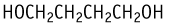
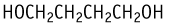
1,4-Butanediol was studied for oral toxicity in rats in an OECD combined repeat dose and reproductive/developmental toxicity screening test at doses of 0, 200, 400 and 800 mg/kg/day.
Acute and transient signs of CNS toxicity were observed after daily administration of 1,4-butanediol in both sexes, the severity increasing with the dosage. At 200 mg/kg hyperactivity was observed. At 400 mg/kg, activity was rather suppressed, although hyperactivity was also observed after a few doses. At 800 mg/kg, severe toxic signs were observed and some animals became even comatose following hypoactivity. By 5 hours after dosing these signs disappeared and animals recovered to normal. Body weight gains were suppressed at 400 and 800 mg/kg during the early period of administration. While weight gain was not further suppressed thereafter, the difference in body weight produced during the early period persisted until the termination. Food consumption also decreased accordingly. At terminal necropsy, no compound-related lesions were apparent macroscopically. On histopathological examination, diffuse transitional epithelial hyperplasia and fibrosis in the lamina propria of the urinary bladder were observed in the 400 and 800 mg/kg groups. Neither the pup viability nor the incidence of morphological abnormalities was changed by administration of the compound, although pup body weights were slightly but significantly decreased in the 800 mg/kg group.
From the results of the test, NOELs of 1,4-butanediol when orally given to parental rats for reproduction and development of offspring are 200 and 400 mg/kg, respectively.
| Purity | : | 98.0 % |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD |
| Test method | : | OECD Combined Repeat Dose and Reproductive/Developmental Toxicity Screening Test |
| Route | : | Oral (gavage) |
| Doses | : | 0(vehicle), 200, 400, 800 mg/kg/day |
| Number of animals/group | : | Males, 13; females, 13 |
| Vehicle | : | Distilled water |
| Administration period | : | Males, 42 days Females, from 14 days prior to mating to day 3 of lactation |
| Terminal killing | : | Males, day 43 Females, day 4 of lactation |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
Animals given 200 mg/kg demonstrated hyperactivity, which subsided in several minutes. At 400 mg/kg, the animals showed hyperactivity, and then hypoactivity, some being recumbent. In the 800 mg/kg group, animals showed hyperactivity and then hypoactivity, with, some animals even becoming comatose. Furthermore, at 800 mg/kg, six males and seven females demonstrated exophthalmos at the 5th week and late pregnancy, respectively. Food consumption of males and females given 400 and 800 mg/kg was significantly lower than that of the controls almost through out the treatment period. Body weight gain of males given 400 and 800 mg/kg was significantly lower than that of the controls during the first week. Body weight gain of females given 800 mg/kg during pre-mating period was also significantly lower than that of the controls. Although body weight gain of administered 1,4-butanediol groups during pregnancy was significantly lower than in the controls, the values did not correlate with the dosage levels. Hematological examination revealed decreases in hemoglobin and hematocrit in males given 800 mg/kg, and in hemoglobin in males receiving 400 mg/kg. The average number of white blood cells in 200 and 400 mg/kg males were significantly lower than those of controls. With regard to clinical chemistry, blood glucose concentrations of dosed males were significantly lower than that of controls. Blood inorganic phosphate and blood potassium concentrations of 200 mg/kg and 800 mg/kg males were significantly higher and lower than those of controls, respectively. The absolute liver weights of 400 and 800 mg/kg males and females were significantly lower than those of controls, while the relative liver weights were significantly lower only in 800 mg/kg males. Although the absolute kidney weights of males and females given 800 mg/kg were significantly lower than those of controls, the relative weights were similar. The relative testis weights of 800 mg/kg males were significantly greater than that of controls. On histopathological examination, the principal lesions associated with the administration occurred in the urinary bladder. Diffuse epithelial hyperplasia was seen seven males and three females given 800 mg/kg, and fibrosis in the lamina propria was apparent in twelve males and females, being absent in the controls.
The no effect dose levels (NOELs) for repeat dose toxicity are considered to be less than 200 mg/kg for both sexes. However, NOAELs are considered to be 200 mg/kg for both sexes.
<Reproductive and developmental toxicity>
The compound showed no effects on mating and fertility in dosed animals, and viability and morphogenesis in pups. The body weights of pups of 800 mg/kg on day 4 of lactation were slightly but significantly lower than those of controls.
The NOEL for reproductive and developmental toxicity is considered to be 400 mg/kg in males, females and offspring.
| 1) | The tests were performed by the Hatano Research Institute, Food and Drug Safety Center, 729-5 Ochiai, Hadano-shi, Kanagawa, 257-8523, Japan. Tel +81-463-82-4751 Fax +81-463-82-9627 |