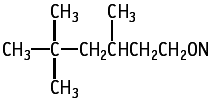
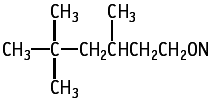
The single dose toxicity test revealed an LD50 value of more than 2000 mg/kg.
In the repeat dose toxicity test, one female of the 300 mg/kg group died on day 21 of gestation, and three females of the 300 mg/kg group had to be killed because of weakness from days 14 to 19 of gestation. Their body weights and food consumption were decreased, and histopathological examination revealed periportal fatty change in the liver, and renal epithelial fatty change and other lesions in these animals that died. Food consumption was increased and body weights tended to be increased in males of the 300 mg/kg group, but the opposite was the case for females receiving this dose. Urinalysis, and hematological and biochemical examinations revealed increases in urine volume and water consumption and slight decreases in red blood cell counts, hematocrit, the hemoglobin concentration, BUN and chloride in males of the 300 mg/kg group. Absolute liver weights were increased in males and females of the 300 mg/kg group, and relative liver weights were increased in males and females of the 60 and 300 mg/kg groups. Absolute and relative weights of the right and left kidneys were increased in males of the 60 and 300 mg/kg groups, and relative weights were also increased in females of the 300 mg/kg group. Autopsy revealed pale discoloration of the kidneys in males of the 60 and 300 mg/kg groups, swelling of the kidneys in males of the 300 mg/kg group, and yellowish white discoloration of the liver in females of the 300 mg/kg group. Histopathological examination revealed a slight degree of periportal fatty change in the livers of males of the 60 and 300 mg/kg groups, and a slight or moderate degree of periportal fatty change in the livers of females of the 300 mg/kg group, a slight or moderate degree of renal tubular epithelial regeneration and granular casts in the kidneys of males of the 60 and 300 mg/kg groups, slight irregularity in the shape of follicles, columnar change of follicular epithelium and decrease in colloid in the kidneys of males of the 300 mg/kg group, slight renal epithelial fatty change in females of the 60 and 300 mg/kg groups, and atrophy of the thymus in females of the 300 mg/kg group. On the basis of these findings, the NOEL of 3,5,5-trimethylhexan-1-ol for repeat dose toxicity was considered to be 12 mg/kg/day for males and females. As for the reproductive ability of parental animals, no effects were detected in males, but continuous diestrous was observed in females of the 300 mg/kg group on estrous cycle examination. All litters of animals in the 300 mg/kg group died, and implantation rate and number of pups born alive were decreased in the 60 and 300 mg/kg groups. With regard to the effects on neonates, viability on day 4 of lactation was decreased in the 300 mg/kg group, and male and female pups of the 300 mg/kg group showed lower body weights on day 0 of lactation. On the basis of these findings, NOELs of 3,5,5-trimethylhexan-1-ol for reproductive/developmental toxicity were considered to be 300 mg/kg/day for males, 60 mg/kg/day for females, and 12 mg/kg/day for the F1 generation, respectively.
3,5,5-Trimethylhexan-1-ol was not mutagenic in Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537 and Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA, with or without an exogeneous metabolic activation system.
Genotoxicity of 3,5,5-trimethylhexan-1-ol was studied by chromosomal aberration test in cultured Chinese hamster lung (CHL/IU) cells.
Structural chromosomal aberrations and polyploidy in CHL/IU cells were not induced up to the high concentration of 0.10 mg/ml with continuous treatment, and with short-term treatment with and without an exogenous metabolic activation system.
