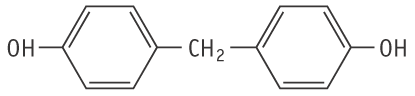
Molecular formula: C13H12O2 Molecular weight: 200.23

4,4'-Methylenediphenol was studied for oral toxicity in rats in a repeat dose toxicity test at doses of 0, 60, 250, 1000 mg/kg/day according to the OECD Test Guideline 407.
On the first day of dosing almost all animals of both sexes in the 1000 mg/kg group showed clinical signs such as adoption of a crouching or prone position, decrease in locomotor activity, ataxic gait and eyelid closure. Decrease of total cholesterol concentration was observed in both sexes of the 250 mg/kg and 1000 mg/kg groups, along with decrease of the A/G ratio and activity of alkaline phosphatase in females. Increased gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase activity and decrease in triglyceride concentrations and activity of aspartate aminotransferase were also observed in 1000 mg/kg females. Relative liver weights were increased in both sexes of 250 mg/kg and 1000 mg/kg groups and centrilobular hypertrophy of hepatocytes was apparent at 1000 mg/kg. Relative organ weights of adrenal glands were increased and diffuse hypertrophy of cortical cell in fascicular zone was observed in females of the 250 mg/kg and 1000 mg/kg groups.
From these results, the NOELs are considered to be 60 mg/kg /day for males and females.
Genotoxicity of 4,4'-methylenediphenol was studied in a reverse mutation test in bacteria. The compound was not found to be mutagenic in Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA98, TA1535 or TA1537 or Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA, with or without an exogenous metabolic activation system.
4,4'-Methylenediphenol induced structural chromosomal aberrations and polyploidy in CHL/IU cells after short-term (6 hr) treatment conditions with and without metabolic activation.
| Purity | : | 99.91% |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD(SD)IGS |
| Test method | : | OECD Test Guideline 407 |
| Route | : | Oral(gavage) |
| Dosage | : | 0(vehicle), 60, 250, 1000 mg/kg/day |
| Number of animals/group | : | Males, 10; females, 10(0, 1000 mg/kg) Males, 5; females, 5(60, 250 mg/kg) |
| Vehicle | : | 0.5 % Sodium carboxymethylcellulose solution mixed with 0.1 % Tween 80 |
| Administration period | : | Males and females, 28 days |
| Terminal killing | : | Males and females, on days 29 and 43 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
No deaths were observed in any treatment group. Food consumption was decreased in both sexes of the 1000 mg/kg group on the first day of dosing, and body weights were depressed through days 4 to 15. On the first day of the dosing period, almost all animals in both sexes of the 1000 mg/kg group showed clinical signs such as adoption of a crouching or prone position, decrease in locomotor activity, ataxic gait and eyelid closure. Clinical signs were reduced as the dosing period progressed and no clinical signs were observed after 7 doses. Decrease of total cholesterol concentration was observed in both sexes of the 250 mg/kg and 1000 mg/kg groups, along with decrease of A/G ratio and activity of alkaline phosphatase in females. Increase of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase activity and decreased triglyceride concentrations and activity of aspartate aminotransferase were also observed in 1000 mg/kg females. Relative liver weights were increased in both sexes receiving 250 mg/kg or 1000 mg/kg and centrilobular hypertrophy of hepatocytes were observed in both sexes given 1000 mg/kg. Relative organ weights of adrenal glands were increased and diffuse hypertrophy of cortical cells in the fascicular zone were observed in females of the 250 mg/kg and 1000 mg/kg dose groups. No liver or adrenal gland changes were detected at the end of the recovery period.
From these results, the NOELs are considered to be 60 mg/kg/day for males and females.
| Purity | : | 99.91% |
| Test species/strains | : | Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537, Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Chemical Substances Control Law of Japan) and OECD Test Guideline 471 |
| Procedures | : | Pre-incubation method |
| Solvent | : | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix; 2-(2-Furyl)-3-(5-nitro-2-furyl)acrylamide (TA100, TA98, WP2 uvrA), sodium azide (TA1535) and 9-aminoacridine (TA1537) +S9 mix; 2-Aminoanthracene (five strains) |
| Dosage | : | -S9 mix; 0, 78.1, 156, 313, 625, 1250, 2500 μg/plate (five strains) +S9 mix; 0,78.1, 156, 313, 625, 1250, 2500 μg/plate (five strains) |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : |
3 (1 for the cytotoxicity test) |
| Number of replicates | : | 2 (plus 1 for the cytotoxicity test) |
| GLP | : | Yes |
This chemical did not induce gene mutation in S. typhimurium TA100, TA98, TA1535, TA1537 or E. coli WP2 uvrA strains with or without S9 mix. Growth inhibition was observed at and above 1250 μg/plate in TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537, and above 1500 μg/plate in WP2 uvrA both with and without S9 mix.
Genetic effects :
Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA98, TA1535, TA1537
| + | ? | - | |
| without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| with metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA
| + | ? | - | |
| without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| with metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| Purity | : | 99.91% |
| Type of cell used | : | Chinese hamster lung (CHL/IU) cells |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Chemical Substances Control Law of Japan) and OECD Test Guideline 473 |
| Solvent | : | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix; Mitomycin C +S9 mix; Cyclophosphamide |
| Dosage | : | -S9 mix(short-term treatment); 0, 0.083, 0.12, 0.19 mg/mL +S9 mix(short-term treatment); 0, 0.083, 0.12, 0.19 mg/mL |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 4 (2: chromosome specimens, 2: measurement of growth rate) |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Cells with structural chromosomal aberrations (19.5 %) were increased significantly with the high dose (0.19 mg/mL) short-term treatment without metabolic activation. After short-term treatment with metabolic activation, cells with structural chromosomal aberrations (7.0 %) were statistically increased at the high dose (0.19 mg/mL). Polyploidy was statistically increased at the middle dose (0.12 mg/mL) after short-term treatment with or without metabolic activation (3.0 % and 1.8 %, respectively).
Lowest concentration producing cytogenetic effects in vitro:
| Without metabolic activation(short-term treatment): | 0.19 mg/mL(clastogenicity) |
| 0.12 mg/mL(polyploidy) | |
| With metabolic activation(short-term treatment): | 0.19 mg/mL(clastogenicity) |
| 0.12 mg/mL(polyploidy) |
| Clastogenicity | polyploidy | |||||
| + | ? | - | + | ? | - | |
| without metabolic activation: | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| with metabolic activation: | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| 1) | The tests were performed by the Hatano Research Institute, Food and Drug Safety Center, 729-5 Ochiai, Hadano-shi, Kanagawa, 257-8523, Japan. Tel +81-463-82-4751, Fax +81-463-82-9627. |