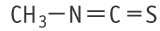
Molecular formula: C2H3NS Molecular weight: 73.12
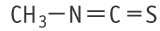
A single dose oral toxicity test of methyl isothiocyanate was conducted in female rats according to the OECD Test Guideline 423. Deaths resulted in all animals at 300 mg/kg, but in none at 50 mg/kg. In the 300 mg/kg group, pale skin, salivation, restlessness, clonic convulsions, reddish lungs and dark red focal areas in the lungs were noted. From the results, methyl isothiocyanate was classified in category 3 of the GHS regarding acute toxicity and the LD50 cut-off value was estimated to be 200 mg/kg.
A combined repeated dose and reproductive/developmental toxicity screening test of methyl isothiocyanate was also conducted in rats according to the OECD Test Guideline 422. Oral administration of the compound at doses of 0, 0.5, 2 and 8 mg/kg did not cause death. Salivation was observed in both sexes at 8 mg/kg and in 1 male at 2 mg/kg group. Suppression of body weight gain and food consumption was further observed in males of the 8 mg/kg group along with increases in the red blood cell count and hemoglobin concentration. Thickening/edema of the mucosa and diffuse squamous cell hyperplasia of the forestomach were observed in both sexes at 2 mg/kg and above. Adverse effects on body weight and hematological parameters proved reversible; however, pathological changes in the forestomach persisted 14 days after withdrawal. In the 8 mg/kg group, abnormal parturition/lactation was observed, resulting in decrease in the number of pups and the viability index. The NOEL for repeated dose toxicity of methyl isothiocyanate is considered to be 0.5 mg/kg/day in both sexes and the NOEL for reproductive toxicity is considered to be 2 mg/kg in females and 8 mg/kg in males and offspring.
A reverse mutation test using bacteria was performed to examine the mutagenic potential of methyl isothiocyanate. The compound did not induce gene mutations in bacteria under the conditions of this study.
An in vitro chromosomal aberration test of methyl isothiocyanate was performed using a fibroblast cell line (CHL/IU) derived from the lung of a Chinese hamster. Methyl isothiocyanate induced chromosomal aberrations under the conditions of this study.
| Purity | : | 99.8% |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/ Crj:CD(SD)IGS |
| Test method | : | OECD Test Guideline 423 |
| Route | : | Oral(gavage) |
| Dosage | : | 50, 300 mg/kg |
| Number of animals/group | : | Females, 3 and 6 |
| Vehicle | : | Corn Oil |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
Deaths of all animals occurred in the 300 mg/kg group on the day of administration and pale skin, salivation, restlessness and clonic convulsions were noted in all 3 animals. Adoption of a prone position and loss of locomotor activity were also observed in 2 of 3 animals and 1 animal adopted a lateral position. Administration of the test compound at the dose of 50 mg/kg did not cause any moribund condition.
Necropsy revealed reddish lungs and dark red focal areas in the lungs in all animals of the 300 mg/kg group, edematous mucosa of forestomach in 1 animal of the 300 mg/kg group, and hard whitish thickening of the mucosa in the forestomach in 1 animal of the 50 mg/kg group.
From the results, methyl isothiocyanate was classified in category 3 of the GHS regarding acute toxicity and the LD50 cut-off value was estimated to be 200 mg/kg.
| Purity | : | 99.8 % |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/ Crj:CD(SD)IGS |
| Test method | : | OECD Test Guideline 422 |
| Route | : | Oral(gavage) |
| Dosage | : | 0(vehicle), 0.5, 2, 8 mg/kg |
| Number of animals/group | : | Males, 12; females, 12+5 |
| Vehicle | : | Corn Oil |
| Administration period | : | Males, 42 days Females, 42 days or from 14 days before mating to day 4 of lactation |
| Terminal killing | : | Males, day 43 and 58 Females, day 58 and day 5 of lactation |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Methyl isothiocyanate was studied for oral toxicity in rats in an OECD combined repeated dose and reproductive/developmental toxicity screening test at doses of 0, 0.5, 2 and 8 mg/kg/day.
Death was not observed in any treated group. Salivation was noted in both sexes of the 8 mg/kg group and in 1 male of the 2 mg/kg group. In males of the 8 mg/kg group, suppression of body weight gain and food consumption were also observed.
Hematological examination revealed increases in the red blood cell count and hemoglobin concentration in males of the 8 mg/kg group. As necropsy findings, thickening/edema of the mucosa of the forestomach was observed in both sexes of the 2 mg/kg and above dose groups, this being diagnosed as papillary squamous cell hyperplasia of the forestomach on histopathological examination.
At 14 days after withdrawal, body weights in males of the 8 mg/kg group had recovered and the red blood cell count and hemoglobin concentration showed no differences from the control group. However, while pathological changes of the forestomach showed some reversibility, the degree of recovery was not complete.
