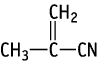
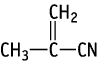
Single and combined repeat dose toxicity studies with a reproductive/developmental toxicity screening test of methacrylonitrile dissolved in olive oil were conducted with oral administration using Crj:CD(SD)IGS rats.
The single doses were 0, 50, 60, 70, 85 and 100 mg/kg for males, and 0, 60, 70, 85, 100 and 120 mg/kg for females. The single dose toxicity test revealed LD50 values of 64 mg/kg for males and 73 mg/kg for females.
The doses for the combined toxicity test were of 0, 7.5, 15, 30 mg/kg/day.
With regard to repeat dose toxicity, hematological examination showed decreases in the erythrocyte count, packed cell volume, and hemoglobin concentration in males given 30 mg/kg. Blood chemical examination showed decreases in potassium in males given 15 and 30 mg/kg, increase in creatinine in males given 30 mg/kg, and increase in total bilirubin and glucose in females given 30 mg/kg. At autopsy, dark red patches on the mucosa of the glandular stomach were observed in some females given 7.5 mg/kg or more, and a male given 30 mg/kg, these being revealed as erosions on histopathological examination. Liver, spleen and heart showed increased weights. On histopathological examination, extramedullary hematopoiesis in the spleen was observed in females given 15 mg/kg or more. From the results the NOELs are considered to be 7.5 mg/kg/day for males, and less than 7.5 mg/kg/day for females.
With regard to reproductive and developmental toxicity, no effects were observed. The NOEL for reproductive/developmental toxicity is thus to be 30 mg/kg/day or more for reproductive performance and offspring development.
A reverse mutation test of methacrylonitrile in bacteria was carried out. This substance was not mutagenic in Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537 and Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA, with or without an exogenous metabolic activation system.
Genotoxicity of methacrylonitrile was studied by chromosomal aberration test using cultured Chinese hamster lung (CHL/IU) cells.
Methacrylonitrile induced structural chromosomal aberrations at three doses (0.068-0.27 mg/mL) on short-term treatment with a metabolic activation system. Polyploidy was also induced (3.13 %) at the lowest dose with short-term treatment and a metabolic activation system.
| Purity | : | 99 % |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD(SD)IGS |
| Test method | : | OECD Test Guideline 401 |
| Route | : | Oral(gavage) |
| Doses | : | Males; 0(vehicle), 50, 60, 70, 85, 100 mg/kg |
| Females; 0(vehicle), 60, 70, 85, 100, 120 mg/kg | ||
| Number of animals/group | : | Males, 5; Females, 5 |
| Vehicle | : | Olive oil |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
The LD50 values were estimated to be 64 mg/kg for males and 73 mg/kg for females.
| Purity | : | 99 % |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD(SD)IGS |
| Test method | : | OECD Test Guideline 422 |
| Route | : | Oral(gavage) |
| Doses | : | 0(vehicle), 7.5, 15, 30 mg/kg |
| Number of animals/group | : | Males, 12; Females, 12 |
| Vehicle | : | Olive oil |
| Administration period | : | Males, 46 days Females, from 14 days before mating to day 4 of lactation |
| Terminal killing | : | Males, day 47 Females, day 5 of lactation |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Hematological examination showed decreases in erythrocyte counts, packed cell volume, and hemoglobin concentrations in males given 30 mg/kg. Blood chemical examination showed decreases in potassium in males given 15 and 30 mg/kg, increase in creatinine in males given 30 mg/kg, and increase in total bilirubin and glucose in females given 30 mg/kg. At autopsy, dark red patches on the mucosa of the glandular stomach was observed in single females given 7.5 or 15 mg/kg, and a male and 2 females given 30 mg/kg, these being revealed to be erosions on histopathological examination. Relative liver weights were increased in males given 30 mg/kg, and in females given both doses. Absolute liver weights were increased in females given 30 mg/kg. Absolute and relative spleen weights were increased in females given 30 mg/kg. Absolute heart weights were increased in females given each dose, and relative heart weights in those given 15 or 30 mg/kg. On histopathological examination, extramedullary hematopoiesis in the spleen was observed in 3 females given 15 mg/kg, and 7 females given 30 mg/kg.
The NOELs are considered to be 7.5 mg/kg/day for males, less than 7.5 mg/kg/day for females.
<Reproductive and developmental toxicity>
No effects were observed on reproductive performance in males and females given each dose, and on developmental performance of the newborns.
The NOEL for reproductive/developmental toxicity is considered to be 30 mg/kg/day or more for reproductive performance and offspring development.
| Purity | : | 99 % |
| Test species/strain | : | Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537, Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals(Chemical Substances Control Law of Japan) and OECD Test Guideline 471 |
| Procedures | : | Pre-incubation method |
| Solvent | : | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix;2-(2-Furyl)-3-(5-nitro-2-furyl)acrylamide (TA100, TA98, WP2 uvrA), Sodium azide (TA1535) and 9-Aminoacridine (TA1537) |
| Doses | : | -S9 mix; 0, 313, 625, 1250, 2500, 5000 μg/plate(five strains) +S9 mix; 0, 313, 625, 1250, 2500, 5000 μg/plate(five strains) |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavon |
| Plates/test | : | 3(1 for cytotoxicity test) |
| Number of animals/group | : | 2(plus 1 cytotoxicity test) |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Genetic effects:
Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| Purity | : | 99 % |
| Test species/strain | : | Chinese hamster lung (CHL/IU) cells |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals(Chemical Substances Control Law of Japan) and OECD Test Guideline 473 |
| Solvent | : | Distilled water |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix; Mitomycin C +S9 mix; Cyclophosphamide |
| Doses | : | -S9 mix (short-term treatment); 0, 0.17, 0.34, 0.67 mg/mL +S9 mix (short-term treatment); 0, 0.068, 0.14, 0.27 mg/mL -S9 mix (continuous treatment for 24 hr); 0, 0.17, 0.34, 0.67 mg/mL |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
| Lowest concentration producing cytogenetic effects in vitro: | ||
| With metabolic activation (short-term treatment) | : | 0.068 mg/mL(clastogenicity and polyploidy) |
Genotoxic effects:
| clastogenicity | polyploidy | |||||
| + | ? | - | + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] |
| 1) | The tests were performed by the Safety Research Institute for Chemical Compounds Co., Ltd., 363-24, Shin-ei, Kiyota-ku, Sapporo, Hokkaido, 004-0839, Japan. Tel +81-11-885-5031 Fax +81-11-885-5313 |
| 2) | The tests were performed by the Hatano Research Institute, Food and Drug Safety Center, 729-5 Ochiai, Hadano-shi, Kanagawa, 257-8523, Japan. Tel +81-463-82-4751 Fax +81-463-82-9627 |