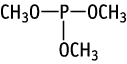
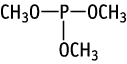
No deaths were observed in any animals. Temporary salivation after dosing was observed in males of the 20 and 80 mg/kg groups and in females of the 80 mg/kg group. There were no changes related to the dosing in body weight and food consumption. Incidence of thickening of the mucosa in the forestomach, accompanied by squamous hyperplasia, was significantly increased at 20 and 80 mg/kg. The findings for internal organs revealed no other adverse changes in any animals. There were no effects on copulation, fertility or estrous cyclicity in any dosing group. In addition, no changes related to the dosing were observed in gestation length, delivery and lactation. There were no changes in body weight and viability of pups. Also, no morphological abnormalities of pups were found except with one dead pup in the 80 mg/kg group, the malformation, being are which is spontaneously observed in Sprague-Dawley rats.
In conclusion, the NOEL for systemic toxicity is considered to be 5 mg/kg/day in male and female rats, and that for reproductive and developmental toxicity is 80 mg/kg/day.
| Purity | : | 99.53 % |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD(SD)IGS |
| Test method | : | OECD Test Guideline 421 |
| Route | : | Oral(gavage) |
| Doses | : | 0(vehicle), 5, 20, 80 mg/kg/day |
| Number of animals/group | : | Males, 13; females, 13 |
| Vehicle | : | Corn oil |
| Administration period | : | Males, 42 days Females, from 14 days before mating to day 3 of lactation |
| Terminal kill | : | Males, day 43 of administration Females, day 4 of lactation |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
| 1) | The test was performed by the Hatano Research Institute, Food and Drug Safety Center, 729-5 Ochiai, Hadano, Kanagawa, 257-8523, Japan. Tel +81-463-82-4751 Fax +81-463-82-9627 |