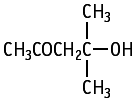
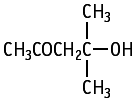
Diacetone alcohol was studied for oral toxicity in rats in an OECD combined repeat dose and reproductive/developmental toxicity screening test at doses of 0, 30, 100, 300 and 1000 mg/kg/day.
With regard to repeat dose toxicity, changes in general condition, such as decreased locomotor activity and response to stimulation by knocking sounds or palpation, were noted at the early stage of the administration period in males and females of the 300 and 1000 mg/kg groups. A decrease in body weight gain was noted during the premating period in females of the 1000 mg/kg group. One female of this group had to be killed in extremis because of difficulty in delivery. Hematological and blood chemical examinations revealed increases of platelet count, GOT, cholinesterase,total protein, total cholesterol, total bilirubin, blood urea nitrogen, creatinine and calcium,and a decrease of glucose at the dose of 1000 mg/kg in males. Histopathological examination revealed increases of deposition of hyaline droplets in the proximal tubular epithelium and basophilic tubules and dilatation of the distal tubules in the male kidneys at doses of 100 mg/kg or more. Changes in female kidneys at doses of 300 and 1000 mg/kg were dilatation of the distal tubules and fatty degeneration of the proximal tubular epithelium. Hepatocellular hypertrophy was evident in both sexes of the 1000 mg/kg group, and vacuolization of the cells of the zona fasciculata in the adrenals in animals receiving 300 or 1000 mg/kg. The NOELs for repeat dose toxicity are considered to be 30 mg/kg/day for males and 100 mg/kg/day for females. In terms of reproductive/developmental toxicity,there was a tendency for decrease in values for reproductive parameters of the parental animals including fertility index, number of implantations and implantation index. One female with difficulty in delivery and another with litter loss due to cannibalism or death in the 1000 mg/kg group were killed. A tendency for decreased values for developmental parameters of the offspring, including total number, live birth and viability indexes, was also noted at the highest dose. The NOELs for reproductive performance and offspring development are considered to be both 300mg/kg/day.
Diacetone alcohol was not mutagenic in Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537 and Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA, with or without an exogenous metabolic activation system.
Genotoxicity of diacetone alcohol was studied by chromosomal aberration test in cultured Chinese hamster lung (CHL/IU) cells. Structural chromosomal aberrations and polyploidy were not induced up to a maximum concentration of 1.2 mg/ml (10 mM) on continuous treatment, and with short-term treatment, with and without an exogenous metabolic activation system.
| Purity | : | 99.8% |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD (SD) |
| Test method | : | OECD Combined Repeat Dose and Reproductive/Developmental Toxicity Screening Test |
| Route | : | Oral (gavage) |
| Doses | : | 0 (vehicle), 30, 100, 300, 1000 mg/kg/day |
| Number of animals/group | : | Males, 10 Females, 10 |
| Vehicle | : | Purified water |
| Administration period | : | Males, 44 days Females, from 14 days before mating to day 3 of lactation |
| Terminal kill | : | Males, day 45 Females, day 4 of lactation |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
In females, there was a decrease in body weight gain during the premating period in the 1000 mg/kg group. One of this group had to be killed in extremis because of difficulty in delivery. Changes similar to those in the same dose-males were evident with regard to general condition, histopathological findings for the liver and adrenals, and the liver weight. Dilatation of distal tubules and fatty degeneration of the proximal tubular epithelium in the kidneys were observed histopathologically at doses of 300 and 1000 mg/kg.
The NOELs for repeat dose toxicity are considered to be 30 mg/kg/day for males and 100 mg/kg/day for females.
The NOELs for reproductive performance and offspring development are considered to be both 300 mg/kg/day.
| Purity | : | 99.8 wt% |
| Test species/strains | : | Salmonella typhimurium, TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537, Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan) and OECD Guideline No. 471 and 472 |
| Procedures | : | Pre-incubation method |
| Solvent | : | Water |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix, 2-(2-Furyl)-3-(5-nitro-2-furyl) acrylamide (TA100, TA98, WP2), Sodium azide (TA1535) and 9-Aminoacridine (TA1537)
+S9 mix, 2-Aminoanthracene (five strains) |
| Doses | : | -S9 mix; 0, 313, 625, 1250, 2500, 5000 μg/plate (five strains)
+S9 mix; 0, - 5000 μg/plate (five strains) |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 3 |
| Number of replicates | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
Genetic effects:
Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537
| + | ? | - | ||
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA
| + | ? | - | ||
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| Purity | : | 99.8 wt% |
| Type of cell used | : | Chinese hamster lung (CHL/IU) cells |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan) and OECD Guideline No. 473 |
| Solvent | : | Distilled water |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix , Mitomycin C
+S9 mix, Cyclophosphamide |
| Doses | : | -S9 mix (continuous treatment):0, 0.30, 0.60, 1.2 mg/ml
-S9 mix (short-term treatment):0, 0.30, 0.60, 1.2 mg/ml +S9 mix (short-term treatment):0, 0.30, 0.60, 1.2 mg/ml |
| S-9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
Genotoxic effects:
| clastogenicity | polyploidy | |||||
| + | ? | - | + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| 1) | The tests were performed by the Research Institute for Animal Science in Biochemistry and Toxicology, 3-7-11 Hashimotodai, Sagamihara-shi, Kanagawa 229, Japan. Tel +81-427-62-2775 Fax +81-427-62-7979 |
| 2) | The tests were performed by the Hatano Research Institute, Food and Drug Safety Center, 729-5 Ochiai, Hadano-shi, Kanagawa, 257, Japan. Tel +81-463-82-4751 Fax +81-463-82-9627 |