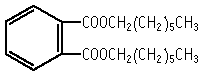
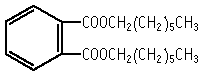
The single dose toxicity test revealed LD50 values of above 2000 mg/kg for both sexes.
In the repeat dose toxicity test, body weight gains and their rates during the administration period were decreased in males given 1000 mg/kg. As for renal changes, the incidence of a urine protein-positive reaction and the relative kidney weights were increased in females given 1000 mg/kg and serum urea nitrogen was increased in males given 1000 mg/kg. Relative to hepatic changes, prothrombin and activated partial thromboplastin times were prolonged in males given 250 mg/kg and above, and the serum b-globulin fraction was decreased and relative liver weights were increased in males given 1000 mg/kg. Histopathologically, centrilobular hypertrophy, centrilobular fatty change and focal necrosis of hepatocytes were observed in males given 1000 mg/kg. In females, activated partial thromboplastin times were prolonged, the serum albumin fraction was increased, the β-globulin fraction was decreased and absolute and relative liver weights were increased in the 1000 mg/kg group. In the male reproductive organs, a bsolute testis and epididymis weights were decreased, and these organs were macroscopically noted to be small. Histopathologically, loss of spermatogenic cells in the testes, decrease in sperm in the ducts and appearance of detached spermatogenic cells in the epididymides were observed in the 1000 mg/kg group.
With regard to the changes in testes and epididymides, no recovery was noted during the 14 days after withdrawal, while many of the other changes disappeared. The repeat dose toxicity revealed NOELs of 62.5 mg/kg/day for males, and 250 mg/kg/day for females.
Diheptyl phthalate was not mutagenic to Salmonella typhimurium, TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537 and Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA. Neither structural nor numerical chromosomal aberrations were induced in CHL/IU cells up to the limit concentration of 5 mg/ml, in the absence or presence of an exogenous metabolic activation system.
| Purity | : | 99.56% |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD (SD) |
| Test method | : | OECD Test Guideline 401 |
| Doses | : | 500, 1000, 2000 mg/kg |
| Number of animals/group | : | Males, 5; females, 5 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
| Purity | : | 99.56% |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD (SD) |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for 28-Day Repeat Dose Toxicity Testing for Chemicals (Japan) |
| Route | : | Oral (gavage) |
| Doses | : | 0 (vehicle), 62.5, 250, 1000 mg/kg/day |
| Number of animals | ||
| Administration period | : | Males and females, 14, 7, 7 and 14/group for the 0, 62.5, 250 and 1000 mg/kg doses, respectively |
| Recovery period | : | Males and females, 7 each for the 0 and 1000 mg/kg groups |
| Vehicle | : | Olive oil |
| Administration period | : | Males and females, 28 days |
| Terminal kill | : | Day 29 or 43 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
| Purity | : | ≧ 99.56 % |
| Test species/strain | : | Salmonella typhimurium, TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537 Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA |
| Test method | : | OECD guideline (No. 471, 472) and Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan) |
| Procedures | : | Pre-incubation method |
| Solvent | : | DMSO |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix, AF-2 (TA100, TA98), sodium azide (TA1535), ENNG (WP2 uvrA) and 9-aminoacridine (TA1537) +S9 mix, 2-aminoanthracene (all strains) |
| Doses | : | 313, 625, 1250, 2500, 5000 μg/plate |
| S-9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 3 |
| Number of replicates | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| Wit metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| Purity | : | ≧ 99.56 % |
| Type of cell used | : | Chinese hamster CHL/IU cells |
| Test method | : | OECD guideline (No. 473) and Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan) |
| Solvent | : | Acetone |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix, Mitomycin C +S9 mix, Benzo[a]pyrene |
| Doses | : | -S9 mix (24 h treatment): 0, 25, 50, 100 μg/ml -S9 mix (48 h treatment): 0, 15, 30, 60 μg/ml -S9 mix (6 h pulse treatment): 0, 1250, 2500, 5000 μg/ml +S9 mix (6 h pulse treatment): 0, 1250, 2500, 5000 μg/ml |
| S-9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
| clastogenicity | polyploidy | |||||
| + | ? | - | + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| 1) | The tests were performed by the Safety Research Institute for Chemical Compounds Co., Ltd., 363-24, Shin-ei, Toyohira-ku, Sapporo, Hokkaido, 004, Japan. Tel +81-11-885-5031 Fax +81-11-885-5313 |
| 2) | The tests were performed by the Mitsubishi Chemical Safety Institute Ltd., 14 Sunayama, Hasaki-machi, Kashima-gun, Ibaraki, 314-02, Japan. Tel +81-479-46-2871 Fax +81-479-46-2874 |