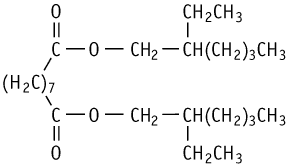

A combined repeat dose and reproductive/developmental toxicity screening test of bis(2-ethylhexyl) azelate was conducted in rats according to the OECD Test Guideline 422. Oral administration of the compound at doses of 0, 100, 300 and 1000 mg/kg did not cause death or a moribund condition in any animals, and no apparent changes were observed in general condition, scores of detailed clinical observations, and findings of functional observation after the final treatment. With 1000 mg/kg, bis(2-ethylhexyl) azelate suppressed male body weight gain, increased the A/G ratio slightly in both male and female animals, and reduced concentrations of total protein and calcium in the females. In addition, the treatment increased either absolute or relative liver and kidney weights in both sexes. Histopathological examination revealed hypertrophy of the centrilobular hepatocytes and reduction in the occurrence of periportal fatty change in the male livers.
While the treatment did not affect ovulation, mating performance, implantation, or delivery and lactational conditions at any dose level, intervals of estrous cycle in the 1000 mg/kg-treated group became longer than in the control. No adverse effects of the compound were observed on viability, morphology and growth of offspring. The NOEL for repeat dose toxicity of bis (2-ethylhexyl) azelate is considered to be 300 mg/kg/day in both sexes of animals. That for reproductive/ developmental toxicity is considered to be 300 mg/kg/day for females and 1000 mg/kg/day for males. The NOEL for offspring is considered to be 1000 mg/kg/day.
The mutagenic potential of bis(2-ethylhexyl) azelate was examined with a reverse mutation test in bacteria. Bis(2-ethylhexyl) azelate did not induce gene mutations in the bacteria under the conditions of this study.
Genotoxicity of bis(2-ethylhexyl) azelate was studied by a chromosomal aberration test in cultured Chinese hamster lung (CHL/IU) cells. Bis(2-ethylhexyl) azelate did not induce chromosomal aberrations under the conditions of this study.
| Purity | : | 77.2 % |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD(SD)IGS |
| Test method | : | OECD Test Guideline 401 |
| Route | : | Oral (Gavage) |
| Dosage | : | 0, 2000 mg/kg |
| Number of animals/group | : | Males, 5; females, 5 |
| Vehicle | : | Corn oil |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
Under the present study conditions, it was concluded that a single oral treatment of 2000 mg/kg of bis(2-ethylhexyl)azelate had no effect on the male and female rats.
| Purity | : | 77.2 % |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD(SD)IGS |
| Test method | : | OECD Test Guideline 422 |
| Route | : | Oral(Gavage) |
| Dosage | : | 0, 100, 300, 1000 mg/kg |
| Number of animals/group | : | Males, 13; females, 13 |
| Vehicle | : | Corn oil |
| Administration period | : | Males, 42 days Females, from 14 days before mating to day 4 of lactation |
| Terminal killing | : | Males, day 43 Females, day 5 of lactation Offspring, 4 days after birth |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
Neither death nor a moribund condition were observed in either sex of animal. No changes caused by the compound treatment were observed on general clinical observation, nor were scores obtained by detailed clinical observations different between control and compound-treated groups. No animals showed abnormalities in functional observations after the final treatment. Whereas body weight gain was suppressed in males of the 1000 mg/kg-treated group, their food consumption was not affected by the treatment. Hematological examination showed no effects of the compound in any groups. On biochemical analysis, 1000 mg/kg of the compound was found to increase the A/G ratio slightly in male and female animals, and reduce concentrations of total protein and calcium in the females. Furthermore, the treatment increased either absolute or relative weights of the liver and kidneys in the males and females. In addition, histopathological examination revealed hypertrophy of centrilobular hepatocytes and a reduction in the grade of periportal fatty change in the males of the 1000 mg/kg-treated group.
<Reproductive/developmental toxicity>
With 1000 mg/kg, the compound altered the estrous cycle, and increased intervals significantly as compared with the control cases. There were a few dams with an unusually small number of implantation sites, newborn, or live newborn in the 1000 mg/kg-treated group, but, significant differences were not observed from the control values. No effects of the treatment were found on the copulation and fertility indices, the mean frequency of vaginal estrus during the mating period and pairing days until copulation. The compound did not cause abnormal delivery or lactational conditions. All of the pregnant females delivered live fetuses. The number of live pups on day 4 of lactation, sex ratios on days 0 and 4 of lactation, and the viability index of pups on day 4 of lactation were not affected by the treatment. The treatment did not affect growth or morphology of the offspring.
<Evaluation>
From the above results, the NOEL for repeat dose toxicity of bis(2-ethylhexyl)azelate is considered to be 300 mg/kg/day for both sexes of animals. The NOEL for reproductive/ developmental toxicity is considered to be 300 mg/kg/day for females and 1000 mg/kg/day for males. That for offspring is considered to be 1000 mg/kg/day.
| Purity | : | 77.2 % |
| Test species/strains | : | Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537, Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Chemical SubstancesControl Law of Japan) and OECD Test Guideline 471 |
| Procedures | : | Pre-incubation method |
| Solvent | : | Absolute ethanol |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix; 2-(2-furyl)-3-(5-nitro-2-furyl)acrylamide (TA100, TA98, WP2 uvrA), Sodium azide (TA1535) and 9-Amino-Acridine (TA1537) +S9 mix; 2-Aminoanthracene (all strains) |
| Dosage | : | -S9 mix; 0, 312.5, 625, 1250, 2500, 5000 μg/plate (all strains) +S9 mix; 0, 312.5, 625, 1250, 2500, 5000 μg/plate (all strains) |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 3 |
| Number of replicates | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
Genotoxic effects:
Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
Escherichia coli WP2uvrA
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| Purity | : | 77.2 % |
| Type of cell used | : | Chinese hamster lung (CHL/IU) cells |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Chemical Substances Control Law of Japan) and OECD Test Guideline 473 |
| Solvent | : | Absolute ethanol |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix; Mitomycin C +S9 mix; Dimethylnitrosamine |
| Dosage | : | -S9 mix (6 hr short treatment method); 0, 150, 300, 600, 1200, 2400 μg/mL +S9 mix (6 hr short treatment method); 0, 150, 300, 600, 1200, 2400 μg/mL -S9 mix (24 hr continuous treatment method); 0, 37.5, 75, 150, 300, 600 μg/mL |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
Genotoxic effects:
| clastogenicity | polyploidy | |||||
| + | ? | - | + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| 1) | The tests were performed by the Hatano Research Institute, Food and Drug Safety Center, 729-5 Ochiai, Hadano-shi, Kanagawa, 257-8523, Japan. Tel +81-463-82-4751 Fax +81-463-82-9627 |
| 2) | The tests were performed by Nihon Bioresearch Inc., 6-104 Majima, Fukuju-cho, Hashima, Gifu, 501-6251, Japan. Tel +81-58-392-6222Fax +81-58-392-1284. |