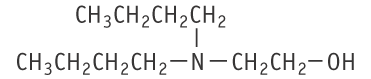
Molecular formula: C10H23NO Molecular weight: 173.30
2-(Di-n-butylamino)ethanol was studied in rats of both sexes with the OECD Test Guideline 407 for repeated dose 28-day oral toxicity study in rodents, at doses of 0, 25, 100 and 400 mg/kg.
Three males and 5 females died in the 400 mg/kg group. Intermittent cage-licking and chewing were observed in the 100 and 400 mg/kg groups. With 400 mg/kg, convulsions, twitching, tremors, vocalization, pale color of the skin, gasping, hypopnea, decrease in movement, adoption of a prone position and salivation were observed. In addition, bradycardia, reddish tears, exophthalmos and piloerection appeared in some animals of the 400 mg/kg group, together with a high frequency of ambulation in the motor activity test, depressed body weight gain in females and decreased food consumption in both sexes. Furthermore, with 400 mg/kg, plasma chloride levels were decreased in both sexes, the plasma sodium level was decreased in males, and cholesterol and glucose levels were increased and cholinesterase activity reduced in females. Pathological findings in the 400 mg/kg groups were as follows; increase in liver weights and kidney weights, centrilobular hypertrophy of hepatocytes and vacuolation of the epithelium in renal collecting tubules. Additionally, increase in adrenal gland weights and hypertrophy of the zona fasciculata were found in 400 mg/kg females. From these results, the NOELs are considered to be 25 mg/kg /day for males and females.
Genotoxicity of 2-(di-n-butylamino)ethanol was studied by a reverse mutation test in bacteria. This substance was not mutagenic in Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA98, TA1535, TA1537 or Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA, with or without an exogenous metabolic activation system.
2-(Di-n-butylamino)ethanol induced structural chromosomal aberrations and polyploidy in CHL/IU cells after short-term (6 hr) treatment, with and without metabolic activation.
| Purity | : | 99.8 % |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD(SD)IGS |
| Test method | : | OECD Test Guideline 407 |
| Route | : | Oral(gavage) |
| Dosage | : | 0(vehicle), 25, 100, 400 mg/kg/day |
| Number of animals/group | : | Males, 10; females, 10(0, 400 mg/kg) Males, 5; females, 5(25, 100 mg/kg) |
| Vehicle | : | Corn oil |
| Administration period | : | Males and females, 28 days |
| Terminal killing | : | Males, on day 29 and 43 Females, on day 29 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
Three males and 5 females died in the 400 mg/kg group. Clinical signs of intermittent cage-licking and chewing were observed in the 100 and 400 mg/kg groups. In the 400 mg/kg group, convulsions, twitching, tremors, vocalization, pale color of the skin, gasping, hypopnea, decrease in movement and adoption of a prone position were observed about 20 to 40 minutes after administration. In this group, salivation was also found from just after holding or administration and then disappeared. Besides, salivation was also apparent sporadically about 30 minuteses after administration. In addition, bradycardia, reddish tears, exophthalmos, piloerection, disappearance of withdrawal reflexes after convulsions and decreased exploration appeared on detailed clinical observation in some animals of the 400 mg/kg group. A high frequency of ambulation in the motor activity test was observed in the 400 mg/kg group for 60 minutes from 60 minutes after administration.
Depressed body weight gain in females and decreased food consumption by both sexes were apparent in the 400 mg/kg group, along with reduced plasma chloride levels in both sexes, and plasma sodium in males, while cholesterol and glucose levels were increased and cholinesterase activity reduced in females. Pathological findings in the 400 mg/kg group were as follows; increase in liver and kidney weights, centrilobular hypertrophy of hepatocytes, vacuolation of the epithelium in renal collecting tubules. Additionally, increase in adrenal gland weights and hypertrophy of zona fasciculata were found in females of the 400 mg/kg group.
From these results, the NOELs are considered to be 25 mg/kg/day for males and females.
| Purity | : | 99.8 % |
| Test species/strains | : | Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537, Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Chemical Substances Control Law of Japan) and OECD Test Guideline 471 |
| Procedures | : | Pre-incubation method |
| Solvent | : | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix; 2-(2-Furyl)-3-(5-nitro-2-furyl)acrylamide (TA100, TA98, WP2 uvrA), sodium azide (TA1535) and 9-aminoacridine (TA1537) +S9 mix; 2-Aminoanthracene (five strains) |
| Dosage | : | -S9 mix; 0, 156, 313, 625, 1250, 2500, 5000 μg/plate (five strains) +S9 mix; 0, 19.5, 39.1, 78.1, 156, 313, 625 μg/plate (five strains) |
| S9 | : |
Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 3 (1 for the cytotoxicity test) |
| Number of replicates | : | 2 (plus 1 for the cytotoxicity test) |
| GLP | : | Yes |
This chemical did not induce gene mutations in S. typhimurium TA100, TA98, TA1535, TA1537 or E. coli WP2 uvrA strains with or without S9 mix. Growth inhibition was observed at and above 2500 μg/plate in TA100, TA1535, TA98, and TA1537 and at 5000 μg/plate in WP2 uvrA without S9 mix, and above 500 μg/plate in all five strains with S9 mix.
Genetic effects:
Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA98, TA1535, TA1537
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| Purity | : | 99.8 % |
| Type of cell used | : | Chinese hamster lung (CHL/IU) cells |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Chemical Substances Control Law of Japan) and OECD Test Guideline 473 |
| Solvent | : | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix; Mitomycin C +S9 mix; Cyclophosphamide |
| Dosage | : | -S9 mix(short-term treatment); 0, 0.43, 0.85, 1.7 mg/mL +S9 mix(short-term treatment); 0, 0.16, 0.33, 0.65, 1.3 mg/mL |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 4 (2: chromosome specimens, 2: measurement of growth rate) |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Lowest concentration producing cytogenetic effects in vitro:
| Without metabolic activation(short-term treatment): | 1.7 mg/mL(clastogenicity) |
| 0.85 mg/mL(polyploidy) | |
| With metabolic activation(short-term treatment): | 0.33 mg/mL(clastogenicity) |
| 0.33 mg/mL(polyploidy) |
| clastogenicity | polyploidy | |||||
| + | ? | - | + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] |
| With metabolic activation: | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] |
| 1) | The tests were performed by the Hatano Research Institute, Food and Drug Safety Center, 729-5 Ochiai, Hadano-shi, Kanagawa, 257-8523, Japan. Tel +81-463-82-4751, Fax +81-463-82-9627. |