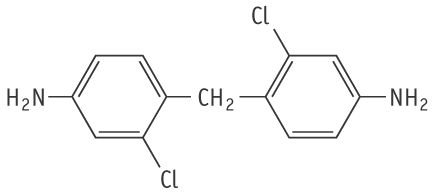
Molecular formula: C13H12Cl2N2 Molecular weight: 267.15

A single dose oral toxicity test of 4,4'-methylenebis(2-chlorobenzenamine) in female rats revealed 2000 mg/kg to bo a lethal dose. Administration at 2000 mg/kg was associated with dark red discoloration in the ear auricles and limbs, increased water intake activity, decreased spontaneous movement, and caused bradypnea and abnormal gait (ataxic gait). After the first administration, one of the three animals given 2000 mg/kg exhibited unkempt fur and deep breathing on the day following administration and died on day 2 after administration.
4,4'-Methylenebis(2-chloroaniline) was studied for oral toxicity in rats in the OECD combined repeated dose and reproductive/developmental toxicity screening test at doses of 0, 0.4, 2, 10 and 50 mg/kg/day.
With regard to repeated dose toxicity, the following were noted in the 50 mg/kg group; salivation in males and females, and decreased body weights in late of pregnancy in females. Hematological examination revealed increase in the methemoglobin concentration, and decrease in the erythrocyte count in both sexes, decreases in mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration and hematocrit and increases in the reticulocyte and platelet counts in males, and an increase in erythrocytes with Heinz bodies in females. Blood biochemical examination revealed decreases in levels of total protein and albumin in both sexes, increases in total cholesterol, triglycerides and inorganic phosphorus in males, increases in levels of LDH and g-GTP, and a decrease in the A/G ratio in females. The absolute and relative weights of the liver were increased in males. The absolute and relative weights of the spleen and relative weights of the liver, kidney and thyroid were increased in females. Gross examination revealed discoloration of the liver in females. Histopathological examination revealed centrilobular swelling and mid-zonal fatty degeneration of hepatocytes in both sexes, centrilobular single cell necrosis of hepatocytes in males, tendencies for increase in kidney basophilic tubules in males and in spleen hemosiderin deposits in both sexes. These changes demonstrated recovery or a tendency for reversibility in the male recovery group and the female satellite group. In the 10 mg/kg group, levels of total protein and albumin were decreased, and the relative kidney weights were increased in females. Tendencies for increase in kidney basophilic tubules and spleen hemosiderin deposits were also noted in males. The NOELs for repeated dose toxicity are considered to be 2 mg/kg/day for parental animals of both sexes.
With regard to reproductive and developmental toxicity, the parental animals exhibited no alterations in reproductive parameters. There were also no significant differences in offspring parameters. The NOELs for reproductive/developmental toxicity are thus considered to be 50 mg/kg/day for reproductive performance of parental animals and for offspring development.
Reverse mutation assays using microorganisms (Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537 and Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA) were conducted to assess the potential of 4,4'-methylenebis(2-chlorobenzeneamine) to induce gene mutations. Mutagenic activity was found in Salmonella typhimurium TA100 and TA98 at 19.5 μg/plate or more with metabolic activation under the present experimental conditions. The maximum specific activity of mutation was 8821 revertants/mg/plate, which was observed in plates of Salmonella typhimurium TA100 treated with the test article at 19.5 μg/plate with metabolic activation.
In vitro chromosomal aberration tests using cultured mammalian cells (CHL/IU) were conducted to assess the potential of 4,4'-methylenebis(2-chloroaniline) to induce chromosomal aberrations. Equivocal induction of structural chromosome aberrations and definite induction of numerical chromosome aberrations were detected under the present experimental conditions.
| Purity | : | 99.76 % |
| Test species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD(SD)IGS |
| Test method | : | OECD Test Guideline 423 |
| Route | : | Oral(gavage) |
| Doses | : | 300, 2000 mg/kg |
| Number of animals/group | : | Females, 6 |
| Vehicle | : | 0.5 % Sodium carboxymethylcellulose solution |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
| Purity | : | 99.76 % |
| Animal species/strain | : | Rat/Crj:CD(SD)IGS |
| Study method | : | OECD Test Guideline 422 |
| Route | : | Oral(gavage) |
| Dosage | : | 0(vehicle), 0.4, 2, 10, 50 mg/kg/day (Satellite group for recovery, 5 females: 0, 50 mg/kg/day) |
| Number of animals/group | : | Males, 12 ; females, 12 |
| Vehicle | : | Olive oil |
| Administration period | : |
42 days for males |
| Terminal killing | : |
Day 43 for males |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Test results:
In the 50 mg/kg group: Salivation was observed in both sexes, and decrease in body weights in late of pregnancy was also noted in females. Hematological examination revealed increase in the methemoglobin concentration, and decrease in erythrocyte counts in both sexes, as well as decreases in mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration and hematocrit, and increases in the reticulocyte and platelet counts in males, and increase in erythrocytes with Heinz bodies in females. Blood biochemical examination revealed decreases in levels of total protein and albumin in both sexes, increases in total cholesterol, triglycerides and inorganic phosphorus in males, and increases in levels of LDH and g-GTP, and decrease of the A/G ratio in females. The absolute and relative weights of the liver were increased in males and the absolute and relative weights of the spleen and relative weights of the liver, kidney and thyroid were increased in females. Gross examination revealed discoloration of the liver in females. Histopathological examination revealed centrilobular swelling and mid-zonal fatty degeneration of hepatocytes in both sexes, centrilobular single cell necrosis of hepatocytes in males, tendencies for increase in kidney basophilic tubules in males and spleen hemosiderin deposits in both sexes. These changes demonstrated recovery or a tendency for reversibility in the male recovery group and the female satellite group.