<Reproductive and developmental toxicity>
In the 8 mg/kg group, some animals showed abnormal parturition/lactation and the number of pups and viability index on day 4 were decreased. The compound had no effect on the other reproductive parameters such as the estrous cycle, mating index, fertility index, gestation index, numbers of corpora lutea and implantations, implantation index and delivery index. On examination of neonates, there was no significant variation in the number of offspring or live offspring, sex ratio, live birth index or body weights. No abnormal findings were noted on external observation.
<Evaluation>
Body weight gain and food consumption were reduced in the 8 mg/kg group, and salivation and pathological change of the forestomach were observed in groups given 2 mg/kg or more. Accordingly, the NOEL for repeated dose toxicity of methyl isothiocyanate is considered to be 0.5 mg/kg/day in both sexes.
The NOEL for reproductive toxicity of methyl isothiocyanate is considered to be 2 mg/kg in females because parturition behavior was altered in the 8 mg/kg group. However, the NOEL for reproductive toxicity in males and offspring is considered to be 8 mg/kg since no adverse effects were seen at this dose.
| Purity | : | 99.8% |
| Type species/strains | : | Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537, Escherichia coli WP 2uvrA |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Chemical Substances Control Law of Japan) and OECD Test Guideline 471 |
| Procedures | : | Pre-incubation method |
| Solvent | : | Absolute ethanol |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix; 2-(2-Furyl)-3-(5-nitro-2-furyl)acrylamide (TA100, TA98, WP2 uvrA), sodium azide (TA1535) and 9-aminoacridine (TA1537) +S9 mix; 2-Aminoanthracene (all strains) |
| Dosage | : | -S9 mix; 0, 2.44, 4.88, 9.77, 19.5, 39.1, 78.1 μg/plate (TA100, TA1535, TA1537), 0, 9.77, 19.5, 39.1, 78.1, 156.3, 312.5 μg/plate(WP2 uvrA), 0, 0.610, 1.22, 2.44, 4.88, 9.77, 19.5 μg/plate (TA98) +S9 mix; 0, 2.44, 4.88, 9.77, 19.5, 39.1, 78.1 μg/plate (TA100, TA1535, TA1537), 0, 9.77, 19.5, 39.1, 78.1, 156.3, 312.5 μg/plate(WP2 uvrA), 0, 0.610, 1.22, 2.44, 4.88, 9.77, 19.5 μg/plate (TA98) |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 3 |
| Number of replicates | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
This chemical did not induce gene mutations in S. typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98 or TA1537 or in E. coli WP2 uvrA with or without S9 mix. Toxicity was observed at 78.1 μg/plate for TA100, at 39.1 μg/plate or more for TA1535 and TA1537, at 156.3 μg/plate or more for WP2uvrA, at 19.5 μg/plate for TA98 without S9 mix, at 78.1μg/plate for TA100, at 39.1 μg/plate or more for TA1535 and TA1537, at 312.5 μg/plate for WP2 uvrA, and at 19.5 μg/plate for TA98 with S9 mix.
Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537
| + | ? | - | |
| without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| with metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA
| + | ? | - | |
| without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| with metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| Purity | : | 99.8% |
| Type of cell used | : | Chinese hamster lung (CHL/IU) cells |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Chemical Substances Control Law of Japan) and OECD Test Guideline 473 |
| Solvent | : | Absolute ethanol |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix; mitomycin C +S9 mix; dimethyl nitrosamine |
| Dosage | : | -S9 mix(6 hr short treatment method); 0, 1.3, 2.5, 5, 10, 20 μg/mL +S9 mix(6 hr short treatment method); 0, 1.3, 2.5, 5, 10, 20 μg/mL -S9 mix(24 hr continuous treatment method); 0, 0.63, 1.3, 2.5, 5, 10 μg/mL |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Structural chromosomal aberrations were induced at 10 and 20 μg/mL with S9 mix (6.5 and 72.5 %, respectively), and at 5 and 10 μg/mL without S9 mix (8.0 and 33.0 %, respectively) with the 6 hr short treatment method. With the 24 hr continuous treatment method, structural chromosomal aberrations were induced at 2.5 and 5 μg/mL (16.0 and 65.5 %, respectively). Polyploidy was not induced.
Lowest concentration producing cytogenetic effects in vitro :
Without metabolic activation(6 hr short treatment method):0.01 mg/mL(clastogenicity)
Without metabolic activation(24 hr continuous treatment method):0.0025
mg/mL(clastogenicity)
With metabolic activation(6 hr short treatment method):0.02 mg/mL(clastogenicity)
| clastogenicity |
|
|||||||||||||||
| + | ? | - | ||||||||||||||
| without metabolic activation: | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | |||||||||||||
| with metabolic activation: | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | |||||||||||||
| 1) | The tests were performed by the Hatano Research Institute, Food and Drug Safety Center, 729-5 Ochiai, Hadano-shi, Kanagawa, 257-8523, Japan. Tel +81-463-82-4751, Fax +81-463-82-9627. |
| 2) | The tests were performed by Nihon Bioresearch Inc., 6-104 Majima, Fukuju-cho, Hashima, Gifu, 501-6251, Japan. Tel +81-58-392-6222, Fax +81-58-392-1284. |