polyploidy | |||||
| + | ? | - | + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| 1) | The tests were performed by the Kashima Laboratory, Mitsubishi Chemical Safety Institute Ltd., 14 Sunayama, Hasaki-machi, Kashima-gun, Ibaraki, 314-0255, Japan. Tel +81-479-46-2871 Fax +81-479-46-2874 |
| 2) | The tests were performed by the Hashima Laboratory, Nihon Bioresearch Inc., 6-104 Majima, Fukuju-cho, Hashima, Gifu, 501-6251, Japan. Tel +81-58-392-6222 Fax +81-58-392-1284 |