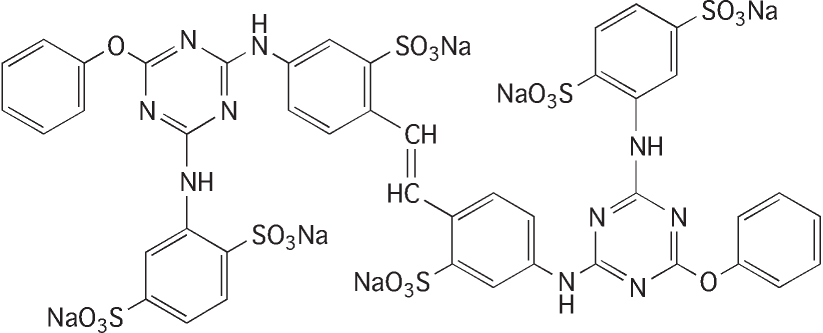
1,4-Benzenedisulfonic acid, 2,2'- [1,2-ethenediylbis [(3-sulfo-4,1-phenylene)imino(6-phenoxy-1,3,5-triazine-4,2-diyl)imino]] bis, hexasodium salt
ヘキサナトリウム= 2,2'-{2,2'-ジスルホナトスチルベン-4,4'-ジイルビス [イミノ(6-フェノキシ-1,3,5-トリアジン-4,2-ジイル)イミノ]}ビス(ベンゼン-1,4-ジスルホナート)
Molecular formula: C44H28N10Na6O20S6 Molecular weight: 1347.08

C.I. Fluorescent brightner 271 was studied for oral toxicity in female rats in a single dose toxicity test at the dose of 2000 mg/kg. The chemical was classified into category 5 of the GHS concerning acute toxicity.
Oral toxicity of C.I. fluorescent brightner 271 was studied in rats according to OECD Test Guideline 422 at doses of 0, 20, 60 and 200 mg/kg.
In the repeated dose oral toxicity test, body weights and food consumption were decreased in both sexes receiving 200 mg/kg. As effects on the kidneys, pale coloring at 60 mg/kg or more, and enlargement and increase in weights were observed at 200 mg/kg in both sexes. Histological evaluation revealed vacuolar degeneration of proximal tubules in both sexes in all treatment groups. With 200 mg/kg in both sexes, anemia on hematological examination and changes in blood chemistry and urinalysis were considered to be effects related to the renal disorder. At the end of the recovery period, clinical alteration was more pronounced than at the end of the administration period. However, on histological evaluation, regeneration of renal tubules was apparent in the cortex. Therefore, it was concluded that the renal disorder was corrected during the recovery period.
The NOAEL for repeated dose oral toxicity is considered to be less than 20 mg/kg/day for both sexes.
With regard to reproductive/developmental toxicity, the test substance showed no effects on the parental animals. Lowered body weights of the pups were observed on day 0 of lactation in the 200 mg/kg group. However, there were no differences in body weights on day 4 of lactation.
The NOAELs for the reproductive and developmental toxicity tests are considered to be 200 mg/kg/day for males and females, and 60 mg/kg/day for offspring.
Reverse mutation tests using microorganisms (Salmonella typhimurium, Escherichia coli) were conducted to assess the potential of C.I. fluorescent brightner 271 to induce gene mutations.
C.I. Fluorescent brightner 271 did not induce gene mutations in bacteria under the conditions of this study.
In vitro chromosomal aberration tests using cultured Chinese hamster cells (CHL/IU) were conducted to assess the potential of C.I. fluorescent brightner 271 to induce chromosomal aberrations.
C.I. Fluorescent brightner 271 induced chromosomal aberrations in cultured cells under the conditions of this study. However the positive response was very weak.
| Purity | : | 91.0 % |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj: CD(SD) |
| Test method | : | OECD Test Guideline 423 |
| Route | : | Oral(gavage) |
| Dosage | : | 2000 mg/kg |
| Number of animals/group | : | Females, 6 |
| Vehicle | : | Distilled water |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
No deaths were found with 2000 mg/kg during the observation period. In all animals, diarrhea was observed on the administration day. Necropsy revealed pale coloration of the kidneys, diffuse red patches/zones in the livers, red patches/zones in the lungs and thin diaphragma among the treated animals. Histological examination revealed inflammatory infiltration, with appearance of macrophages, thickening of the alveolar wall and hemorrhage with hematoidin crystals in the lungs, necrosis in the cortex, with vacuolation of tubules and degeneration of tubular epithelium in the kidneys, multifocal necrosis of hepatocytes, sporadic single cell necrosis, hemorrhage, inflammatory infiltration, capsulitis, and extramedullary hematopoiesis in the livers.
