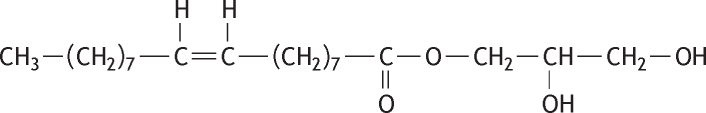
Molecular formula: C21H40O4 Molecular weight: 356.54
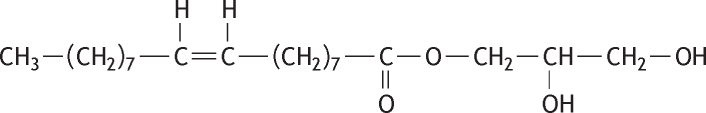
A single dose oral toxicity test of 2,3-dihydroxypropyl 9-cis-octadecenoate in rats allowed classification of the chemical into category 5 of the GHS regarding acute toxicity. There were no abnormalities in general condition, body weight or gross pathological findings in any animal.
2,3-Dihydroxypropyl 9-cis-octadecenoate was studied for oral toxicity in the OECD Combined Repeated Dose and Reproductive/Developmental Toxicity Screening Test at doses of 0, 100, 300 and 1000 mg/kg/day.
With regard to repeated toxicity, there were no changes attributable to administration of the test substance on observation of general condition, or for detailed clinical signs in the FOB, responses in the sensory/reflex function test, landing foot splay, grip strength, motor activity, body weights, food consumption, urinalysis (male only), hematological examination, blood biochemical examination, necropsy, organ weights and histopathological examination.
From these results, the NOAELs for repeated dose toxicity are considered to be 1000 mg/kg/day or more for parental animals of both sexes.
The male and female parental animals exhibited no alteration in reproductive parameters. On examination of neonates, there were no alterations in developmental parameters.
The NOAELs for reproductive/developmental toxicity are therefore considered to be 1000 mg/kg/day or more for reproductive performance of male parental animals, female parental animals and for offspring development.
Reverse mutation tests using microorganisms (Salmonella typhimurium, Escherichia coli) were conducted to assess the potential of 2,3-dihydroxypropyl 9-cis-octadecenoate to induce gene mutations.
2,3-Dihydroxypropyl 9-cis-octadecenoate did not induce gene mutations in bacteria under the conditions of this study.
In vitro chromosomal aberration tests using cultured Chinese hamster cells (CHL/IU) were conducted to assess the potential of 2,3-dihydroxypropyl 9-cis-octadecenoate to induce chromosomal aberrations.
2,3-Dihydroxypropyl 9-cis-octadecenoate did not induce chromosomal aberrations in cultured cells under the conditions of this study.
| Purity | : | 99.93 % |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD(SD)IGS |
| Test method | : | OECD Test Guideline 423 |
| Route | : | Oral(gavage) |
| Doses | : | 2000 mg/kg |
| Number of animals/group | : | Females, 3 |
| Vehicle | : | Corn oil |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
| Purity | : | 99.7 % |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD(SD)IGS |
| Test method | : | OECD Test Guideline 422 |
| Route | : | Oral(gavage) |
| Dosage | : | 0(vehicle), 100, 300, 1000 mg/kg/day |
| Number of animals/group | : | Males, 12; females, 12(satellite group for recovery of females: 0 mg/kg/day, 5; 1000 mg/kg/day, 5) |
| Vehicle | : | Corn oil |
| Administration period | : |
Males, 42 days |
| Terminal killing | : |
Males, day 43 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
Through the administration and recovery periods, there were no changes attributable to administration of the test substance.
<Reproductive and developmental toxicity>
The male and female parental animals exhibited no alteration in reproductive parameters. On examination of neonates, there were no alterations in developmental parameters.
