
With regard to repeat dose toxicity, two female rats given 150 mg/kg died at the end of the gestation period (one of them during delivery). Body weight gain of females given 150 mg/kg was lower than that of the control during the gestation period. Hematological examination showed decreases of hematocrit, hemoglobin and red blood cells, and increases of reticulocytes and a slight tendency for anemia in male rats given 150 mg/kg. Blood chemical examination revealed decreases in levels of GOT and increases in γ-GTP in males given 30 and 150 mg/kg. Liver and kidney weights was showed increases or a tendency for increase in the male rats given 30 mg/kg or more and in the females given 150 mg/kg. As gross findings, enlargement of the liver was observed in males given 30 and 150 mg/kg, and enlargement of the liver and kidneys was observed in females given 150 mg/kg. Histopathological examination revealed swelling of liver cells in the centrilobular zone in males and females of the 150 mg/kg group, and degeneration of liver cells, necrosis of centrilobular hepatocytes and single cell necrosis in the females of the same group. NOELs for repeat dose toxicity are considered to be 6 mg/kg/day in males and 30 mg/kg/day in females of the group. In terms of reproductive/developmental toxicity, one female given 150 mg/kg died during the delivery. With three females in the same all pups died treatment group during the lactation period. NOELs for reproductive performance of males and for that of females and pup development are considered to be 150 mg/kg/day and 30 mg/kg/day, respectively.
6-tert-Butyl-2,4-xylenol was not mutagenic in Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA98, TA1535, TA1537 and Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA.
Neither structural chromosomal aberrations nor polyploidy were induced in CHL/IU cells up to the concentration giving 50% cell growth inhibition, in the absence or presence of an exogenous metabolic activation system.
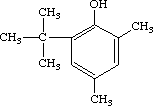
| Purity | : | 98.5% |
| Test species/strain | : | Rats/Crj:CD (SD) |
| Test method | : | OECD Test Guideline 401 |
| Route | : | Oral (gavage) |
| Doses | : | Males: 0, 819, 1024, 1280, 1600, 2000 mg/kg Females: 0, 655, 819, 1024, 1280, 1600 mg/kg |
| Number of animals | : | Males, 5; females, 5/group |
| Vehicle | : | Corn oil |
| GLP | : | Yes |
| Test results | : | LD50: males, 910 mg/kg; females, 972 mg/kg |
| Purity | : | 98.5% |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD (SD) |
| Test method | : | OECD Combined Repeat Dose and Reproductive/Developmental Toxicity Screening Test |
| Route | : | Oral (gavage) |
| Doses | : | 0 (Vehicle), 6, 30, 150 mg/kg/day |
| Number of animals | : | Males,12; females, 12/group |
| Vehicle | : | Corn oil |
| Administration period | : | Males, 45 days Females, from 14 days before mating to day 3 of laction |
| Terminal killing | : | Males, day 45 Females, day 4 of laction |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
| Purity | : | 98.5% |
| Test species/strain | : | S.typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537 E. coli WP2 uvrA |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan) |
| Procedures | : | plate incorporation method |
| Solvent | : | DMSO |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 Mix, AF-2 (TA100, WP2. TA98), sodium azide (TA1535) and 9-aminoacridine (TA1537) +S9 Mix, 2-aminoanthracene (all strains), |
| Doses | : | 0, 6.25, 12.5, 2550, 100 and 200 μg/plate on -S9 Mix and 0, 12.5, 25, 50, l00, 200 and 400 (6.25 - 200 in TA1537) on +S9 Mix Rat liver. induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone, |
| Plates/test | : | 3 |
| Number of replicates | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
| + | ? | - | |
| without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| with metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
E. Coli WP2 uvrA
| without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| with metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| Purity | : | 98.5 % |
| Type of cell used | : | Chinese hamster lung (CHL/IU) cells |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan) |
| Solvent | : | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| Positive controls | : | -S9, Mitomycin C +S9, Cyclophosphamide |
| Doses | : | -S9 (continuous treatment): 0, 0.008, 0.017, 0.033 mg/ml -S9 (short-term treatment): 0, 0.008, 0.017, 0.033 mg/ml +S9 (short-term treatment): 0, 0.014, 0.028, 0.056 mg/ml |
| S-9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
| clastogenicity | polyploidy | |||||
| + | ? | - | + | ? | - | |
| without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| with metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| 1) | The tests were performed by the Biosafety Research Center, Foods, Drugs and Pesticides (An-pyo Center), Japan, 582-2 Shioshinden Arahama, Fukude-cho, Iwata-gun, Shizuoka, 437-12, Japan. Tel 81-538-58-1266 Fax 81-538-58-1393 |
| 2) | The tests were performed by the Hatano Research Institute, Food and Drug Safety Center, 729-5 Ochiai, Hadano-shi, Kanagawa, 257, Japan. Tel +81-463-82-4751 Fax +81-463-82-9627 |