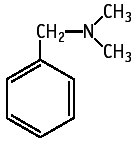

N,N-Dimethylbenzylamine was studied for oral toxicity in a 28 day repeat dose toxicity test. Mortalities of both males and females receiving 400 mg/kg were observed from week 2. Clinical observation revealed miosis in both sexes receiving 100 mg/kg and miosis and salivation in those receiving 200 and 400 mg/kg. Body weight gain was suppressed in males receiving 400 mg/kg. Slight increases in total cholesterol were observed in males receiving 200 mg/kg. Pathological examination revealed no abnormalities attributable to the test substance treatment. The NOEL for repeat dose toxicity is considered to be 50 mg/kg/day for both sexes.
N,N-Dimethylbenzylamine was not mutagenic to Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537 and Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA, with or without an exogeneous metabolic activation system.
N,N-Dimethylbenzylamine induced structural chromosomal aberrations with an exogeneous metabolic activation system.
| Purity | : | 99.93wt% |
| Test species/strain | : | Rats/Crj:CD (SD) |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for 28-day Repeat Dose Toxicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan) |
| Route | : | Oral (gavage) |
| Doses | : | 0 (vehicle), 50, 100, 200, 400 mg/kg/day |
| Number of animals | : | Males, 5; females, 5/group |
| Vehicle | : | Corn oil |
| Administration period | : | Males and females, 28 days |
| Terminal kill | : | Males and females, Days 29 or 43 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
Hematological testing revealed a decreased white blood cell count in the one male receiving 400 mg/kg which survived until the termination of the dosing. No other findings attributable to test substance were observed at the termination of the dosing and recovery periods. Blood chemistry revealed an elevated total cholesterol in males receiving 200 mg/kg. After the recovery period, the A/G ratio was decreased in males receiving 200 mg/kg. Urinalysis revealed slight increases in urine volume in males receiving 100, 200 and 400 mg/kg and females receiving 200 mg/kg.
Organ weight analyses revealed increases in absolute spleen weights in males receiving 200 mg/kg and absolute and relative liver weights in females receiving 200 mg/kg. Slight decreases in absolute spleen weights and absolute and relative thymus weights were noted in males receiving 400 mg/kg. Increases in absolute and relative adrenal gland weights were observed at the termination of recovery period in males receiving 200 mg/kg. Moreover, slight increase in absolute adrenal glands weights and slight decrease in absolute testis weights were also noted in males receiving 400 mg/kg. Pathological examination revealed no abnormalities attributable to the test substance in animals which were scheduled to be sacrificed at the termination of dosing. In dead animals, inclusion bodies in hepatocytes were observed in both sexes and degeneration of the adrenal gland cortex was observed in females.
The NOEL for repeat dose toxicity is considered to be 50 mg/kg/day for both sexes.
| Purity | : | 99.93 wt% |
| Test species/strains | : | S. typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537, E. coli WP2 uvrA |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan) |
| Procedures | : | Pre-incubation method |
| Solvent | : | DMSO |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix; AF-2 (TA100, TA98 and WP2 uvrA), Sodium azide (TA1535) and 9-Aminoacridine (TA1537) +S9 mix; 2-Aminoanthracene (all strains) |
| Doses | : | -S9 mix; 78.1, 156, 313, 625, 1250, 2500 and 5000 μg/plate (TA100) 156, 313, 625, 1250, 2500 and 5000 μg/plate (WP2 uvrA and TA98) 39.1, 78.1, 156, 313, 625, 1250, 2500 and 5000 μg/plate (TA1535 and TA1537) +S9 mix; 156, 313, 625, 1250, 2500 and 5000 μg/plate (all strains) |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 3 |
| Number of replicates | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
Genetic effects:
S. typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98 and TA1537
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
E. coli WP2 uvrA
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| Purity | : | 99.93 wt% |
| Type of cell used | : | Chinese hamster lung (CHL) cells |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Japan) |
| Solvent | : | DMSO |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix, Mitomycin C +S9 mix, Cyclophosphamide |
| Doses | : | -S9 mix (continuous exposure): 0, 75.0, 150, 300 μg/ml -S9 mix (short-term exposure): 0, 375, 750, 1500 μg/ml +S9 mix (short-term exposure): 0, 188, 375, 750 μg/ml |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
Lowest concentration producing cytogenetic effects in vitro:
With methabolic activation (+S9 mix): 0.213mg/ml (clastgenicity)
Genetic effects:
| clastogenicity | polyploidy | |||||
| + | ? | - | + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| 1) | The tests were performed by the Biosafety Research Center, Foods, Drugs and Pesticides (An-pyo Center), Japan, 582-2 Shioshinden Arahama, Fukude-cho, Iwata-gun, Shizuoka, 437-12, Japan. Tel +81-538-58-1266 Fax +81-538-58-1393 |