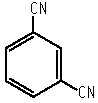
1,3-Dicyanobenzene
1,3-ジシアノベンゼン
[CAS No. 626-17-5]
m-Phthalodinitrile
m-フタロジニトリル
Molecular formula: C8H4N2 Molecular weight: 128.13
ABSTRACT
1,3-Dicyanobenzene was studied for oral toxicity in rats in a 28-day repeat dose toxicity test at doses of 0, 8, 40 and 200 mg/kg/day. Salivation, hypoactivity, bradypnea, soiled perineals, lacrimation and loss of hair were observed in males and/or females of the 200 mg/kg group. Body weights and food consumption decreased in males and females of the 200 mg/kg group during the early stage of the administration period. Thereafter, body weight gain and food consumption recovered in females, but their decrease continued to be recorded throughout the administration period in males. Urinalysis showed increase in urine volume and decrease in specific gravity in males and females of the 40 and 200 mg/kg groups, and decrease in pH in males and females of the 200 mg/kg group. Blood chemical examination showed increases in total protein, albumin, total cholesterol, phospholipids and calcium, and decrease in chloride in males and females of the 200 mg/kg group. Further, decrease in alkaline phosphatase in males receiving 200 mg/kg, and increases in glutamic pyruvic transaminase, triglycerides and glucose, as well as decrease in sodium in 200 mg/kg females were detected. Absolute and relative liver and kidney weights increased in males and females of the 200 mg/kg group, and relative liver weights also increased in males of the 40 mg/kg group. Absolute and relative weights of the adrenals increased in females receiving 200 mg/kg, and the relative adrenal weights were also increased in males given 200 mg/kg. Histopathologically, hypertrophy of hepatocytes was observed in many males of the 40 mg/kg group and all males and females of the 200 mg/kg group. The incidence of hyaline droplets in proximal tubules of the kidney was increased in males of the 8 mg/kg and higher dosage groups, and papillary necrosis, pelvis dilatation, basophilic change of proximal tubules and dilatation of distal tubules were also observed in one male of the 200 mg/kg group. In the recovery test, all changes observed during the administration period demonstrated decrease in their extent or severity. The NOELs are considered to be 8 mg/kg/day for females and less than 8 mg/kg/day for males.
1-Methoxynaphthalene was not mutagenic to Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA98, TA1535, TA1537 and Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA, with or without an exogeneous metabolic activation system.
1,3-Dicyanobenzene induced neither structural chromosomal aberrations nor polyploidy in CHL/IU cells up to the limit concentration of 10 mM, in the absence or presence of an exogenous metabolic activation system.
SUMMARIZED DATA FROM THE STUDIES
1. Repeat Dose Toxicity 1)
| Purity | : | 99.9% |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD (SD) |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for 28-Day Repeat Dose Toxicity Testing for Chemicals (Japan) |
| Route | : | Oral (gavage) |
| Doses | : | 0 (vehicle), 8, 40, 200 mg/kg |
| Number of animals/group | : | Males, 6 and 12 (0, 200 mg/kg)
Females, 6 and 12 (0, 200 mg/kg) |
| Vehicle | : | 0.5% MC solution |
| Administration period | : | Males and females, 28 days |
| Terminal kill | : | Days 29 or 43 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
- Salivation, hypoactivity, bradypnea, perineal soiling, lacrimation and loss of hair were observed in males and/or females of the 200 mg/kg group. Body weight and food consumption decreased in males and females of the 200 mg/kg group during the early stage of the administration period. Urinalysis showed increase in urine volume and decrease in specific gravity in males and females of the 40 and 200 mg/kg groups, and decrease in pH in males and females given 200 mg/kg. Blood chemical examination showed increases in total protein, albumin, total cholesterol, phospholipids and calcium, and decrease in chloride in males and females of the 200 mg/kg group. Further, decrease in alkaline phosphatase in males receiving 200 mg/kg, and increases in glutamic pyruvic transaminase, triglycerides and glucose, and decrease in sodium in females given 200 mg/kg, were detected. Absolute and relative liver and kidney weights increased in males and females of the 200 mg/kg group, and relative liver weights were also increased in males of the 40 mg/kg group. Absolute and relative weights of the adrenals increased in females of the 200 mg/kg group, and relative adrenal weights were also increased in the 200 mg/kg males. Histopathologically, hypertrophy of hepatocyts was observed in many males of the 40 mg/kg group and all males and females of the 200 mg/kg group. The incidence of hyaline droplets in proximal tubules of the kidney increased in males of the 8 mg/kg and higher dosage groups, and papillary necrosis, pelvis dilatation, basophilic change of proximal tubules and dilatation of distal tubules were also observed in one male of the 200 mg/kg group.
- The NOELs are considered to be 8 mg/kg/day for females and less than 8 mg/kg/day for males.
2. Genetic Toxicity
2-1. Bacterial test 2)
| Purity | : | 99.9% |
| Test species/strains | : | Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537,
Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA |
| Test methods | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan) and OECD (471 and 472) |
| Procedures | : | Plate incorporation method |
| Solvent | : | Acetone |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix, 2-(2-Furyl)-3-(5-nitro-2-furyl)acrylamide (TA100, WP2, TA98),
Sodium azide (TA1535) and 9-Aminoacridine (TA1537),
+S9 mix, 2-Aminoanthracene (five strains) |
| Doses | : | 0, 313, 625, 1250, 2500 and 5000 μg/plate, -S9 mix and +S9 mix. |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 3 |
| Number of replicates | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
- This chemical did not induce gene mutations in the S. typhimurium and E. coli strains. Toxicity was not observed at 5000 μg/plate in the five strains either without S9 mix or with S9 mix.
- Genetic effects:
- Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537
| + | ? | - |
| without metabolic activation | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| with metabolic activation | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
- Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA
| + | ? | - |
| without metabolic activation | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| with metabolic activation | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
2-2. Non-bacterial in vitro test (chromosomal aberration test) 2)
| Purity | : | 99.9% |
| Type of cell used | : | Chinese hamster lung (CHL/IU) cells |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan) |
| Solvent | : | 0.5% Carboxymethylcellulose sodium solution |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix, Mitomycin C
+S9 mix, Cyclophosphamide |
| Doses | : | -S9 mix (continuous treatment): 0, 0.33, 0.65, 1.3 mg/ml
-S9 mix (short-term treatment): 0, 0.33, 0.65, 1.3 mg/ml
+S9 mix (short-term treatment): 0, 0.33, 0.65, 1.3 mg/ml |
| S-9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
- Cytogenetic effects were not seen under the conditions of this experiment.
- Genotoxic effects:
| clastogenicity | polyploidy |
| + | ? | - | + | ? | - |
| without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| with metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| 1) | The tests were performed by Safety Assessment Laboratory, Panapharm Laboratories Co., Ltd. 1285 Kurisaki-machi, Uto-shi, Kumamoto, 869-04, Japan. Tel +81-964-23-5111 Fax +81-964-23-2282 |
| 2) | The tests were performed by the Hatano Research Institute, Food and Drug Safety Center, 729-5 Ochiai, Hadano-shi, Kanagawa, 257, Japan. Tel +81-463-82-4751 Fax +81-463-82-9627 |