The LD50 value was found to be higher than 2000 mg/kg, so that the chemical was classified into category 5 of the GHS concerning acute toxicity.
| Purity | : | 91.0 % |
| Test species/strains | : | Rat/Crl:CD(SD) |
| Test method | : | OECD Test Guideline 422 |
| Route | : | Oral(gavage) |
| Dosage | : | 0(vehicle), 20, 60, 200 mg/kg/day |
| Number of animals/group | : | Males, 12; females, 12 Satellite males, 5; satellite females, 5(0 and 200 mg/kg/ day) |
| Vehicle | : | Water for injection |
| Administration period | : |
Males, satellite males and satellite females, 43 days |
| Terminal killing | : |
Males, day 44 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
<Repeated dose toxicity>
There were no treatment-related effects on clinical signs or results of a functional observation battery (FOB) test. Body weights were decreased in males in the latter half of the administration period in the 200 mg/kg group and suppression of body weight gain was observed in females in the 200 mg/kg group during the gestation and lactation periods. Food consumption was lowered in males in the latter half of the administration period and in females during the gestation period in the 200 mg/kg group. However, during the recovery period, body weight gain and cumulative food consumption in both sexes in the 200 mg/kg group were the same as in the control group.
On blood coagulation examination, prothrombin time showed a tendency for extension in males in the 200 mg/kg group at the end of the administration period, but was shortened at the end of the recovery period.
On pathological examination, pale coloration of the kidneys was observed in both sexes in groups treated with 60 mg/kg or more, with enlargement and higher organ weights observed in both sexes in the 200 mg/kg group. On histological examination, vacuolar degeneration of proximal tubules was observed in both sexes in all treatment groups, and the extent was dose-dependent. Necrosis of the proximal tubules was observed in the 200 mg/kg group. In addition, regenerative or inflammatory findings were observed related to vacuolar degeneration and necrosis of proximal tubules. Moreover, in the 200 mg/kg group, anemia was indicated on hematological examination. Changes in blood chemistry and the results of the urinalysis were statistically significant.
At the end of the recovery period, changes noted in the clinical examination were more pronounced than at the end of the administration period. However, on histological evaluation, regeneration of renal tubules was apparent in the cortex. Therefore, it was revealed that the renal disorder was corrected during the recovery period.
The NOAEL for repeated dose oral toxicity test is considered to be less than 20 mg/kg/day for both sexes.
<Reproductive and developmental toxicity>
No adverse effects were observed on the estrous cycle, copulation, fertility, delivery conditions, gestation length, number of corpora lutea or implantations, sex ratio, implantation index, gestation index, live birth index, or delivery index.
Lowered body weights of pups were observed on day 0 of lactation in the 200 mg/kg group, but no treatment-related abnormal findings were noted for external parameters and clinical signs, or on necropsy of offspring.
The NOAELs for the reproductive and developmental toxicity tests are considered to be 200 mg/kg/day for parental animals and 60 mg/kg/day for offspring.
3-1. Bacterial test 1)
| Purity | : | 91.0 % |
| Test species/strains | : | Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537, Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Chemical Substances Control Law of Japan) and OECD Test Guideline 471 |
| Procedures | : | Pre-incubation method |
| Vehicle | : | Water for injection |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix; 2-(2-Furyl)-3-(5-nitro-2-furyl)acrylamide (TA100, TA98, WP2 uvrA), sodium azide (TA1535) and 9-aminoacridine hydrochloride (TA1537) +S9 mix; 2-Aminoanthracene (all strains) |
| Dosage | : | [Dose-finding study] -S9 mix; 0, 8.19, 20.5, 51.2, 128, 320, 800, 2000, 5000 μg/plate (all strains) +S9 mix; 0, 8.19, 20.5, 51.2, 128, 320, 800, 2000, 5000 μg/plate (all strains) [Main study] -S9 mix; 0, 156, 313, 625, 1250, 2500, 5000 μg/plate (TA100, TA1535, WP2 uvrA, TA98), 0, 78.1, 156, 313, 625, 1250, 2500, 5000 μg/plate (TA1537) +S9 mix; 0, 156, 313, 625, 1250, 2500, 5000 μg/plate (all strains) |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 3 |
| Number of replicates | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
No increase in revertant colonies was observed in the test with either the non-activation method (-S9 mix) or the activation method (+S9 mix).
Genetic effects :
Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| Purity | : | 91.0 % |
| Type of cell used | : | Chinese hamster lung (CHL/IU) cells |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Chemical Substances Control Law of Japan) and OECD Test Guideline 473 |
| Vehicle | : | Isotonic sodium chloride solution |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix; Mitomycin C +S9 mix; Cyclophosphamide |
| Dosage | : | -S9 mix (short-term treatment); 0, 1250, 2500, 5000 μg/mL +S9 mix (short-term treatment); 0, 1250, 2500, 5000 μg/mL -S9 mix (continuous treatment); 0, 78.1, 156, 313, 625 μg/mL |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
| clastogenicity | polyploidy | |||||
| + | ? | - | + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| 1) | The tests were performed by the Biosafety Research Center, Foods, Drugs and Pesticides (An-pyo Center), 582-2 Shioshinden, Iwata-shi, Shizuoka, 437-1213, Japan. Tel +81-538-58-1266, Fax +81-538-58-1393 |