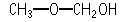
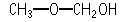
Methoxymethanol was studied for oral toxicity in rats in a single dose toxicity test at doses of 707, 1000, 1414, 2000, and 2828 mg/kg, and in an OECD combined repeat dose and reproductive/developmental toxicity screening test at doses of 12, 60, and 300 mg/kg/day. Genotoxicity of methoxymethanol was also studied by the reverse mutation assay in bacteria and the chromosomal aberration test in cultured Chinese hamster lung (CHL/IU) cells.
The single dose oral toxicity test revealed LD50 values of 1269 mg/kg for males and 1451 mg/kg for females.
With regard to repeat dose toxicity, increased salivation was evident in both sexes, one male died, and suppression of body weight gain and a decrease in food consumption in males occurred in the 300 mg/kg group. Histopathologically, erosion or ulcer of the stomach and thickening of the mucosa of the duodenum were observed in males and females of the 300 mg/kg group. In the 60 mg/kg group, similar histopathological changes of the stomach were noted in males. Hematological examination revealed decreases in red blood cell counts, hematocrit value and hemoglobin concentration, and increases in reticulocyte counts and platelet counts in the males of the 300 mg/kg group. NOELs for repeat dose toxicity are considered to be 12 mg/kg/day for males and 60 mg/kg/day for females. In terms of reproductive/developmental toxicity, the compound showed no effects on any relevant parameters except for an increase in the incidence of persistent foramen ovale in the 300 mg/kg group. NOELs for reproductive and developmental toxicity are considered to be 300 mg/kg/day for parental animals and 60 mg/kg/day for offspring.
Methoxymethanol was mutagenic in Salmonella typhimurium TA100 and TA98 with or without metabolic activation. Structural chromosomal aberrations were induced dose dependently in CHL/IU cells in the absence and presence of exogenous metabolic activation system. Polyploid cells were also marginally induced.
| Purity | : | 46.73% |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD (SD) |
| Test method | : | OECD Test Guideline 401 |
| Doses | : | 707, 1000, 1414, 2000, and 2828 mg/kg |
| Number of animals | : | Male, 5; female, 5/group |
| Vehicle | : | Pure water |
| GLP | : | Yes |
| Purity | : | 46.73% |
| Test species/strains | : | Rat/Crj:CD (SD) |
| Test method | : | OECD Combined Repeat Dose and Reproductive/Developmental Toxicity Screening Test |
| Route | : | Oral (gavage) |
| Dosage | : | 0 (vehicle),12, 60, 300 mg/kg/day |
| Number of animals | : | Male, 10; female, 10/group |
| Vehicle | : | Pure water |
| Administration period | : | Male, 44 days Female, from 14 days before mating to day 3 of lactation |
| Terminal kill | : | Male, day 45
Female, day 4 of lactation |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
NOELs for repeat dose toxicity are considered to be12 mg/kg for males and 60 mg/kg for females.
NOELs for reproductive/developmental toxicity are considered to be 300 mg/kg/day for parent animals and 60 mg/kg/day for offspring.
| Purity | : | 46.73% |
| Test species/strains | : | S.typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537, E. coli WP2 uvrA |
| Test method | : | Guideline for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan) |
| Procedures | : | Plate incorporation method |
| Solvent | : | Acetone |
| Positive controls | : | -S9, AF-2 (TA100, WP2, TA98), sodium azide (TA1535) and 9-aminoacridine (TA1537) +S9, 2-aminoanthracene (all strains) |
| Dosage | : | 0, 19.53, 39.06, 78.12, 156.2, 312.5, 625 μg/plate (TA100, TA98, TA1535, TA1537), 0, 39.06, 78.12, 156.2, 312.5, 625, 1250, 2500 μg/plate (WP2) |
| S-9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavonee |
| Plates/test | : | 3 |
| Number of replicates | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
| + | ? | - | |
| with metabolic activation | [*] | [ ] | [ ] |
| without metabolic activation | [*] | [ ] | [ ] |
| + | ? | - | |
| with metabolic activation | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| without metabolic activation | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| with metabolic activation | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| without metabolic activation | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| Purity | : | 46.73% |
| Type of cell used | : | Chinese hamster CHL/IU cells |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan) |
| Solvent | : | Acetone |
| Positive controls | : | -S9, Mitomycin C +S9, Cyclophosphamide |
| Doses | : | -S9 (continuous treatment): 0, 0.005, 0.01, 0.02 mg/ml
-S9 (short-term treatment): 0, 0.005, 0.01, 0.02 mg/ml +S9 (short-term treatment): 0, 0.008, 0.016, 0.032 mg/ml |
| S-9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
| without metabolic activation (continuous treatment ) | : | 0.01 mg/ml (clastogenicity) 0.02 mg/ml (polyploidy) |
| without metabolic activation (short-term treatment) | : | 0.020mg/ml (clastogenicity) |
| with metabolic activation (short-term treatment) | : | 0.032 mg/ml (clastogenicity 0.032 mg/ml (polyploidy) |
| clastogenicity | polyploidy | |||||
| + | ? | - | + | ? | - | |
| without metabolic activation: | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] |
| with metabolic activation: | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] |
| 1) | The tests were performed by the Mitsubishi-Kasei Institute of Toxicological and Environmental Sciences (New name: Mitsubishi Chemical Safety Institute Ltd.), 14 Sunayama, Hasaki-machi, Kashima-gun, Ibaraki 314-02, Japan. Tel +81-479-46-2871 Fax +81-479-46-2874 |
| 2) | The tests were performed by the Hatano Research Institute, Food and Drug Safety Center, 729-5 Ochiai, Hadano-shi, Kanagawa 257, Japan. Tel +81-463-82-4751 Fax +81-463-82-9627 |