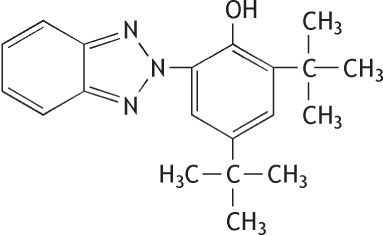
Molecular formula: C20H25N30 Molecular weight: 323.44

A fifty-two-week repeated dose toxicity test of 2-(2'-hydroxy-3',5'-di-tert-butylphenyl) benzotriazole was carried out in male and female rats with oral administration at 0, 0.1, 0.5 and 2.5 mg/kg for the males and at 0, 0.5, 2.5 and 12.5 mg/kg for the females. Ten animals each in all group were used for necropsy at the end of the 13- and 52-week administration periods.
There were no deaths related to administration of the test article.
The males of the 2.5 mg/kg group showed low body weights and high food consumption during the administration period.
On urinalysis, the males of the 2.5 mg/kg group exhibited high values for osmotic pressure and/or specific gravity at weeks 13 and 52. At week 52, high values for osmotic pressure and specific gravity were also observed in males of the 0.5 mg/kg group, and high urine volume and low osmotic pressure in females given 12.5 mg/kg.
On hematological examination, high platelet and low erythrocyte values were observed in males of the 2.5 mg/kg group, and low values for hematocrit and/or hemoglobin in males of the 0.5 and 2.5 mg/kg groups, at weeks 13 and 52. At week 52, high platelet values were observed in females of the 12.5 mg/kg group, and prolongation for the PT and APTT in males of the 2.5 mg/kg group.
On blood chemical examination, males of the 0.5 and 2.5 mg/kg groups showed high values for A/G and albumin ratios, ALP, glucose and/or BUN and low values for a1-, a2- and/or b-globulin ratios at weeks 13 and 52. Females of the 12.5 mg/kg group also showed high values for A/G and albumin ratios and/or ALP and low values for a2- and/or b-globulin ratios. At week 52, males of the 0.5 mg/kg group also exhibited high A/G ratios, and females of the 12.5 mg/kg group showed high values for glucose and BUN and low a1-globulin ratios.
At necropsy, enlargement of the liver was observed in males of the 2.5 mg/kg group and in females of the 12.5 mg/kg group at weeks 13 and 52. At week 52, enlargement of the liver was observed in males of the 0.5 mg/kg group, and light gray macules in livers of males in the 2.5 mg/kg group and one female of the 12.5 mg/kg group.
On organ weight measurement, high values for absolute and relative liver weights were observed for males of the 0.5 and 2.5 mg/kg groups and for females of the 12.5 mg/kg group, along with high values for relative kidney weights in males of the 2.5 mg/kg group at weeks 13 and 52.
On histopathological examination, centrilobular hypertrophy of hepatocytes was observed mildly or moderately in males of the 0.5 and 2.5 mg/kg groups and in females of the 12.5 mg/kg group at weeks 13 and 52. At week 52, the incidence of focal necrosis of hepatocytes also tended to be increased in males of the 2.5 mg/kg group in comparison with the controls.
From the above, the NOAELs are considered to be 0.1 mg/kg/day for males and 2.5 mg/kg/day for females.
SUMMARIZED DATA FROM THE STUDY
| Purity | : | 100 % |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD(SD)IGS |
| Test method | : | Chronic Oral Toxicity Study |
| Route | : | Oral(gavage) |
| Dosage | : | 0(vehicle), 0.1, 0.5, 2.5 mg/kg/day for males 0(vehicle), 0.5, 2.5, 12.5 mg/kg/day for females |
| Number of animals/group | : | Males, 20; females, 20 |
| Vehicle | : | Corn oil |
| Administration period | : | Males and females, 52 weeks |
| Terminal killing | : | Males and females, 13 or 52 weeks |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test Results:
There were no deaths or abnormal clinical signs related to administration of the test article.
On body weight measurement, a low value was observed in the males of the 2.5 mg/kg group on and after day 36.
A high value was observed for food consumption, in males of the 2.5 mg/kg group on and after day 120.
On urinalysis, high values for osmotic pressure and specific gravity were observed in males of the 2.5 mg/kg group at week 13. In week 52, high values for osmotic pressure were also observed in males of the 0.5 and 2.5 mg/kg groups, and for specific gravity in males of the 0.5 mg/kg group. Females of the 12.5 mg/kg group demonstrated high urine volume and low osmotic pressure.
On hematological examination, high platelet and low erythrocyte counts were observed in males of the 2.5 mg/kg group, and low values for hematocrit and hemoglobin in males of the 0.5 and 2.5 mg/kg groups at week 13. At week 52, high platelet counts were observed in males of the 2.5 mg/kg group and females of the 12.5 mg/kg group, and lowering or a tendency toward to lower values for erythrocytes and hematocrit in males of the 0.5 and 2.5 mg/kg groups. PT and APTT were prolonged or tended to be prolonged in males of the 2.5 mg/kg group.
On blood chemical examination, high or tendencies toward elevated values for A/G and albumin ratios and ALP and lowered values for a2- and b-globulin ratios were observed in males of the 0.5 and 2.5 mg/kg groups and in females of the 12.5 mg/kg group at week 13. Males of the 0.5 and 2.5 mg/kg groups also showed high values for glucose and BUN and low values for the a1-globulin ratio, and females of the 12.5 mg/kg group showed high values for total protein. In week 52, high or tendencies toward elevated values for A/G ratio and ALP and lowered or tendencies for lowered values for a1- and a2-globulin ratios were observed in males of the 0.5 and 2.5 mg/kg groups and females of the 12.5 mg/kg group. High values for the albumin ratio were also observed in males of the 0.5 and 2.5 mg/kg groups, elevated BUN and low b-globulin ratios in males of the 2.5 mg/kg group, and high glucose values in females of the 12.5 mg/kg group.
On necropsy, enlargement of the liver was observed in 5 males of the 2.5 mg/kg group and in one female of the 12.5 mg/kg group at week 13. At week 52, enlargement of the liver was observed in 7 and 9 males in the 0.5 and 2.5 mg/kg groups, respectively, and in 5 females in the 12.5 mg/kg group. Light gray macules in the liver were also observed in 2 males of the 2.5 mg/kg group and in one female of the 12.5 mg/kg group.
On organ weight measurement, elevated absolute and relative liver weights were observed in males of the 0.5 and 2.5 mg/kg groups and in females of the 12.5 mg/kg group, and high values for relative kidney weights in males of the 2.5 mg/kg group at weeks 13 and 52.
On histopathological examination, centrilobular hypertrophy of hepatocytes in the livers was observed mildly or moderately in 3 and 9 males of the 0.5 and 2.5 mg/kg groups, respectively, and in 6 females of the 12.5 mg/kg group at week 13. At week 52, centrilobular hepatocyte hypertrophy was again observed mildly or moderately in 5 and 8 males of the 0.5 and 2.5 mg/kg groups, respectively, and in 4 females of the 12.5 mg/kg group. The incidence of focal necrosis of hepatocytes also tended to be increased in males of the 2.5 mg/kg group in comparison with the controls.
From above results, the NOAELs are considered to be 0.1 mg/kg/day for males and 2.5 mg/kg/day for females.
| 1) | The test was performed by the Safety Assessment Laboratory, Panapharm Laboratories Co., Ltd., 1285 Kurisaki-machi, Uto-shi, Kumamoto, 869-0425, Japan. Tel +81-964-23-5111, Fax +81-964-23-2282 |