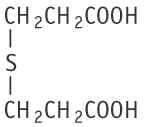
Molecular formula: C6H10O4S Molecular weight: 178.21
3,3'-Thiobispropionic acid was studied for oral toxicity in rats according to the OECD Test Guideline 421 at doses of 0, 100, 300, and 1000 mg/kg/day.
In the repeated dose oral toxicity test, 1 male and 2 female rats receiving 1000 mg/kg were found dead. Body weight gain and food consumption in females receiving 1000 mg/kg also tended to be lower than in the control group. Histological evaluation demonstrated testicular lesions in males receiving 300 mg/kg or more.
The NOELs for repeated dose oral toxicity are considered to be 100 mg/kg/day for males, and 300 mg/kg/day for females.
With regard to reproductive/developmental toxicity, infertility was observed in 2 pairs and 1 pair in the control and 300 mg/kg groups, respectively. With 300 mg/kg, a treatment-related effect on male fertility was suggested, because lesions in some reproductive organs were observed on histological evaluation of males. The test substance did not demonstrate any adverse effects on other relevant parameters.
The NOELs for reproductive and developmental toxicity test are considered to be 100 mg/kg/day for males, and 1000 mg/kg/day for females and offspring.
| Purity | : | 99.4 % |
| Test species/strains | : | Rat/Crj:CD(SD)IGS |
| Test method | : | OECD Test Guideline 421 |
| Route | : | Oral(gavage) |
| Dosage | : | 0(vehicle), 100, 300, 1000 mg/kg/day |
| Number of animals/group | : | Males, 12; females, 12 |
| Vehicle | : | 0.5 % Sodium carboxymethylcellulose solution |
| Administration period | : | Males, 52 days Females, from 14 days before mating to day 4 of lactation |
| Terminal killing | : | Males, day 53 Females, day 4 of lactation |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
One male and 2 females receiving 1000 mg/kg were found dead. There were no treatment-related clinical signs observed in either sex.
There were no treatment-related effects on body weights, body weight gain, or food consumption in males. Body weight gain and food consumption in females receiving 1000 mg/kg tended to be lower than those in the control group, indicating effects of the test substance. Atrophy of seminiferous tubules in the testis and dilatation of prostate glands were slightly increased in the 1000 mg/kg group, but without significance. Testicular lesions were also observed in the group receiving 300 mg/kg. Testicular and epididymal lesions were considered to be treatment-related, because there were no such lesions in the control group. There were no treatment-related lesions detected on histological evaluation in females.
The NOELs for the repeated dose oral toxicity test are considered 100 mg/kg/day for males, and 300 mg/kg/day for females.
<Reproductive and developmental toxicity>
There were no adverse effects observed on the estrus cycle, copulation, delivery conditions, gestation length, number of corpora lutea or implantations, sex ratio, implantation index, gestation index, live birth index, or delivery index. One pair in the 300 mg/kg group demonstrated infertility. Lesions in the testis on histological evaluation were observed in this infertile male. It was suggested that there was a treatment-related effect on male fertility, because lesions in reproductive organs were observed on histopathological evaluation of males receiving 300 mg/kg or more.
There were no treatment-related abnormal findings noted on external observation, clinical signs, viability, growth, or necropsy of the offspring.
The NOELs for reproductive and developmental toxicity test are considered to be 100 mg/kg/day for males, and 1000 mg/kg/day for females and offspring.
| 1) | The test was performed by the Biosafety Research Center, Foods, Drugs and Pesticides(An-Pyo Center), 582-2 Arahama, Shioshinden, Fukude-Cho, Iwata-Gun, Shizuoka 437-1213, Japan. Tel +81-538-58-1266, Fax +81-538-58-1393. |