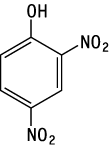

The single dose toxicity test revealed LD50 values of 49 mg/kg for males and 51 mg/kg for females.
With regard to repeat dose toxicity, decreased locomotor activity and increased salivation were detected in both sexes at a dose of 30 mg/kg. Adoption of a prone position, panting, ptosis, a crawling position, soiling of the perigenital region and deaths were detected at a dose of 80 mg/kg, in addition to the clinical signs of decreased locomotor activity and increased salivation in both sexes. Tonic convulsions shortly before death and rigidity of body shortly after death were also apparent. Suppression of body weight gain was detected in the early phase of the administration period in females, and a tendency for suppression of the body weight gain was also evident in the latter half of the administration period in males at the same dose. On urinalysis, brown-colored urine in both sexes at doses of 30 and 80 mg/kg, and decreases in specific gravity and ketone bodies were observed in males given the dose of 80 mg/kg. Hematological examination revealed increases in hemoglobin, hematocrit and MCH in males at a dose of 80 mg/kg, and blood chemical examination revealed decrease in serum chloride in males at doses of 30 and 80 mg/kg. The relative weights of livers in both sexes and of brain, kidney and testis in males were increased at a dose of 80 mg/kg. Histopathological examination revealed mineralization in the kidney in both sexes, and atrophied red pulp due to decrease in extramedullary hematopoesis in the spleen in males at a dose of 80 mg/kg. In recovery groups, decreases in erythrocyte counts, hemoglobin and hematocrit, and increases in extramedullary hematopoesis in the spleen were detected in males at a dose of 80 mg/kg. Mineralization in the kidney was also observed at the end of the recovery period. The other changes observed in administration period or at the end of administration period had disappeared or showed a tendency for reduction. The NOELs are considered to be 10 mg/kg/day for both sexes.
Genotoxicity of 2,4-dinitrophenol was studied by a reverse mutation test in bacteria and a chromosomal aberration test in cultured Chinese hamster lung (CHL/IU) cells.
2,4-Dinitrophenol was possibly mutagenic in Salmonella typhimurium TA98 without an exogenous metabolic activation system.
2,4-Dinitrophenol induced structural chromosomal aberrations in CHL/IU cells after short-term treatment with or without an exogenous metabolic activation system.
| Purity | : | 85.2 % |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD(SD)IGS |
| Test method | : | OECD Test Guideline 401 |
| Route | : | Oral(gavage) |
| Dosage | : | 0(vehicle), 45, 59, 76, 99, 129, 167 mg/kg |
| Number of animals/group | : | Males, 5; females, 5 |
| Vehicle | : | 1 % Methylcellulose solution |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
The LD50 values were estimated to be 49 mg/kg for males and 51 mg/kg for females.
| Purity | : | 85.2 % |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD(SD)IGS |
| Test method | : | Guideline for 28-Day Repeat Dose Toxicity Test in Mammalian Species (Chemical Substances Control Law of Japan) |
| Route | : | Oral(gavage) |
| Dosage | : | 0(vehicle), 3, 10, 30, 80 mg/kg Number of animals/group |
| Administration period | : | Males, 12; females, 12(0, 30, 80 mg/kg) Males, 6; females, 6(3, 10 mg/kg) |
| Recovery period | : | Males and females; 6, 6 and 6/group for the 0, 30 and 80 mg/kg, respectively |
| Vehicle | : | 1 % Methylcellulose solution |
| Administration period | : | Males and females, 28 days |
| Terminal kill | : | Days 29 and 43 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
The NOEL is considered to be 10 mg/kg/day for both sexes.
| Purity | : | 85.2 % |
| Test species/strain | : | Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537, Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals(Chemical Substances Control Law of Japan) and OECD Test Guideline 471 |
| Procedure | : | Pre-incubation method |
| Solvent | : | DMSO |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix; 2-(2-Furyl)-3-(5-nitro-2-furyl)acrylamide (TA100, TA98, WP2 uvrA), Sodium azide (TA1535) and
9-Aminoacridine (TA1537) +S9 mix; 2-Aminoanthracene (all strains) |
| Doses | : | -S9 mix; 0, 78.1, 156, 313, 625, 1250, 2500 μg/plate(TA98, TA1537) -S9 mix; 0, 156, 313, 625, 1250, 2500, 5000 μg/plate(TA100, TA1535, WP2 uvrA) +S9 mix; 0, 156, 313, 625, 1250, 2500, 5000 μg/plate(TA98, WP2 uvrA) +S9 mix; 0, 78.1, 156, 313, 625, 1250, 2500 μg/plate(TA100, TA1535, TA1537) [Confirmative test] -S9 mix; 0, 78.1, 156, 313, 469, 625, 938, 1250, 2500 μg/plate(TA98) |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 3 |
| Number of replicates | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
Genotoxic effects:
Salmonella typhimurium TA98
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [*] | [ ] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA1537
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| Purity | : | 85.2 % |
| Type of cell used | : | Chinese hamster lung (CHL/IU) cells |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Chemical Substances Control Law of Japan) and OECD Test Guideline 473 |
| Solvent | : | DMSO |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix; 1-Methyl-3-nitro-1-nitrosoguanidine +S9 mix; 3,4-Benzo[a]pyrene |
| Doses | : | -S9 mix(6 hr short-term treatment); 0, 300, 600, 900, 1200, 1500, 1800 μg/mL +S9 mix(6 hr short-term treatment); 0, 300, 600, 900, 1200, 1500, 1800 μg/mL |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
Cytotoxicity was observed at 1800 μg/mL after 6 hr short-term treatment without S9 mix.
| Lowest concentration producing cytogenetic effects in vitro: | ||
| With and without metabolic activation (6 hr short-term treatment) | : | 1200 μg/mL(clastogenicity) |
Genotoxic effects:
| clastogenicity | polyploidy | |||||
| + | ? | - | + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| 1) | The tests were performed by the Research Institute for Animal Science in Biochemistry and Toxicology, 3-7-11 Hashimotodai, Sagamihara-shi, Kanagawa 229-1132, Japan. Tel +81-42-762-2775 Fax +81-42-762-7979 |