The NOAELs for reproductive/developmental toxicity are considered to be 1000 mg/kg/day or more for reproductive performance of male and female parental animals and for offspring development.
| Purity | : | 99.93 % |
| Test species/strains | : | Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537, Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Chemical Substances Control Law of Japan) and OECD Test Guideline 471 |
| Procedures | : | Pre-incubation method |
| Solvent | : | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix; 2-(2-Furyl)-3-(5-nitro-2-furyl)acrylamide (TA100, TA98, WP2 uvrA),
sodium azide (TA1535) and 9-aminoacridine hydrochloride (TA1537) +S9 mix; 2-Aminoanthracene (all strains) |
| Dosage | : | [Dose-finding study] -S9 mix; 0, 8.19, 20.5, 51.2, 128, 320, 800, 2000, 5000 μg/plate (all strains) +S9 mix; 0, 8.19, 20.5, 51.2, 128, 320, 800, 2000, 5000 μg/plate (all strains) [Dose-finding restudy] -S9 mix; 0, 8.19, 20.5, 51.2, 128, 320, 800, 2000, 5000 μg/plate (all strains) +S9 mix; 0, 8.19, 20.5, 51.2, 128, 320, 800, 2000, 5000 μg/plate (all strains) [Dose-finding additional study] -S9 mix; 0, 6.25, 12.5, 25.0, 50.0, 100, 200 μg/plate (TA100), 0, 3.13, 6.25, 12.5, 25.0, 50.0, 100 μg/plate (TA98), 0, 0.0977, 0.195, 0.391, 0.781, 1.56, 3.13, 6.25, 12.5 μg/plate (TA1537) +S9 mix; 0, 6.25, 12.5, 25.0, 50.0, 100, 200 μg/plate (TA1537) [Main study] -S9 mix; 0, 4.88, 9.77, 19.5, 39.1, 78.1, 156 μg/plate (TA100, TA98), 0, 156, 313, 625, 1250, 2500, 5000 μg/plate (TA1535, WP2 uvrA), 0, 0.153, 0.305, 0.610, 1.22, 2.44, 4.88, 9.77 μg/ plate (TA1537) +S9 mix; 0, 9.77, 19.5, 39.1, 78.1, 156, 313, 625 μg/plate (TA100), 0, 156, 313, 625, 1250, 2500, 5000 μg/plate (TA1535, WP2 uvrA, TA98), 0, 9.77, 19.5, 39.1, 78.1, 156, 313 μg/plate (TA1537) |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 3 |
| Number of replicates | : | 4 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
No increase in revertant colonies was observed in the test with either the non-activation method (-S9 mix) or the activation method (+S9 mix).
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| Purity | : | 99.93 % |
| Type of cell used | : | Chinese hamster lung (CHL/IU) cells |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Chemical Substances Control Law of Japan) and OECD Test Guideline 473 |
| Solvent | : | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix; Mitomycin C +S9 mix; Cyclophosphamide |
| Dosage | : | -S9 mix (short-term treatment); 0, 891, 1783, 3565 μg/mL +S9 mix (short-term treatment); 0, 891, 1783, 3565 μg/mL -S9 mix (continuous treatment); 0, 55.7, 111, 223 μg/mL |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
No increase in chromosomal aberrations was observed with either the short-term treatment (-S9 mix and +S9 mix) or the continuous treatment.
| clastogenicity | polyploidy | |||||
| + | ? | - | + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| 1) | The test was performed by Bozo Research Center Inc, 1284, Kamado, Gotemba-shi, Shizuoka, 412-0039, Japan. Tel +81-550-82-2000, Fax +81-550-82-2379 |
| 2) | The test was performed by the Research Institute for Animal Science in Biochemistry and Toxicology, 3-7-11 Hashimotodai, Sagamihara-shi, Kanagawa, 229-1132, Japan, Tel +81-42-762-2775, FAX +81-42-762-7979 |
| 3) | The tests were performed by the Biosafety Research Center, Foods, Drugs and Pesticides(An-pyo Center), 582-2 Shioshinden, Iwata-shi, Shizuoka, 437-1213, Japan. Tel +81-538-58-1266, Fax +81-538-58-1393 |