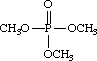
Trimethyl phosphate
リン酸トリメチル
CAS No. 512-56-1
Phosphoric acid trimethyl ester
リン酸トリメチルエステル
Molecular formula: C3H9O4P Molecular weight: 140.09

With regard to repeat dose toxicity, twelve males and one female given 250 mg/kg died during the 4th to 6th week of the dosing period. These rats showed progressive development of a paralytic gait and decreased motor activity before death. Body weight gain of the 250 mg/kg males and females, and food consumption of the 250 mg/kg males were significantly reduced. Twelve and 2 pregnant females given 40 and 100 mg/kg, respectively, demonstrated significant decrease in body weight gain during mid and late pregnancy. In the 100 mg/kg males, significantly decreased erythrocyte counts, hemoglobin concentration, hematocrit and A/G ratio, and increased platelet count, percentage of segmented neutrophils, cholinesterase activity, total cholesterol and calcium levels were noted. Similar alteration in hematological and clinical chemistry parameters was observed in one surviving 250 mg/kg male. On histopathological examination, major lesions noted in males and females given 100 mg/kg or more included nephropathy, atrophy of the thymus, liver and testis, and degeneration of nerve fibers in the spinal cord or the peripheral nerves. The incidence and severity of these lesions increased with dose and were greater in males than in females. The NOELs for repeat dose toxicity are considered to be less than 40 mg/kg/day for both sexes. In terms of reproductive/developmental toxicity, the copulation rate of the paired animals was significantly decreased in the 250 mg/kg group and the fertility index and number of implantation sites were decreased significantly in the 100 mg/kg group. In the 40 mg/kg group, intrauterine mortality of embryos was increased significantly and pup weights were significantly greater than those in the control group. The NOELs for reproductive/developmental toxicity are considered to be less than 40 mg/kg/day.
Neither structural chromosomal aberrations nor polyploidy were induced up to the limit concentration of 10 mM, in the absence or presence of an exogenous metabolic activation system in CHL/IU cells.
| Purity | : | 99.9 wt% |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD (Sprague-Dawley) |
| Test method | : | OECD Combined Repeat Dose and Reproductive/Developmental Toxicity Screening Test |
| Route | : | Oral (Gavage) |
| Doses | : | 0 (vehicle), 40, 100, 250 mg/kg/day |
| Number of animals | : | Males, 13; Females, 13/group |
| Vehicle | : | Distilled Water |
| Administration period | : | Males, 42 days Females, from 14 days prior to mating to Day 3 of lactation |
| Terminal killing | : | Males, Day 43 Females, Day 4 of lactation |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
| Purity | : | 99.9 % |
| Type of cell used | : | Chinese hamster lung (CHL/IU) cells |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan) |
| Solvent | : | Acetone |
| Positive controls | : | -S9, Mitomycin C +S9, Cyclophosphamide |
| Doses | : | -S9 (continuous treatment): 0, 0.4, 0.7, 1.4 mg/ml -S9 (short-term treatment): 0, 0.4, 0.7, 1.4 mg/ml +S9 (short-term treatment): 0, 0.4, 0.7, 1.4 mg/ml |
| S-9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Genotoxic effects:
| clastogenicity | polyploidy | ||||||
| + | ? | - | + | ? | - | ||
| without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | |
| with metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | |
| 1) | The tests were performed by the Hatano Research Institute, Food and Drug Safety Center, 729-5 Ochiai, Hadano-shi, Kanagawa, 257, Japan. Tel +81-463-82-4751 Fax +81-463-82-9627 |