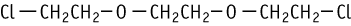
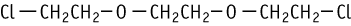
A repeated dose oral toxicity test was conducted at doses of 0, 50, 100, and 200 mg/kg/day using male and female rats. One male receiving 200 mg/kg was found dead and another male receiving the same dose was moribund at the termination of the administration period. Salivation was observed in both sexes in the treatment groups but it disappeared during the recovery period. Therefore, salivation was considered to be a conditional reflex to administration of the test substance. Decreased spontaneous motor activity, wasting, piloerection, dirty hair, and abnormal respiratory noises were observed in animals which died or were moribund receiving 200 mg/kg.
A functional observation battery revealed salivation in both sexes in the treatment groups but this was not considered to be a sign of neurotoxicity.
The serum levels of ALT activity and potassium concentration were elevated and the sodium concentration was depressed in males receiving 200 mg/kg as compared to control values.
The relative liver weights in females receiving 100 and 200 mg/kg were higher than in the controls.
Histopathological evaluation revealed degeneration of myocardium and necrosis in the hearts in both sexes receiving 200 mg/kg but these findings disappeared in the recovery period.
The NOEL for the repeated dose oral toxicity test is considered to be 100 mg/kg/day for males and 50 mg/kg/day for females.
Genotoxicity of 1,2-bis(2-chloroethoxy)ethane was studied by a reverse mutation test in bacteria. This substance was mutagenic in Salmonella typhimurium TA1535, with and without an exogenous metabolic activation system.
Genotoxicity of 1, 2-bis(2-chloroethoxy)ethane was studied by chromosomal aberration test in cultured Chinese hamster lung (CHL/IU) cells.
1, 2-Bis(2-chloroethoxy)ethane induced structural chromosomal aberrations in the metabolic activation system. Statistically significant increase in polyploid cells, was observed in the absence of S9 mix, but it was judged to be negative biologically because of the low incidence (1.5 %).
| Purity | : | 99.7 % |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD(SD)IGS |
| Test method | : | OECD Test Guideline 401 |
| Route | : | Oral (Gavage) |
| Dosage | : | 0 (Vehicle), 180, 270, 400, 600 mg/kg/day |
| Number of animals/group | : | Males and females; 5 |
| Vehicle | : | Corn oil |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
| Purity | : | 99.7 % |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD(SD)IGS |
| Test method | : | Guideline for 28-Day Repeated Dose Toxicity Test in Mammalian Species (Chemical Substances Control Law of Japan) |
| Route | : | Oral (Gavage) |
| Dosage | : | 0 (Vehicle), 50 100, 200 mg/kg/day |
| Number of animals/group | : | Males and females; 5 |
| Vehicle | : | Corn oil |
| Administration period | : | Males and females; 28 days |
| Terminal killing | : | Males and females, days 29 or 43 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
A functional observation battery revealed salivation in both sexes in the treatment groups but this was not considered to be a sign of neurotoxicity.
The serum levels of ALT activity and potassium concentration were elevated and the sodium concentration was depressed in males receiving 200 mg/kg as compared to the control values. The relative liver weights in female receiving 100 and 200 mg/kg were higher than in the controls.
Histopathological evaluation revealed degeneration of myocardium and necrosis of hearts in both sexes receiving 200 mg/kg but these findings disappeared in the recovery period.
The NOEL for the repeated dose oral toxicity test is considered to be 100 mg/kg/day for males and 50 mg/kg/day for females.
| Purity | : | 99.7 % |
| Test species/strains | : | Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537, Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Chemical Substances Control Law of Japan) and OECD Test Guideline 471 |
| Procedures | : | Pre-incubation method |
| Solvent | : | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix; 2-(2-Furyl)-3-(5-nitro-2-furyl)acrylamide (TA100, TA98, WP2 uvrA), Sodium azide (TA1535) and 9-Amino-acridine (TA1537) +S9 mix; 2-Aminoanthracene (five strains) |
| Dosage | : | -S9 mix; 0, 313, 625, 1250, 2500, 5000 μg/plate (five strains) +S9 mix; 0, 313, 625, 1250, 2500, 5000 μg/plate (five strains) |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavon |
| Plates/test | : | 3 (1 for the cytotoxicity test) |
| Number of replicates | : | 2 (plus 1 cytotoxicity test) |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
Genetic effects:
Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA98, TA1537
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
Salmonella typhimurium TA1535
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [*] | [ ] | [ ] |
| With metabolic activation: | [*] | [ ] | [ ] |
Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| Purity | : | 99.7 % |
| Type of cell used | : | Chinese hamster lung (CHL/IU) cells |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Chemical Substances Control Law of Japan) and OECD Test Guideline 473 |
| Solvent | : | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix; Mitomycin C +S9 mix; Cyclophosphamide |
| Dosage | : | -S9 mix (short-term treatment); 0, 0.48, 0.95, 1.9 mg/mL +S9 mix (short-term treatment); 0, 0.015, 0.030, 0.060 mg/mL |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
| Lowest concentration producing cytogenetic effects in vitro | : | ||
| With metabolic activation (short-term treatment) | : | 0.060 mg/mL | |
Genotoxic effects:
| clastogenicity | polyploidy | |||||
| + | ? | - | + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| 1) | The tests were conducted at the Biosafety Research Center, Foods, Drugs and Pesticides(An-Pyo Center), 582-2, Arahama Shioshinden Fukude-Cho Iwata-Gun, Shizuoka 437-1213, Japan. Tel +81-538-58-1266, Fax +81-538-58-1393 |
| 2) | The tests were performed by the Hatano Research Institute, Food and Drug Safety Center, 729-5 Ochiai, Hadano-shi, Kanagawa, 257-8523, Japan. Tel +81-463-82-4751 Fax +81-463-82-9627 |