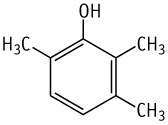

A single oral dose LD50 value of 2,3,6-trimethylphenol was between 1400 and 2000 mg/kg in both sexes.
2,3,6-Trimethylphenol was studied for oral toxicity in rats in a 28-day repeat dose toxicity test at doses of 0, 100, 300 and 1000 mg/kg. In the 1000 mg/kg group of both sexes, body weight gain and food consumption were suppressed. Similar changes were sporadically found in the 300 mg/kg treated animals. Yellowish urine was observed in both sexes of the 1000 mg/kg group. In female animals given 1000 mg/kg, proteinuria with increased excretion of bilirubin and urobilinogen was observed. The RBC count, hemoglobin content and hematocrit were decreased in the 1000 mg/kg females. Plasma levels of inorganic phosphorus were increased and that of albumin decreased in males of the 300 mg/kg and 1000 mg/kg groups. Weight of the adrenal glands were decreased in the males. Weights of the spleen and the liver were increased in 1000 mg/kg females. Hypertrophy with ground glass appearance of centrilobular hepatocytes, and hemosiderin deposition, dilatation of sinus in the spleen, and diffuse squamous cell hyperplasia of the forestomach were observed in both sexes of the 1000 mg/kg group. Most of the changes disappeared after withdrawal. Therefore, the NOEL for the 28-day repeat dose oral toxicity test of 2,3,6-trimethylphenol is considered to be 100 mg/kg/day for male and female rats.
2,3,6-Trimethylphenol was not mutagenic in Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537 and Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA, with or without an exogenous metabolic activation system.
2,3,6-Trimethylphenol induced structural chromosomal aberrations in CHL/IU cells with 6 hr short-term treatment with and without an S9 mix and on continuous treatment for 48 hr. Polyploidy was not induced in any treatment group.
| Purity | : | 99.67 % |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD(SD) |
| Test method | : | OECD Test Guideline 401 |
| Route | : | Oral (gavage) |
| Doses | : | 0 (vehicle), 1000, 1400, 2000mg/kg |
| Number of animals/group | : | Males, 5; females, 5 |
| Vehicle | : | Corn oil |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
| Purity | : | 99.67 wt% |
| Test species/strain | : | Rats/Crj:CD(SD) |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for 28-Day Repeat Dose Toxicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan) |
| Route | : | Oral (gavage) |
| Doses | : | 0 (vehicle), 100, 300, 1000 mg/kg/day |
| Number of animals/group | : | Males, 10; females, 10 (0, 1000 mg/kg) |
| : | Males, 5; females, 5 (100, 300 mg/kg) | |
| Vehicle | : | Corn oil |
| Administration period | : | Males and females, 28 days |
| Terminal kill | : | Males and females, on day 29 or 43 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
| Purity | : | 99.67 % |
| Test species/strain | : | Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537, Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan) and OECD Test Guidelines 471 and 472 |
| Procedures | : | Pre-incubation method |
| Solvent | : | DMSO |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix; AF-2 (TA100, TA98), Sodium azide (TA1535), ENNG (WP2 uvrA) and 9-Aminoacridine (TA1537) +S9 mix; 2-Aminoanthracene (all strains) |
| Doses | : | -S9 mix; 39.1, 78.1, 156, 313, 625 and 1250 μg/plate +S9 mix; 39.1, 78.1, 156, 313, 625 and 1250 μg/plate |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 3 |
| Number of replicates | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
Genetic effects:
Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| Purity | : | 99.67 % |
| Type of cell used | : | Chinese hamster CHL/IU cells |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan) and OECD Test Guideline 473 |
| Solvent | : | Acetone |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix, Mitomycin C +S9 mix, Benzo[a]pyrene |
| Doses | : | -S9 mix (24 and 48 hr continuous treatment); 0, 25, 50, 100, 200 μg/mL (main test) 0, 12.5, 25, 50, 100, 200 μg/mL (confirmation test) -S9 mix (6 hr short-term treatment); 0, 25, 50, 100, 200 μg/mL +S9 mix (6 hr short-term treatment); 0, 25, 50, 100, 200 μg/mL |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
Genotoxic effects:
| clastogenicity | polyploidy | |||||
| + | ? | - | + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| 1) | The tests were performed by the Hatano Research Institute, Food and Drug Safety Center, 729-5 Ochiai, Hadano-shi, Kanagawa, 257-8523, Japan. Tel +81-463-82-4751 Fax +81-463-82-9627 |
| 2) | The tests were performed by the Mitsubishi Chemical Safety Institute Ltd., 14 Sunayama, Hasaki-machi, Kashima-gun, Ibaraki, 314-0255, Japan. Tel +81-479-46-2871 Fax +81-479-46-2874 |