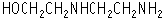
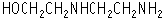
N-(Aminoethyl)ethanolamine was studied for oral toxicity in rats in a 28-day repeat dose toxicity test at doses of 0, 60, 250 and 1000 mg/kg/day.
In the repeat dose test, laboratory examinations revealed an increase in urinary protein in females given 250 mg/kg and in both sexes given 1000 mg/kg, an increase in the specific gravity of the urine in females given 250 or 1000 mg/kg, a decrease in urinary volume in females given 1000 mg/kg, a decrease in hemoglobin in both sexes given 1000 mg/kg, an increase in GOT in males given 250 and 1000 mg/kg, a decrease in total cholesterol in females given 1000 mg/kg and a decrease in chloride in males given 1000 mg/kg. The kidney weights were increased in both sexes given 1000 mg/kg and histopathologically, deposition of amphophilic bodies and swelling were noted in the renal proximal tubules in males given 250 mg/kg and in both sexes given 1000 mg/kg. In the stomach, mucosal thickening at the limiting ridge was noted in both sexes given 250 and 1000 mg/kg. Compound-related changes disappeared except for those in the kidney and stomach after a 14-day recovery period. The NOEL is considered to be 60 mg/kg/day for both sexes.
N-(Aminoethyl)ethanolamine induced polyploidy (0.88-4.00%) without an exogenous metabolic activation system. Structural chromosomal aberrations were not induce under the present experimental conditions.
N-(Aminoethyl)ethanolamine did not induce micronuclei in bone marrow cells of male and female mice.
| Purity | : | 99.9 % |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD (SD) |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for 28-Day Repeat Dose Toxicity Test of Chemicals (Japan) |
| Route | : | Oral (gavage) |
| Doses | : | 0 (vehicle), 60, 250, 1000 mg/kg/day |
| Number of animals/group | : | Male, 6; female, 6 |
| Vehicle | : | Water for injection |
| Administration period | : | Male and female, 28 days |
| Terminal kill | : | Days 29 or 43 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
Compound-related changes disappeared except for those in the kidney and stomach after a 14-day recovery period. The NOEL is considered to be 60 mg/kg/day for both males and females under the conditions of the present study.
| Purity | : | more than 99.9% |
| Type of cell used | : | Chinese hamster lung (CHL/IU) cells |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan) |
| Solvent | : | Water for injection |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix, Mitomycin C
+S9 mix, Cyclophosphamide |
| Doses | : | -S9 mix (continuous treatment): 0, 0.25, 0.50, 1.0 mg/ml
-S9 mix (short-term treatment): 0, 0.25, 0.50, 1.0 mg/ml +S9 mix (short-term treatment): 0, 0.25, 0.50, 1.0 mg/ml |
| S-9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
With the mid (0.50 mg/ml) and high (0.10 mg/ml) concentrations after 48 h continuous treatment, polyploidy was significantly increased (0.88 - 4.00%) with dose-dependency.
Lowest concentration producing cytogenetic effects in vitro:
without metabolic activation (continuous treatment ): 0.50 mg/ml (polyploidy)
Genotoxic effects:
| clastogenicity | polyploidy | |||||
| + | ? | - | + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| Purity | : | above 99.9% |
| Test species/strains | : | Mice/Crj:BDF1, male and female |
| Test methods | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan) and OECD (474) |
| Procedure | : | Bone marrow/acridine orange staining |
| Solvent | : | Water |
| Positive control | : | Cyclophosphamide 50 mg/kg |
| Doses | : | 0, 500, 1000 and 2000 mg/kg |
| Mice/group | : | 5 males and females |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Genetoxic effect:
| + | ? | - | |
| Micronucleus test: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| 1) | The tests were performed by Bozo Research Center Inc, 1284, Kamado, Gotemba-shi, Shizuoka, 412, Japan. Tel +81-550-82-2000 Fax +81-550-82-2379 |
| 2) | The tests were performed by the Hatano Research Institute, Food and Drug Safety Center, 729-5 Ochiai, Hadano-shi, Kanagawa, 257, Japan. Tel +81-463-82-4751 Fax +81-463-82-9627 |