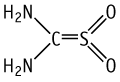

Thiourea dioxide was studied for oral toxicity in rats in a single dose toxicity test at doses of 0, 1024, 1280, 1600 and 2000 mg/kg for both sexes. The single dose oral toxicity test revealed LD50 values of 1565 mg/kg for males and 1496 mg/kg for females.
Thiourea dioxide was studied for oral toxicity in rats in an OECD combined repeat dose and reproductive/developmental toxicity screening test at doses of 0, 4, 20 and 100 mg/kg.
With regard to repeat dose toxicity, depression of body weight gain, decrease of food consumption, and increases of liver and kidney weights were observed in both sexes of the 100 mg/kg group. Hematological examination showed decreases in reticulocyte count and hematocrit and shortening of the activated partial thromboplastin time and prothrombin time in males of the 100 mg/kg group. Bone marrow examination showed decreases in nucleated cell count and the M/E ratio, and decrease in cell counts of neutrophils, eosinophils, lymphocytes, basophilic erythroblasts, and polychromatophilic and orthochromatophilic erythroblasts in males of the 100 mg/kg group. Furthermore, blood chemical examination showed decrease in alkaline phosphatase in males of the 20 mg/kg or more groups. The NOELs for repeat dose toxicity are considered to be 4 mg/kg/day for males and 20 mg/kg/day for females. In terms of reproductive/developmental toxicity, there were no effects related to the test article in reproductive performance of males. In the reproductive performance of females, decreases in estrus frequency, numbers of corpora lutea and implantations, the birth index, and prolongation of the estrous cycle and gestation days were observed in females of the 100mg/kg group. Decreases in numbers of newborn, live newborn and the birth index were found in the 100 mg/kg group. The NOELs are considered to be 100 mg/kg/day for males, 20 mg/kg/day for females, and 20 mg/kg/day for offspring development.
Thiourea dioxide was mutagenic in Salmonella typhimurium TA1535 with or without an exogenous metabolic activation system.
Genotoxicity of thiourea dioxide was studied by chromosomal aberration test in cultured Chinese hamster lung (CHL/IU) cells.
Thiourea dioxide induced structural chromosomal aberrations at the high dose of 0.60 mg/mL with continuous treatment for 24 hr. On short-term treatment, structural chromosomal aberrations were also induced at high doses of 0.55 mg/mL and 1.1 mg/mL (10 mM) with and without metabolic activation system, respectively. No polyploidy was induced.
| Purity | : | 99.7 % |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD (SD) IGS |
| Test method | : | OECD Test Guideline 401 |
| Route | : | Oral (gavage) |
| Doses | : | 0 (vehicle), 1024, 1280, 1600, 2000 mg/kg |
| Number of animals/group | : | Males, 5; females, 5 |
| Vehicle | : | 0.5 w/v% Carboxymethyl cellulose sodium solution |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
LD50: Male, 1565 mg/kg; female, 1496 mg/kg
| Purity | : | 99.4 % |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD (SD) |
| Test method | : | OECD Combined Repeat Dose and Reproductive/Developmental Toxicity Screening Test |
| Route | : | Oral (gavage) |
| Dosage | : | 0 (vehicle), 100, 300, 1000 mg/kg/day |
| Number of animals/group | : | Males, 12 ; females, 12 |
| Vehicle | : | Water for injection |
| Administration period | : | Males, 49 days Females, from 14 days before mating to day 3 of lactation |
| Terminal kill | : | Males, day 50 Females, day 4 of lactation |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
Depression of body weight gain, decrease of food consumption, and increases of organ weights in the liver and the kidney were observed in both sexes of the 100 mg/kg group. Hematological examination showed decreases in reticulocyte rate and hematocrit values and shortening of the activated partial thromboplastin time and prothrombin time in males of the 100 mg/kg group. Bone marrow examination showed decreases in nucleated cell counts and the M/E ratio, and decrease in cell counts of neutrophils, eosinophils, lymphocytes, basophilic erythroblasts, and polychromatophilic and orthochromatophilic erythroblasts in males of the 100 mg/kg group. Blood chemical examination showed increases of albumin, the A/G ratio, triglycerides, phospholipids, total bilirubin, BUN, creatinine, inorganic phosphorus and calcium, decreases of glucose, GOT, GPT and potassium in males of the 100 mg/kg group, and decrease in alkaline phosphatase in males of the 20 mg/kg or more groups. Weights of the liver, the spleen and the testis increased in males and/or females of the 100 mg/kg group. Histopathological examination showed centrilobular hypertrophy and focal necrosis of hepatocytes, basophilic material in the bile duct, and deposits of hemosiderin in the Kupffer cells in the liver in both sexes of the 100 mg/kg group. In the kidney, necrosis of the tubules in females, basophilic tubules dilatation of tubules, and infiltration of lymphocytes were noted in both sexes of the 100 mg/kg group. In glandular stomach, erosion and/or ulceration were noted in both sexes of the 100 mg/kg group. In the spleen, extramedullary hematopoiesis and deposits of hemosiderin in the red pulp were noted in both sexes of the 100 mg/kg group. In the femur, decreased hematopoiesis was noted in the 100 mg/kg group. In the testis, dilatation and atrophy of the seminiferous tubules, degeneration of germ cells, multinucleated giant cells, vacuolization of the Sertoli cells and spermatic granulomas were noted in the 100 mg/kg group. In the epididymis, germ cell debris in the lumen, edema, infiltration of lymphocytes and spermatic granulomas were noted in the 100 mg/kg group. The NOELs for repeat dose toxicity are considered to be 4 mg/kg/day for males and 20 mg/kg/day for females.
