
On hematological examination, the prothrombin time was significantly shortened in females given 20 mg/kg or more, while the activated partial thromboplastin time was prolonged in both sexes given 500 mg/kg. On histopathological examination, hyaline droplet and eosinophilic body depositions and epithelial regeneration were observed in the renal tubules of males given 20 mg/kg or more. The change in female kidneys at 100 mg/kg was characterized by dilated glomerular capillaries. The test compound also exerted some effects on the liver, adrenal glands and small intestine of both sexes given 100 and/or 500 mg/kg, with blood chemical changes which were indicative of hepatic dysfunction, an increase in liver weights, hepatocellular swelling, vacuolation of adrenocortical cells and epithelial vacuolation of the intestinal mucosa. The NOEL for repeat dose toxicity is considered to be 4 mg/kg/day for both sexes.
1,4-Dibromobenzene was not mutagenic in Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA98, TA1535, TA1537 and Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA. In the presence of an exogenous metabolic activation system, this chemical substance induced structural chromosomal aberrations in CHL/IU cells. Polyploid cells were not induced under the experimental conditions.
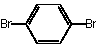
| Purity | : | 99.9% |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD (SD) |
| Test method | : | Guideline for 28-Day Repeat Dose Toxicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan) |
| Route | : | Oral (gavage) |
| Dosage | : | 0 (vehicle), 4, 20, 100 and 500mg/kg/day |
| Number of animals | : | Male, 6; female, 6/group |
| Vehicle | : | Sesame oil |
| Administration period | : | Male and female, 28 days |
| Terminal kill | : | Male and female, days 29 or 43 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
The NOEL for repeat dose toxicity is considered to be 4 mg/kg/day for both sexes.
| Purity | : | 99.9% |
| Test species/strains | : | S.typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537 E. coli WP2 uvrA |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan) |
| Procedures | : | Plate incorporation method |
| Solvent | : | Acetone |
| Positive controls | : | -S9, AF-2 (TA100, WP2, TA98), sodium azide (TA1535) and 9-aminoacridine (TA1537) +S9, 2-aminoanthracene (all strains) |
| Dosage | : | without metabolic activation 0, 6.3, 12.5, 25, 50, 100, 200, 400 μg/plate (TA1535, TA98, WP2, TA1357), 0, 1.6, 3.1, 6.3, 12.5, 25, 50, 100, 200, 400 μg/plate (TA100) metabolic activation method 0, 12.5, 25, 50, 100, 200, 400, 800 μg/plate (TA1535, TA98, WP2, TA1357), 0, 1.6, 3.1, 6.3, 12.5, 25, 50, 100, 200, 400, 800 μg/plate (TA100) |
| S-9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 3 |
| Number of replicates | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Genetic effects:
S. typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA 98, TA1537
| + | ? | - | |
| with metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
E. coli WP2 uvrA
| with metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| Purity | : | 99.9% |
| Type of cell used | : | Chinese hamster CHL/IU cells |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan) |
| Solvent | : | 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose sodium |
| Positive controls | : | -S9, Mitomycin C +S9, Cyclophosphamide |
| Dosage | : | -S9 (continuous treatment): 0, 0.3, 0.6, 1.2 mg/ml -S9 (short-term treatment): 0, 0.6, 1.1, 2.2 mg/ml +S9 (short-term treatment): 0, 0.6, 1.1, 2.2 mg/ml |
| S-9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
| clastogenicity | polyploidy | |||||
| + | ? | - | + | ? | - | |
| without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| with metabolic activation: | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| 1) | The tests were performed by the Research Institute for Animal Science in Biochemistry and Toxicology, 3-7-11 Hashimotodai, Sagamihara-shi, Kanagawa 229, Japan. Tel 81-427-62-2775 Fax 81-427-62-7979 |
| 2) | The tests were performed by the Hatano Research Institute, Food and Drug Safety Center, 729-5 Ochiai, Hadano-shi, Kanagawa 257, Japan. Tel +81-463-82-4751 Fax +81-463-82-9627 |