In the 10 mg/kg group; blood biochemical examination revealed decrease in total protein and albumin in females, along with increase in relative kidney weights. Histopathological examination revealed tendencies for increase in basophilic tubules of the kidney and hemosiderin deposits of the spleen in males.
The NOELs for repeated dose toxicity are considered to be 2 mg/kg/day for parental animals of both sexes.
<Reproductive and developmental toxicity>
The parental animals exhibited no alterations in reproductive parameters. There were also no significant differences in offspring parameters.
The NOELs for reproductive/developmental toxicity are considered to be 50 mg/kg/day for reproductive performance of parental animals and for offspring development.
| Purity | : | 99.76 % |
| Test species/strains | : | Salmonella typhimurium TA100, TA1535, TA98, TA1537, Escherichia coli WP2 uvrA |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Chemical Substances Control Law of Japan) and OECD Test Guideline 471 |
| Procedures | : | Pre-incubation method |
| Solvent | : | Dimethylsulfoxide |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix; 2-(2-Furyl)-3-(5-nitro-2-furyl)acrylamide (TA100, TA98 and WP2 uvrA), sodium azide (TA1535) and 2-methoxy-6-chloro-9-[3-(2-chloroethyl)- aminopropylamino] acridine・2HCl (TA1537) +S9 mix; Benzo[a]pyrene (TA100, TA98, TA1537) and 2-aminoanthracene (TA1535 and WP2 uvrA) |
| Dosage | : | -S9 mix; 0, 2.44, 4.88, 9.77, 19.5, 39.1, 78.1, 156, 313 μg/plate (all strains) +S9 mix; 0, 2.44, 4.88, 9.77, 19.5, 39.1, 78.1, 156, 313 μg/plate (all strains) |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5, 6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 3 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
Mutagenic activity was found in the Salmonella typhimurium TA100 and TA98 at 19.5 μg/plate or more with metabolic activation. The maximum specific activity of mutation was 8821 revertants/mg/plate, which was observed in plates of Salmonella typhimurium TA100 treated with the test article at 19.5 μg/plate with metabolic activation. Toxicity was observed at 313 μg/plate or more (all strains) with and without metabolic activation.
Genetic effects:
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [*] | [ ] | [ ] |
Genetic effects:
S. typhimurium TA1535, TA1537| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
E. coli WP2 uvrA
| + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| Purity | : | 99.76 % |
| Type of cell used | : | Chinese hamster lung (CHL/IU) cells |
| Test method | : | Guidelines for Screening Mutagenicity Testing of Chemicals (Chemical Substances Control Law of Japan) and OECD Test Guideline 473 |
| Solvent | : | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| Positive controls | : | -S9 mix; Mitomycin C +S9 mix; Cyclophosphamide |
| Dosage | : | -S9 mix(short-term treatment); 0, 2.60, 5.30, 10.6, 21.1, 42.2 and 84.4 μg/mL +S9 mix(short-term treatment); 0, 2.60, 5.30, 10.6, 21.1, 42.2 and 84.4 μg/mL -S9 mix(continuous treatment 24 hr); 0, 1.30, 2.60, 5.30, 10.6, 21.1 and 42.2 μg/mL -S9 mix(continuous treatment 48 hr); 0, 1.30, 2.60, 5.30, 10.6, 21.1 and 42.2 μg/mL -S9 mix(additional confirmative test); 0, 24.4, 29.3, 35.2 and 42.2 μg/mL |
| S9 | : | Rat liver, induced with phenobarbital and 5,6-benzoflavone |
| Plates/test | : | 2 |
| GLP | : | Yes |
No increase in chromosomal aberrations was observed in the test with the short-term treatment (-S9 and +S9). Equivocal increase in structural chromosomal aberrations and definite increase in numerical chromosomal aberrations (polyploidy) was observed in the test with the continuous treatment for 48 hr.
Lowest concentration producing cytogenetic effects in vitro:
Without metabolic activation (continuous treatment for 48 hr): 35.2 μg/mL (polyploidy)
| clastogenicity | polyploidy | |||||
| + | ? | - | + | ? | - | |
| Without metabolic activation: | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] |
| With metabolic activation: | [ ] | [ ] | [*] | [ ] | [ ] | [*] |
| 1) | The tests were performed by the Bozo Research Center Inc, 1284 Kamado, Gotemba-shi, Shizuoka, 412-0039, Japan. Tel +81-550-82-2000, Fax +81-550-82-2379. |
| 2) | The test was performed by the Research Institute for Animal Science in Biochemistry and Toxicology, 3-7-11 Hashimotodai, Sagamihara-shi, Kanagawa, 229-1132, Japan. Tel +81-42-762-2775, Fax +81-42-762-7979. |