| Purity | : | 92.7% |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD (SD) |
| Test method | : | OECD Test Guideline 401 |
| Dosage | : | 2000 mg/kg |
| Number of animals | : | Males, 5; females, 5/group |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
LD50: Male, > 2000 mg/kg; female, > 2000 mg/kg
| Purity | : | 92.7% |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD (SD) |
| Test method | : | OECD Combined Repeat Dose and Reproductive/Developmental Toxicity Screening Test |
| Route | : | Oral (gavage) |
| Dosage | : | 0 (vehicle), 12, 60, 300 mg/kg/day |
| Number of animals | : | Males, 12; females, 12/group |
| Vehicle | : | Olive oil |
| Administration period | : | Males, 46 days Females, from 14 days before mating to day 3 of lactation |
| Terminal kill | : | Males, day 47 Females, day 4 of lactation |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
Food consumption was increased and body weights tended to be increased in males of the 300 mg/kg group, but the opposite was the case for females receiving the highest dose. Urinalysis, hematological and biochemical examinations revealed increases in urine volume and water consumption and slight decreases in red blood cell counts, hematocrit, hemoglobin concentrations, BUN and chloride in males of the 300 mg/kg group. Absolute liver weights were increased in males and females of the 300 mg/kg group, relative liver weights were increased in males and females of the 60 and 300 mg/kg groups, absolute and relative weights of the right and left kidneys were increased in males of the 60 and 300 mg/kg groups, and relative weights of the right and left kidneys were increased in females of the 300 mg/kg group. Autopsy revealed pale discoloration of the kidneys in males of the 60 and 300 mg/kg groups, swelling of the kidneys in males of the 300 mg/kg group, and yellowish white discoloration of the liver in females of the 300 mg/kg group. Histopathological examination revealed a slight degree of periportal fatty change in the liver in males of the 60 and 300 mg/kg groups, a slight or moderate degree of perioportal fatty change in the liver in females of the 300 mg/kg group, a slight or moderate degree of renal tubular epithelial regeneration and formation of granular casts in the kidneys in males of the 60 and 300 mg/kg groups, a slight degree of irregularity in the shape of follicles, columnar change of follicular epithelium and decrease in colloid in the kidneys in males of the 300 mg/kg group, a slight degree of renal epithelial fatty change in females of the 60 and 300 mg/kg groups, and atrophy of the thymus in females of the 300 mg/kg group.
On the basis of these findings, the NOEL of 3,5,5-trimethylhexan-1-ol for repeat dose toxicity was considered to be 12 mg/kg/day for males and for females.
On the basis of these findings, NOELs of 3,5,5-trimethylhexan-1-ol for reproductive/developmental toxicity were considered to be 300 mg/kg/day for males, 60 mg/kg/day for females, and 12 mg/kg/day for the F1 generation, respectively.
| Purity | : | 92.7 wt% |
| Test species/strains | : | Salmonella typhimurium, TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537, Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan) and OECD Guideline No. 471 and 472 |
| Procedures | : | Pre-incubation method |
| Solvent | : | DMSO |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix, 2-(2-Furyl)-3-(5-nitro-2-furyl) acrylamide (TA100, TA98, WP2), Sodium azide (TA1535) and 9-Aminoacridine (TA1537) +S9 mix, 2-Aminoanthracene (five strains) |
| Doses | : | -S9 mix; 0, 6.25, 12.5, 25.0, 50.0, 100, 200 μg/plate (TA100, TA1537) 0, 15.6 - 500 μg/plate (TA1535, TA98, WP2) +S9 mix; 0, 6.25 - 200 μg/plate (TA100, TA1537) 0, 15.6 - 500 μg/plate (TA1535, TA98, WP2) |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 3 |
| Number of replicates | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
Genetic effects:
Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| Purity | : | 92.7 wt% |
| Type of cell used | : | Chinese hamster lung (CHL/IU) cells |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan) and OECD Guideline No. 473 |
| Solvent | : | Dimethylsulfoxide |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix, Mitomycin C +S9 mix, Cyclophosphamide |
| Doses | : | -S9 mix (continuous treatment):0, 0.025, 0.050, 0.10 mg/ml -S9 mix (short-term treatment):0, 0.025, 0.050, 0.10 mg/ml +S9 mix (short-term treatment):0, 0.025, 0.050, 0.10 mg/ml |
| S-9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
| clastogenicity | polyploidy | |||||
| + | ? | - | + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| 1) | The tests were performed by the Safety Research Institute for Chemical Compounds Co., Ltd., 363-24, Shin-ei, Kiyota-ku, Sapporo, Hokkaido, 004, Japan. Tel +81-11-885-5031 Fax +81-11-885-5313 |
| 2) | The tests were performed by the Hatano Research Institute, Food and Drug Safety Center, 729-5 Ochiai, Hadano-shi, Kanagawa, 257, Japan. Tel +81-463-82-4751 Fax +81-463-82-9627 |