<Reproductive and developmental toxicity>
As for reproductive performance, decreases in estrus count, numbers of corpora lutea and implantation, and the birth index, as well as extension of the estrous cycle and increased gestation days were observed in females of the 100 mg/kg group. No effects related to the test article were observed for the copulation or fertility indices and duration of copulation for males or females. All embryo absorption was observed in three dams of the 100 mg/kg group, and decrease in numbers of newborn, live newborn and the birth index were observed in 100 mg/kg group. No effects related to the test article were observed for the sex ratio, newborn body weights and the viability index. There were no external anomalies. The NOELs are considered to be 100 mg/kg/day for males, 20 mg/kg/day for female, and 20 mg/kg/day for offspring development.
| Purity | : | 99.7 % |
| Test species/strains | : | Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537, Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Toxicity Testings of Chemicals (Japan) and OECD Test Guideline 471 |
| Procedures | : | Pre-incubation method |
| Solvent | : | Distilled water |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix; 2-(2-Furyl)-3-(5-nitro-2-furyl) acrylamide (TA100, TA98,WP2 uvrA), Sodium azide (TA1535) and 9-Aminoacridine (TA1537) +S9 mix; 2-Aminoanthracene (five strains) |
| Doses | : | -S9 mix; 0, 313, 625, 1250, 2500, 5000 μg/plate (five strains) +S9 mix; 0, 313, 625, 1250, 2500, 5000 μg/plate (five strains) |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 3 |
| Number of replicates | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
Genetic effects:
Salmonella typhimurium TA1535
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [*] | [ ] | [ ] |
| With metabolic activation: | [*] | [ ] | [ ] |
Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA98, TA1537
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| Purity | : | 99.7 % |
| Type of cell used | : | Chinese hamster lung (CHL/IU) cells |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan) and OECD Test Guideline 473 |
| Solvent | : | Distilled water |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix, Mitomycin C +S9 mix, Cyclophosphamide |
| Doses | : | -S9 mix (24 hr continuous treatment); 0, 0.15, 0.30, 0.60 mg/mL -S9 mix (48 hr continuous treatment); 0, 0.038, 0.075, 0.15 mg/mL -S9 mix (short-term treatment); 0, 0.28, 0.55, 1.1 mg/mL +S9 mix (short-term treatment); 0, 0.14, 0.28, 0.55 mg/mL |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
| Lowest concentration producing cytogenetic effects in vitro: | ||
| Without metabolic activation (continuous treatment ) | : | 0.60 mg/mL |
| Without metabolic activation (short-term treatment) | : | 1.1 mg/mL (10 mM) |
| With metabolic activation (short-term treatment) | : | 0.55 mg/mL |
Genotoxic effects:
| clastogenicity | polyploidy | |||||
| + | ? | - | + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| 1) | The tests were performed by Safety Assessment Laboratory, Panapharm Laboratories Co., Ltd., 1285 Kurisaki-machi, Uto-shi, Kumamoto, 869-0425, Japan. Tel +81-964-23-5111 Fax +81-964-23-2282 |
| 2) | The tests were performed by the Hatano Research Institute, Food and Drug Safety Center, 729-5 Ochiai, Hadano-shi, Kanagawa, 257-8523, Japan. Tel +81-463-82-4751 Fax +81-463-82-9627 |