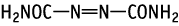
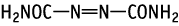
While no adverse effects of 1,1'-azobisformamide were found in males, treatment with 1000 mg/kg to females caused death during the lactation period due to pelvic pyelonephritic kidney lesions.
Under the present conditions, NOELs for reproductive toxicity of 1,1'-azobisformamide are considered to be 1000 mg/kg/day for males and females, and those for toxicity other than reproduction are considered to be 1000 mg/kg/day for males and 300 mg/kg/day for females.
| Purity | : | 99.5 % |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD(SD) |
| Test method | : | OECD Test Guideline 415 |
| Route | : | Oral(gavage) |
| Doses | : | 0, 100, 300 and 1000 mg/kg |
| Number of animals/group | : | Males, 25; females, 25 |
| Vehicle | : | Corn oil |
| Administration period | : | Males, 98 days Females, from 14 days before mating to day 20 of lactation |
| Terminal kill | : | Males, day 99 Females, day 21 of lactation Offspring, 21 days after birth |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
No adverse effects on reproductive parameters of parent animals including viability, growth and morphology of offspring were observed.
The NOELs for reproduction are considered to be 1000 mg/kg/day for males and females including offspring. Those for toxicity other than reproduction are considered to be 1000 mg/kg/day for males and 300 mg/kg/day for females.
| 1) | The test was performed by the Hatano Research Institute, Food and Drug Safety Center, 729-5 Ochiai, Hadano-shi, Kanagawa, 257-0025, Japan. Tel +81-463-82-4751 Fax +81-463-82-9627 |