
A single dose oral toxicity test revealed an LD50 value of above 2000 mg/kg for the compound in both sexes.
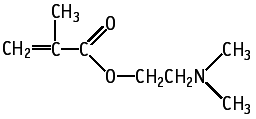
2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate was studied for oral toxicity in rats in an OECD combined repeat dose and reproductive/developmental toxicity screening test at doses of 0, 40, 200 and 1000 mg/kg/day.
With regard to repeat dose toxicity, three females died in the 1000 mg/kg group. Soiled tail, twitching, chronic convulsion and suppression of body weight gain in both sexes, and a decrease in food consumption in females were also observed in the late period of administration in this group. Histopathological examination revealed degeneration of nerve fibers in the brain and spinal cord, and hyperplasia of the mucosa, edema and inflammatory cell infiltration in the forestomach in both sexes, and atrophy of the thymus in females in the 1000 mg/kg group. Increases in organ weights without histopathological changes were observed for the kidneys of both sexes, the livers of males, and the adrenals of females in this group. BUN was slightly increased in males in the same group. Slight anemic changes were observed in males of the 200 and 1000 mg/kg groups. The NOELs for repeat dose toxicity are considered to be 40 mg/kg/day for males and 200 mg/kg/day for females. In terms of reproductive/developmental toxicity, the compound exerted effects on maternal behavior, the body weight of neonates and the viability index in the 1000 mg/kg group. The NOELs for reproductive/developmental toxicity are considered to be 1000 mg/kg/day for parental males, and 200 mg/kg/day for parental females and offspring.
2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate was mutagenic in Salmonella typhimurium TA1537 without an exogenous metabolic activation system.
2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate induced structural chromosomal aberrations in CHL cells with and without an exogenous metabolic activation system.
| Purity | : | 99.9 % |
| Test species/strain | : | Rats/Crj:CD(SD)IGS |
| Test method | : | OECD Test Guideline 401 |
| Route | : | Oral(gavage) |
| Dosage | : | 0(Vehicle), 500, 1000, 2000 mg/kg/day |
| Number of animals/group | : | Males, 5; females, 5 |
| Vehicle | : | Corn oil |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
| Purity | : | 99.9% |
| Test species/strain | : | Rats/Crj:CD(SD)IGS |
| Test method | : | OECD Combined Repeat Dose and Reproductive/ Developmental Toxicity Screening Test |
| Route | : | Oral(gavage) |
| Dosage | : | 0(Vehicle), 40, 200, 1000 mg/kg/day |
| Number of animals/group | : | Males, 12; females, 12 |
| Vehicle | : | Corn oil |
| Administration period | : | Males, 43 days Females, from 14 days before mating to day 3 of lactation |
| Terminal kill | : | Males, day 44 Females, day 4 of lactation |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
In the 1000 mg/kg group, three females died. Soiled tail, twitching, chronic convulsion and suppression of body weight gain were observed in both sexes in the late period of administration. Food consumption was reduced in females during the lactation period. At necropsy, thickening of the wall of the forestomach was observed in both sexes. Histopathological examination revealed degeneration of nerve fibers in the brain and spinal cord, and hyperplasia of the mucosa, edema and inflammatory cell infiltration in the forestomach in both sexes. Atrophy of the thymus was also observed in females. Increases in organ weights without histopathological changes were observed for the kidneys of both sexes, the liver of males, and the adrenals in females. Slight increase of BUN in males was observed on blood chemical examination. Hematological examination in males showed slight anemic changes such as decreases in erythrocyte counts, hemoglobin concentration and hematocrit, and an increase in the reticulocyte ratio.
In the 200 mg/kg group, decreases in hemoglobin concentration and hematocrit were observed in males.
The NOELs for repeat dose toxicity are considered to be 40 mg/kg/day for males and 200 mg/kg/day for females.
<Reproductive and developmental toxicity>
The compound had no effects on reproductive parameters such as the mating index, the fertility index, numbers of corpora lutea or implantations, the implantation index, the delivery index, the gestation index, gestation length or parturition. Three dams of the 1000 mg/kg group, however, lost all their pups in the lactation period. On examination of neonates, the 1000 mg/kg dose was associated with a decrease in body weight and a low viability index. There were no significant differences in numbers of offspring or live offspring, the sex ratio or the live birth index. No abnormalities ascribable to the compound were found for external features, clinical signs or necropsy findings for the offspring.
The NOELs for reproductive and developmental toxicity are considered to be 1000 mg/kg/day for parental males, 200 mg/kg/day for parental females and offspring.
| Purity | : | 99.9 % |
| Test species/strain | : | Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537, Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan)and OECD Guidelines No. 471 and 472 |
| Procedures | : | Pre-incubation method |
| Solvent | : | Distilled water |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix; 2-(2-Furyl)-3-(5-nitro-2-furyl)acrylamide(TA100, TA98, WP2 uvrA), Sodium azide(TA1535) and 9-Aminoacridine(TA1537) +S9 mix; 2-Aminoanthracene(all strains) |
| Doses | : | -S9 mix; 156, 313, 625, 1250, 2500, 5000 μg/plate +S9 mix; 156, 313, 625, 1250, 2500, 5000 μg/plate [Confirmative test] -S9 mix; 1000, 1500, 2000, 2500, 3000, 3500, 4000, 4500, 5000 μg/plate |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 3 |
| Number of replicates | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
Genotoxic effects:
S. typhimurium TA1537
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [*] | [ ] | [ ] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
S. typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
E. coli WP2 uvrA
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| Purity | : | 99.9 % |
| Type of cell used | : | Chinese hamster lung(CHL)cells |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan)and OECD Guideline No. 473 |
| Solvent | : | Distilled water |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix, N-Methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine +S9 mix, Benzo[a]pyrene |
| Doses | : | -S9 mix(24 and 48-hr continuous treatment): 0, 20, 39, 78, 156, 313, 625 μg/mL -S9 mix(6-hr short-term treatment): 0, 200, 400, 600, 800, 1400, 1600 μg/mL +S9 mix(6-hr short-term treatment): 0, 200, 400, 600, 800, 1400, 1600 μg/mL |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
Cytotoxicity was observed at more than 800 μg/mL on 6-hr short-term teatment without an S9 mix.
Genotoxic effects:
| clastogenicity | polyploidy | |||||
| + | ? | - | + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| 1) | The tests were performed by the Mitsubishi Chemical Safety Institute Ltd., 14 Sunayama, Hasaki-machi, Kashima-gun, Ibaraki, 314-0255, Japan. Tel +81-479-46-2871 Fax +81-479-46-2874 |
| 2) | The tests were performed by the Research Institute for Animal Science in Biochemistry and Toxicology, 3-7-11 Hashimotodai, Sagamihara-shi, Kanagawa 229-1132, Japan. Tel +81-42-762-2775 Fax +81-42-762-7979 |